|
All population | ||||||
|
including the average cash revenues per month, rub.: | ||||||
|
over 12000.0. |
Purchasing power cash income Population - reflects the potential population in the acquisition of goods and services and is expressed through the commodity equivalent of various goods and services that can be purchased on the average income.
To characterize the standard of living and differentiation of income and consumption of the population, it is necessary to collect data on the income and consumption of households. At the same time, the problems of rationalization of the principles of selection arise to obtain a representative sample of households, processing, analyzing and distributing the information received to the entire population living in this territory.
The main complexity of the selection is the lack of information on the income and the property position of the entire population or households living in a given territory. Therefore, a multistage selection is used, taking into account indirect signs associated with income.
According to the census of the population, all households are divided into the family load coefficient for the following types: with full load (all persons in the household are not occupied), with high (persons non-working in the family more than working), with medium, low and without load (All persons work). As a result of proportional selection, a territorial sample can be formed from each type of households, which will allow analyzing not only as a whole, but also differentiated by dedicated categories of households. The sample can be adjusted after the census of the population.
To study the differentiation of income and consumption of the population, household rearrangements are carried out:
- by deciling groups - ten groups are distinguished, in each group of 10% of households;
- by quintile groups - five groups, in each group of 20% of the population;
- by purchasing power of the population - by groups, multiple size of the subsistence minimum or value of a set of 25 (or 31) products of food.
For each dedicated group, the average cash income is calculated; its composition; Middle consumer consumption and its structure; The average size of food consumption of food, not food products and services (calculated on 100 households); Indicator of the purchasing power of money income (cash income, divided into the average purchase price of this product).
Based on the distribution of the population in income size, the following statistical indicators are calculated.
Modal income . The level of income most common among the population.
Median income - An indicator of income located in the middle of a ranked range of distribution. Half of the population has an income below the median, and the second half is higher.
Decile Differentiation Coefficient income of the population ( TO d.), which characterizes how many times the minimum income of 10% of the richest population exceeds the maximum income of 10% of the least secured population:
where d. 9 and d. 1 Accordingly, the ninth and first decile.
Fund coefficient
(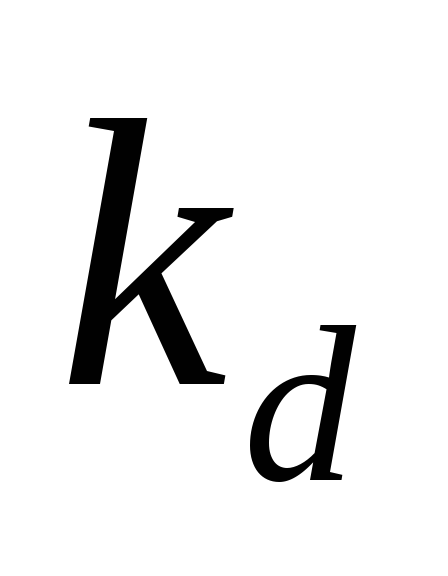 ), defined as the ratio between average income of the population in the tenth and first decyl groups:
), defined as the ratio between average income of the population in the tenth and first decyl groups:
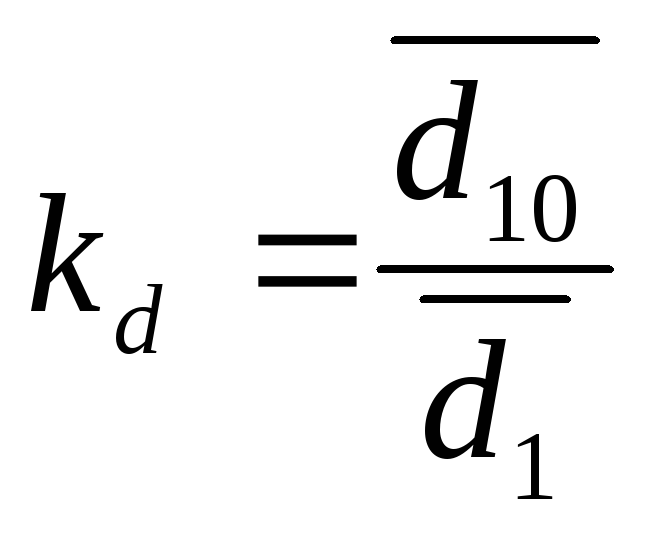 where
where
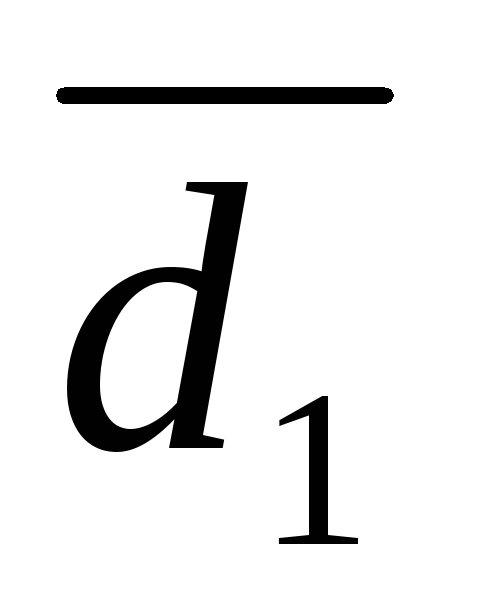 and
and 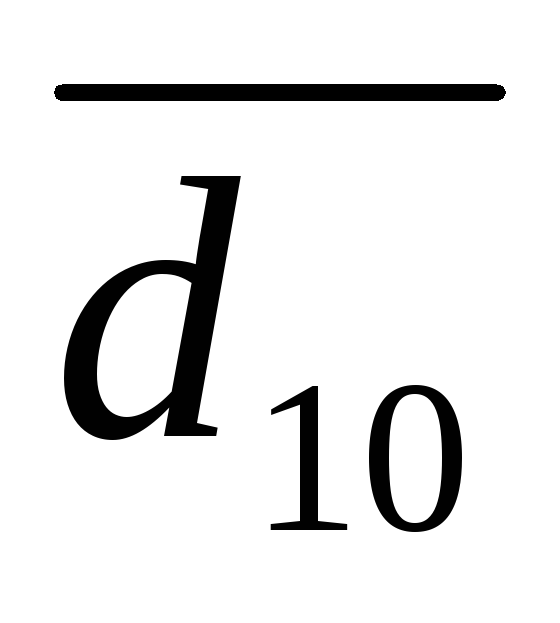 - The average income per month, respectively, 10% of the population, which has a minimum income and 10% of its richest part.
- The average income per month, respectively, 10% of the population, which has a minimum income and 10% of its richest part.
Considering that when calculating average income for 10% of the population in denominator indicators 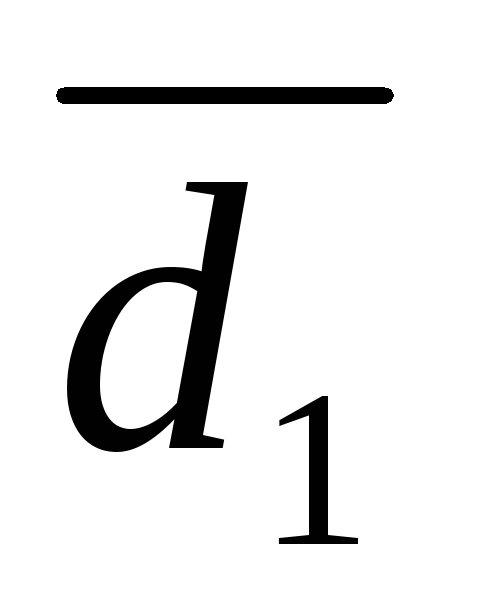 and
and 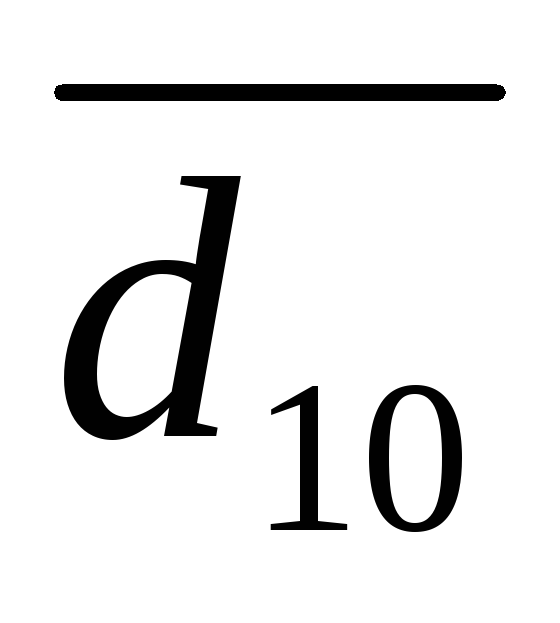 there are the same values, the fund's coefficient can be represented as follows:
there are the same values, the fund's coefficient can be represented as follows:
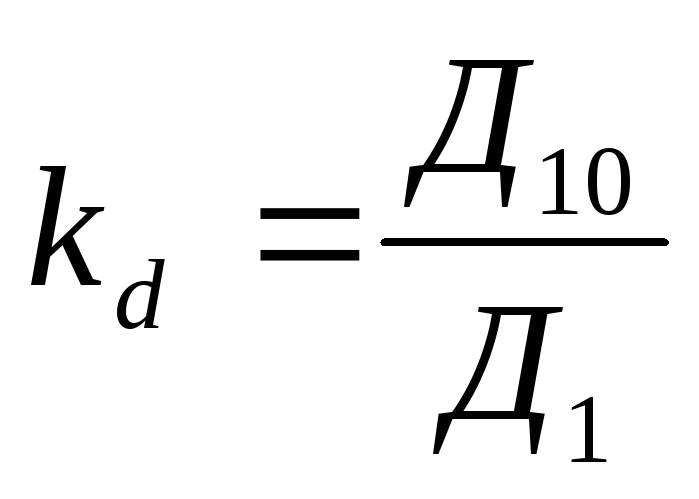 where
where
 and
and 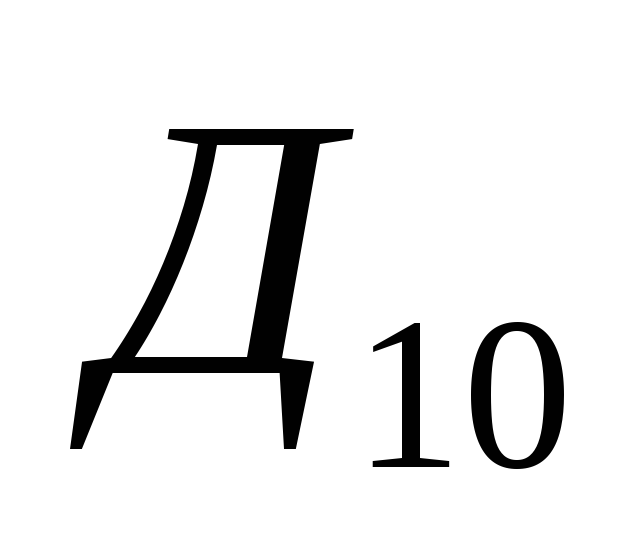 - respectively, the total income of 10% of the poorest and 10% of the richest population;
- respectively, the total income of 10% of the poorest and 10% of the richest population;
Gini income concentration coefficient
(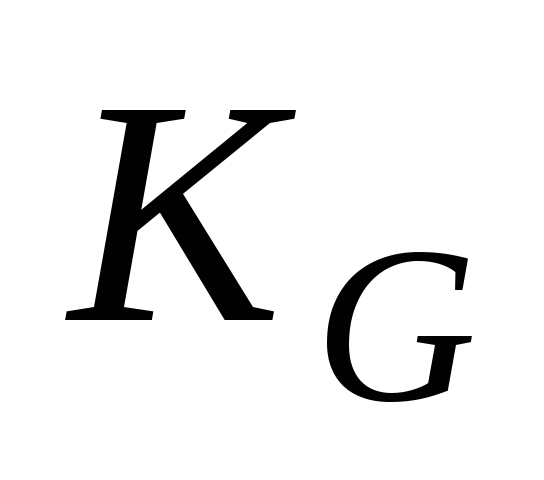 ), characterizing the degree of inequality in the distribution of income of the population. It is calculated by the formula:
), characterizing the degree of inequality in the distribution of income of the population. It is calculated by the formula:
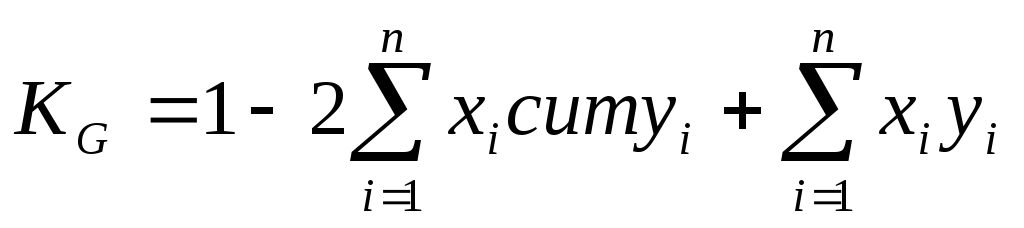 ,
where
,
where
h. i. - the proportion of the population belonging to i.Social group in the total population;
y. i. - share of revenues focused on i.- a social group of the population;
n.- the number of social groups;
cum Y. i. - Cumulative share of income.
For graphic illustration of the degree of unevenness in the distribution of income, Lorentz curve is built. The Lorentz curve is a concentration curve of individual elements of a statistical aggregate in groups. Direct AV reflects the model of complete equality in the distribution, when, for example, 20% of the population is obtained by 20% of all income, etc. The Lorentz curve (curve of the QU) is built on the basis of data on the actual distribution of income. What it is more concave, the uneven distribution of income and above their concentration.
According to the Lorentz curve, it is also possible to calculate the Gini coefficient as the attitude of the area of \u200b\u200bthe figure formed by the curve and the linen of the uniform distribution ( S. a.), to the triangle area below the uniform distribution line ( S. a. + S. b.):
TO G. \u003d S. a. / (S. a. + S. b) .

Fig. 7.1. Curve Lorentz
The Gini coefficient varies in the range from 0 to 1. In case of complete equality in the income distribution, the Lorentz coefficient is 0, and with full inequality - 1. According to the 2006 data, the Jini Index in Russia is 41%, which is 0.4% higher than In 2005 .. Thus, a high degree of stratification of society remains. Among the European Union countries, the lowest Gini coefficient in Denmark is 24.7%. In Germany, it is 28.3%, in France - 32.7%.
To measure the level of poverty, the threshold of money incomes is established, below which faces or households are considered to have lack of funds to ensure the cost of living, determined by minimal needs. . In this way, poverty level - that's specific gravity population with income below subsistence minimum. In 2007, 21.6 million Russians had an average per capita income below the officially established subsistence minimum of 3809 rubles, which amounted to 15.8% of the country's total population.
The size of the subsistence minimum In accordance with the Federal Law of October 24, 1997 №134-ФЗ "On the subsistence minimum in the Russian Federation" is a valuation consumer basket, as well as mandatory payments and fees. The subsistence minimum is calculated on various socio-demographic groups of the population (able-bodied population, broken down by sex and age), pensioners, children of two age groups (0-6 years and 7-15 years), as well as by regions of Russia by the formula:
A \u003d b + c + d + ewhere
BUT - the amount of the subsistence minimum;
IN - Cost of minimal food basket: 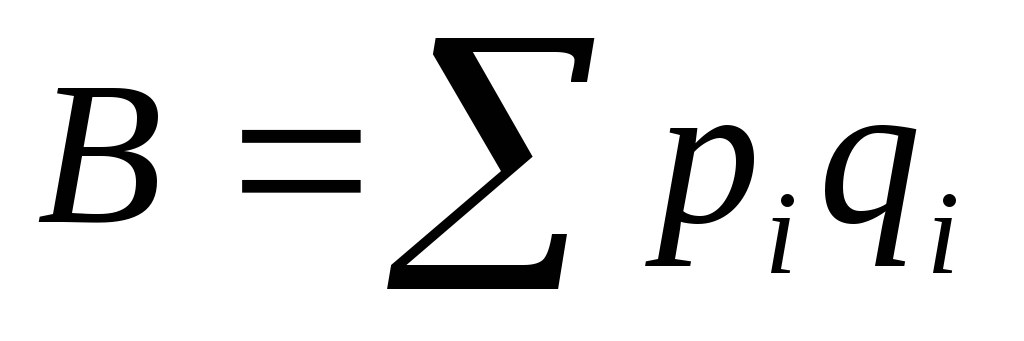 (
( -average price i-cao food;
-average price i-cao food; 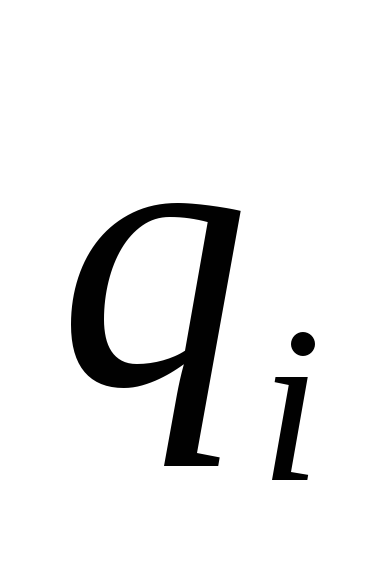 - Consumption standard i-cao food);
- Consumption standard i-cao food);
FROM− valuation Consumption of non-food products;
D. - value evaluation of expenses for paid services;
E. - Tax expenses and compulsory payments.
The last three components are calculated based on the cost structure for these goals of 10% of the least secured population.
The magnitude of the subsistence minimum as a whole in the Russian Federation is determined quarterly and is established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Based on data on the income of the poor population, the indicator is calculated income deficit , equal to the total income of the population missing to the amount of the subsistence minimum.
To analyze the dynamics of poverty in the country, two indicators may be calculated: poverty depth index and poverty sharpness index .
Poverty Depth Index: Poverty Acute Index:
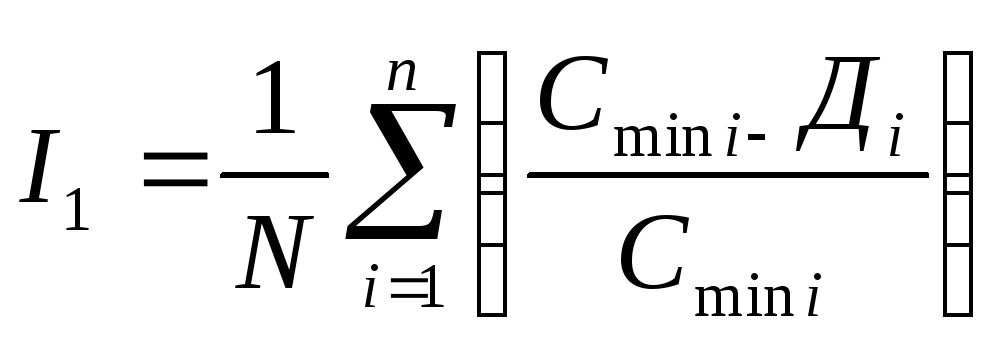 ,
, ![]() where
where
N. - the total number of household surveyed;
n. - the number of households with income below the subsistence minimum;
i. - their sequence numbers;
 - The average subsistence minimum i.-to household, calculated in view of its age-age structure;
- The average subsistence minimum i.-to household, calculated in view of its age-age structure;
D. - Secondary income i.A household that has incomes below the subsistence minimum.
2.3 Analysis of the statistical distribution of the population by the magnitude of the average money income
To calculate the analysis of the statistical distribution of the population by the magnitude of the average per capita cash income, it is necessary to close the first and last intervals and make a subsidiary table, where:
The number of man (in percent);
Midstand interval;
Accumulated frequencies.
Table 6 - distribution of population in terms of average percentage income (in percent)
| Current money income, rubles per month for 2009 | Population |
| until 2000. | 0,1 |
| from 2000 to 4000 | 1,4 |
| from 4000 to 6000 | 4,1 |
| from 6000 to 8000 | 6,5 |
| from 8000 to 10,000 | 7,8 |
| from 10,000 to 15000 | 20,0 |
| from 15,000 to 25000 | 28,8 |
| over 25000. | 31,3 |
| TOTAL | 100 |
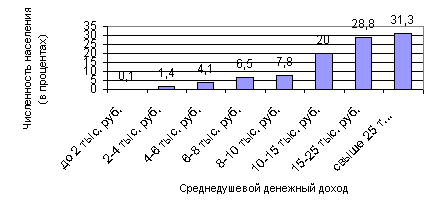
Figure 2.7 - distribution of the population of the Kamchatka Territory in the magnitude of the average per capita cash income in 2009
As you can see from the data provided, the greatest number Populations 31.3% have a per capita income per month over 25 thousand rubles. Next follows a group of income from 15 thousand rubles. up to 25 thousand rubles. (28.8%) and closes the Troika district population group with an income of 10 thousand rubles. up to 15 thousand rubles. (20.0%).
Table 7 - Auxiliary Table
| 0,1 | 1000 | 100 | 0,1 | 18055 | 1805,5 | 325983025 | 32598302,5 |
| 1,4 | 3000 | 4200 | 1,5 | 16055 | 22477,0 | 257763025 | 360868235 |
| 4,1 | 5000 | 20500 | 5,6 | 14055 | 57625,5 | 197543025 | 809926402,5 |
| 6,5 | 7000 | 45500 | 12,1 | 12055 | 78357,5 | 145323025 | 944599662,5 |
| 7,8 | 9000 | 70200 | 19,9 | 10055 | 78429,0 | 101103025 | 788603595,0 |
| 20,0 | 12500 | 250000 | 39,9 | 6555 | 131100,0 | 42968025 | 859360500,0 |
| 28,8 | 20000 | 576000 | 68,7 | 945 | 27216,0 | 893025 | 25719120,0 |
| 31,3 | 30000 | 939000 | 100 | 10945 | 342578,5 | 119793025 | 3749521683,0 |
| 100 | 87500 | 1905500 | - | 88720 | 739589,0 | 1191369200 | 7571197500,0 |
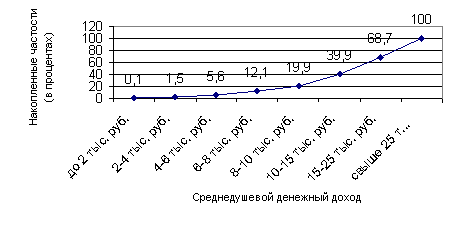
Figure 2.8 - Cumulating population distribution by the magnitude of the average per capita income
1. Determine the indicators of the distribution center:
1.1) Average arithmetic:
Based on these subsidiary table, the Fashion is 25.74 thousand rubles. The modal interval is selected for the calculation (25,000 rubles. up to 35,000 rubles), since it has the greatest frequency (31.3%). Thus, the most common average of the average per capita income in the variational series is 25,740 rubles.
1.3) Mediana
The median interval is selected for the calculation, in which the amount of accumulated frequencies is more than 50% (from 15,000 rubles. Up to 25,000 rubles). Consequently, half of the inhabitants of Kamchatka Territory have a monthly average income less than $ 21493.1 rubles, and half more than this amount.
2. Determine the indicators of the variation:
2.1) Variation variation
2.2) Medium linear deviation
weighted: 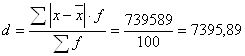
2.3) secondary quadratic deviation
weighted: 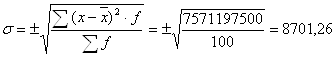
2.4) Dispersion
weighted:
2.5) Camefficient of Variation
Average variation, a totality relatively homogeneous
3. Determine the distribution form indicators:
3.1) asymmetry coefficient
![]()
asymmetry significant, right-sided
1) Determine the Decile Differentiation Coefficient
To determine the deceyl amount of differentiation of income of the population of the Kamchatka Territory, it is necessary to calculate the upper and lower decil.
To work in the conditions of a single treasury account, due to the presence of its own software product, on the basis of which the distribution of income received into the budgets of the subject of the Russian Federation is carried out. 2.2 Treasury performance of the revenue part of the regional budget according to Art. 215 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation in the Russian Federation establishes the treasury execution of budgets. It means that...
The actual filling of which is very low. The size of wages, the regularity of its payments largely determines the standard of living of the population and especially its parts with low income. The timeliness of payments in general represents one of of essential factors socio-political situation in Russia. With the development of commodity and money relations in our country, an additional source of income employees, ...
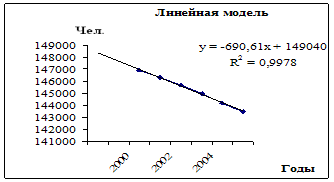
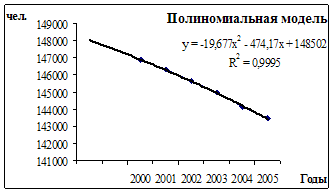
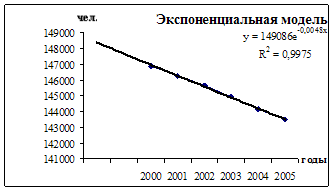
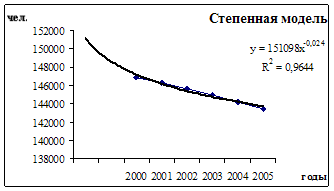
Separately for urban and rural population, for men and women, for individual nationalities, for the employed population, for individual sectors of the economy and classes. 1.3 The concept of the mechanical and natural movement of the population under the natural movement of the population understands demographic events affecting the population natural way. These events include ...
The corresponding level of inflation in the country. Such a budget deficit is usually covered by low-cost or interest-free credits of the Central Bank. International Standards Assuming a possible budget deficit at 2 - 3% GNP. Such or larger deficit The state budget is funded by the emission of state securities, the yield of which is usually lower than the average yield on ...
Secondary money income isthe average nominal cash income, without taking into account taxes per person in the study group, is calculated by division total amount Monetary incomes of the population for the year on the cash population.
The average characteristics are calculated not only in all nominal and real indicators in general, but also by their separate components. These are, for example, indicators of the average nominal and real wages, a prescribed pension, benefits having special meaning To assess the standard of living of the population. Thus, the average per capita income is determined not only for the entire population as a whole, but also for its individual contingents - working in the economy, students, pensioners, etc.
The incomes of the population are the following elements:
1. Warm.
2. Revenues of workers and employees from enterprises and organizations other than wages.
3. Dividends.
4. Arrivals from selling agricultural products.
5. Pensions and benefits.
6. Scholarships.
7. Receipts from the financial system, including:
o insurance compensation;
o loans for individual housing construction and other goals;
o Changes in debt on loans issued for consumer purposes;
o interest on deposits;
o winnings and repayment on loans;
o winnings for lottery;
o Changes in the population's debt for the purchase of goods on credit (increase +, decrease -);
o Changes in debt on loans to persons operating without education legal entity (increase +, decrease -); reimbursement of expenses to disabled (on fuel, repair of cars);
o Compensation of damage to repressed citizens.
7. Public incomes from the sale of foreign currency.
8. Other arrivals:
a. from the sale of things through commission stores and buying points;
b. from sales of scrap, scrap metal and other (non-agricultural billets);
c. Other income.
9. Money received by translation (minus translated and submitted amounts).
A statistical analysis of the average foreign monetary incomes of the population of the Russian Federation from 1990 was held. in 2010
In general, in the Russian Federation there is a trend of the growth of this indicator:
In 1990 he was less value 1995 by 57.95% (299 rubles),
In 1995, less than 2000, by 77.38% (1765 rubles),
In 2000, less than 71.88% (by 5831 rubles) than in 2005,
In 2005, less than 57.05% (by 10775 rubles) than in 2010
A graphically change of this factor is shown in the following figure:
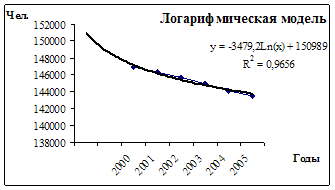
Fig. 3 - Dynamics of middle-wide cash income
the population of the Russian Federation from 1990 to 2010
From the figure it is clear that the size of the average per capita cash income of the country's population increases.
Since the size of the average per capita cash incomes of the population depends not only on the size of the income of the population, but also on the population. Consider how the last indicator behaves in the dynamics.
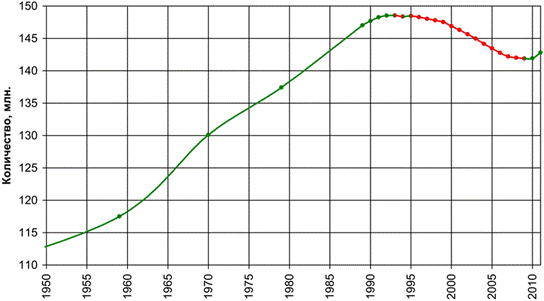
Fig. 4 - Dynamics of the population of the Russian Federation for the period 1950-2010.
Figure 4 shows that the population in 1990-2010. decreased. Thus, an increase in the size of the average per capita income is caused not only to an increase in the size of the income of the population, but also by a decrease in their number. In addition, this indicator has had a significant impact of the purchasing capacity of income, which depends on the level of expenses.
If during 1998-1999 there was a sharp decline in the purchasing power of the population in most food products, by 2000, together with the growth of solvent supply of the population, the purchasing power of its cash income has increased.
The position in most food products has significantly improved and for the period from 2000 to 2002. In 2003, the situation continued to remain relatively prosperous: periods of noticeable increase in prices in the consumer market were replaced by periods of minor changes.
So, back to the change in the studied indicator. Significant difference of indicators 1990, 1995, 2000. It is also explained, first of all, changes in the economic text of the country caused by economic reforms.
In 2000, the Russian Federation rose on the path of modernization of the economy, special attention was paid to the level of living of the population. In the period from 2000 to 2010 The government conducts an active policy in the field social DevelopmentNamely: to increase the standard of living of pensioners (the size of pensions), students, to regulate and coordinate the degree of solvency of the population through such indicators as a minimum wage, consumer basket, as well as the payment of various benefits and subsidies to the relevant segments of the population.
We analyze the dynamics of the average per capita cash income by the Federal Districts of Russia.
1. Central Federal District:
In 1995, less than 2000 by 78.58% (2539 rubles),
In 2000, less on -70.85% (7853.00 rubles) than in 2005,
In 2005, less than 54.85% (at -13 462.8 rubles) than in 2010
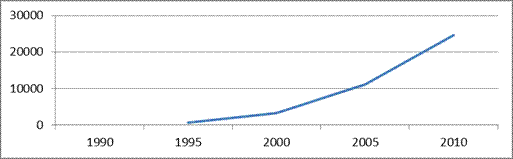
Fig. 5- Dynamics of the average permanent cash income of the population in the Central Federal District
Maximum values Observed in Moscow and Moscow region: in 2010 they amounted to 43,917 rubles, respectively. and 22 317.6 rubles. This is due to the fact that in the capital and in the area of \u200b\u200bliving standard above compared to other regions.
2. Northwest Federal District:
In 1995, less than 2000 at 75.10% (1704.00 rubles),
In 2005, less than 54.05% (by 10,639,6 rubles) than in 2010
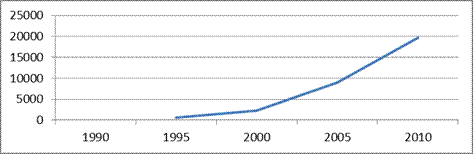
Fig. 6 - Dynamics of the average permanent cash income of the population in the Central Federal District
The leader is the Nenets Autonomous District: in 2010 - 51,515.5 rubles. The minimum value is characteristic of the Pskov region (12,622,6 rubles in 2010). Such a difference is caused by the potential of the region, natural conditions, as well as large squares Forests, gas and oil reserves, which the Nenets Autonomous District has. Living wage in Nenets autonomous District In 2010 amounted to 12,068 rubles.
3. Southern Federal District
In 1995, less than 2000, 78.38% (1120.00 rubles),
In 2000 less than 73.20% (by 3904.00 rubles) than in 2005,
In 2005, less than 64.47% (by 9,676.9 rubles) than in 2010
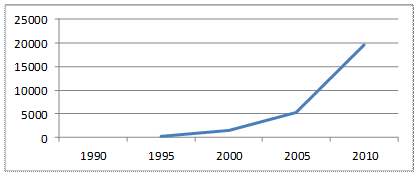
Fig. 7 - Dynamics of the average permanent cash income of the population
in the southern Federal District
According to 2004, average monthly salary One employee, on average in Russia, was 6,739 rubles, on average in the South Federal District - 4648 rubles (including in the North Caucasian republics - 3-3.5 thousand). Middle earnings in Chechnya were significantly higher - 4586 rubles per month. According to Rosstat at the beginning of 2008, the most high level Unemployment from the Russian regions was in Chechnya (53%) and Ingushetia (47.3%). In Dagestan, Karachay-Cherkessia and Kabardino-Balkaria, the unemployment rate ranged from 17% to 20%.
According to the results of 2008, the average monthly salary in the Southern Federal District amounted to 11,734 rubles (on average in Russia - 17,290 rubles) the unemployment rate in the district decreased to 10.2% (in Chechnya - up to 35.5%)
4. Volga Federal District:
In 1995, less than 2000 at 78.62% (by 1357.00 rubles),
In 2000, less than 72.25% (by 4494.00 rubles) than in 2005,
In 2005, less than 60.47% (at 9,513.1 rubles) than in 2010
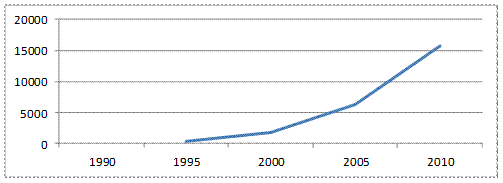
Fig.8 - Dynamics of the average permanent cash income of the population
in the Volga Federal District
Regions of the Volga District, depending on the magnitude of the population's money incomes, can be divided into four groups. In the first group in which cash incomes of the population exceed the average income in the district include the Republic of Bashkortostan and Tatarstan, Perm region and Samara Region. To the second group, where cash incomes are equal to the average in the district, refers Nizhny Novgorod Region. The third group includes regions with income below average: Udmurtia and Kirov, Orenburg, Penza, Saratov and Ulyanovsk region. The quadruple group is the regions where monetary incomes are significantly lower than the medium in the district: Republic of Mordovia, Chuvash and Mari El. Thus, in most part of the regions of the Volga Federal District, including Saratov region, Cash income is below average around the district.
5. Ural Federal District:
In 1995, less than 2000 by 77.95% (by 2139.00 rubles),
In 2000, less than 71.14% (by 6763.00 rubles) than in 2005,
In 2005, less than 55.96% (by 12 082.6 rubles) than in 2010
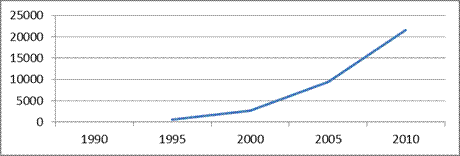
Fig. 9 - Dynamics of the average per capita cash income of the population
in the Ural Federal District
Differentiation of secondary cash income in the Urals Federal District Significant: A group of commodity regions is clearly allocated. Tyumen region With high average per capita cash and a group of industrial areas of the Urals. In 2002, the maximum average per capita cash incomes per person per month (13388 rubles) were observed in Yamalo-Nenets AO. Since 1998, the average per capita cash incomes of the population in Yamalo-Nenets AO increased 3.9 times from 3394 rubles. per person. At the same time, the average per capita cash incomes of the population in Sverdlovsk region increased by 4.8 times (from 823 rubles per person in 1998 to 3918 rubles per person in 2002). This is the maximum growth among the remaining regions of the Ural Federal District. The smallest per capita cash incomes of the population in the URFO are observed in the Kurgan region: 2315 rubles. per person per month in 2002. It is about 6 times less than in the Leader region - Yamalo-Nenets AO.
Differential differences in the quality of the provision of level of services in the field of education, health care and other areas are even more recovered. As a result, the most mobile part of the population prefers to migrate to the regions with a higher life level of the population.
Existing tenfold differences between the most secured and the most poor regions of the district in terms of the GRP per capita indicate a huge asymmetry economic Development. The main trends in the economic asymmetry of the regions of the Ural Federal District are similar to the situation in social asymmetry. The region with the greatest GRP per capita per capita in 2002 was the Yamalo-Nenets AO - here the indicator reached 544128.6 rubles. per person. It is 18 times more than the GRP per capita in the Kurgan region (30205.3 rubles.). The biggest growth of VRP per capita in 1998-02 is observed in Chelyabinsk region: In 2002, GRP per capita (50874.2 rubles) increased 4 times compared with 1998 (12715.2 rubles). The counting of the VRP of autonomous districts was not conducted until 2000, so the comparison is impossible.
6. Siberian Federal District:
In 1995, less than 2000 at -74.44% (by 1439.00 rubles),
In 2000, less than 71.06% (by 4747.00 rubles) than in 2005,
In 2005, less than 55.14% (by 8 211.7 rubles) than in 2010
![]()
Fig. 10 - Dynamics of the average permanent cash income of the population
in the Siberian Federal District
Table 3 - population distribution Altai Region The magnitude of the average per capita cash income.
| thousand people | in% to the outcome | thousand people | in% to the outcome | thousand people | in% to the outcome | thousand people | in% to the outcome | thousand people | in% to the outcome | |
| All population | 2583,4 | 100,0 | 2565,6 | 100,0 | 2543,3 | 100,0 | 2523,3 | 100,0 | 2508,5 | 100,0 |
| Including with average per capita cash income, per month, rubles: | ||||||||||
| up to 1500, 0 | 473,4 | 18,3 | 251,4 | 9,8 | 109,4 | 4,3 | 60,6 | 2,4 | 24,8 | 1,0 |
| 1500,1-2500,0 | 663,3 | 25,7 | 500,3 | 19,5 | 307,7 | 12,1 | 214,5 | 8,5 | 113,2 | 4,5 |
| 2500,1-3500,0 | 503,1 | 19,5 | 477,2 | 18,6 | 373,9 | 14,7 | 300,3 | 11,9 | 193,8 | 7,7 |
| 3500,1-4500,0 | 330,1 | 12,8 | 372,0 | 14,5 | 348,4 | 13,7 | 310,4 | 12,3 | 232,6 | 9,3 |
| 4500,0-6000,0 | 284,0 | 11,0 | 374,6 | 14,6 | 417,1 | 16,4 | 411,3 | 16,3 | 353,2 | 14,1 |
| 6000,1-8000,0 | 176,6 | 6,8 | 274,5 | 10,7 | 371,3 | 14,6 | 403,7 | 16,0 | 406,1 | 16,2 |
| 8000,1-12000,0 | 112,9 | 4,4 | 212,9 | 8,3 | 363,7 | 14,3 | 444,1 | 17,6 | 538,6 | 21,5 |
| Over 12000.0. | 40,0 | 1,5 | 102,7 | 4,0 | 251,8 | 9,9 | 378,4 | 15,0 | 646,2 | 25,7 |
In January-June 2012, the Krasnoyarsk Territory occupied the first place in the Siberian Federal District in terms of medium-sized money incomes of the population (19968.0 ruble).
On the last place Republic of Tuva (10309.8 rubles). Such data of the monthly monitoring of 12 constituent entities of the Russian Federation within the Siberian Federal District leads to Krasnoyarskstat.
The average monthly nominal accrued salary of workers in the Krasnoyarsk Territory was 27,428.1 rubles in the first half of the year (first among the subjects of the Siberian Federal District).
High wages along with Krasnoyarsk Territory Forest in Tomsk (26310.9 rubles) and Irkutsk (24646.5 rubles) regions, the lowest - in the Altai Territory (15093.6 rubles).
The average size Appointed monthly pensions in the Krasnoyarsk Territory at the end of June 2012 amounted to 9841.1 rubles - this is the second place after the Tomsk region (10012.9 rubles). The lowest size of pensions in the Altai Republic is 8293.6 rubles.
At the end of June 2012, the level of officially registered unemployment in the Krasnoyarsk Territory was 1.6% of the number of economically active population. The minimum level of registered unemployment is recorded in Omsk region (1.0%), maximum - in Tuva (5.1%).
The lowest index consumer prices All goods and services for half a year have been celebrated in the Trans-Baikal Territory (102.1%), Novosibirsk region (102,3 %), Irkutsk region and the Republic of Khakassia (102.5%), the highest - in the Tomsk region (103.4 percent). In the Krasnoyarsk Territory, the consumer price index for all goods and services amounted to 103.1%.
The lowest cost minimum set The food at the end of June 2012 was observed in the Omsk region (2073.0 rubles), the highest - in the Trans-Baikal Territory (2931.6 rubles). In the Krasnoyarsk Territory, the cost of a minimum set of food for the end of June 2012 was 2820.4 rubles.
7. Far Eastern Federal District:
In 1995, less than 2000 is 74.02% (by 1849.00 rubles),
In 2000 less than 71.91% (6394.00 rubles) than in 2005,
In 2005, less than 57.28% (by 11 92.8.B.) than in 2010
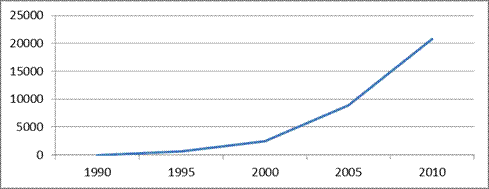
Fig. 11 - Dynamics of the average permanent cash income of the population
in the Far Eastern Federal District
The most relatively high incomes have residents of DVFO entities equivalent to the territories of the Far North. Wages In these subjects are higher than in most regions of the Russian Federation. The greatest size The average per capita income of the population in 2010 is observed in the Chukotka Autonomous District (37 424.9 rubles).




