The state budget, as well as all the balance, involves leveling income and expenses. However, as a rule, when adopting a budget, planned receipts and expenses do not coincide. Exceeding income on expenses forms budget surplus (or surplus), excess of income expenses means Budget deficit (or disadvantage). As a rule, the budget deficit is expressed as a percentage of GNP (GDP).
If in the past, the budget deficit was rarely related and was associated with emergency circumstances, first of all with wars, today, and in peacetime, the budget deficit became typical for most countries of the market economy. At the same time, the budget deficit is not simply chronic, but also constantly increasing.
Table 11.4.
Budget deficit (% to GNP)
|
Year |
USA |
Japan |
Germany |
Italy |
|
1970 |
0,3 |
0,9 |
0,1 |
5,1 |
|
1985 |
4,1 |
3,1 |
2,7 |
12,0 |
|
1995 |
2,1 |
1,7 |
2,8 |
8,6 |
Budget deficit arises due to many reasons for an objective and subjective nature. Most often - due to the inability to mobilize the necessary revenues as a result of a decline or falling the pace of production, low labor productivity and other reasons causing the instability of the economy, a decrease in production efficiency.
The reason for the budget deficit lies and in the unrestrained growth of expenses without taking into account financial capabilities, in insufficient appropriateness, efficiency. High level Unproductive expenses (military spending, the content of the administrative apparatus, covering the losses of enterprises, etc.) leads to the downtown of budget funds, and not to multiply of public wealth. Inflation, increasing money circulation and settlement system, irrational tax and investment and credit policies have a negative impact on the balance of the budget.
However, the budget deficit cannot serve as an indicator characterizing the state of the country's economy, and the short-state budget does not mean economic well-being. Since macroeconomic equilibrium can be achieved with a different state of the budget, the budget deficit (up to certain limits) is not dangerous.
Today, many economists proceed from the fact that in the period of recession, a significant budget deficit is quite admissible, and a small budget deficit may exist for a long time. The problem becomes a long and significant budget deficit, the consequence of which inflation may become. The International Monetary Fund recognizes a permissible deficiency in the range of 2-3% GNP.
Budget imbalance can be useful in terms of stabilization of the economy. The planned discrepancy between the income and expenses of the state budget can be used as a means of combating inflation and a decline in production. On the contrary, the firm course on the balance of the budget would require increasing taxes and reduce government spending during the decline in the economy and would lead to a further reduction in total demand.
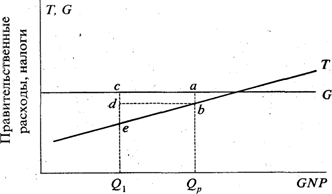
The nature of the budget balance (residue) is a deficit or surplus - is determined by the state of the economy as a whole. With this volume of government spending and this tax rate, the budget balance depends on the scale of national production. The greater the volume of production and the level of income, the higher the tax revenues. At the same time, government expenses (for defense, social needs, management) do not depend on the level of income. Thus, with a low income, a budget deficit will be observed, with high - budget surplus (Fig. 11.3).
Ground National Product (income)
Fig. 11.3. Deficiency and excess state budget
In the GNP, equal, the budget is balanced, under GNP, less Q, The budget will be reduced with a deficit. (G\u003e t); Under GNP, more, surplus occurs (G.< Т).
This or that budget balance is not always evidenced by the change in the macroeconomic situation, it may be consequence of the fiscal policy held by the Government aimed at solving certain macroeconomic tasks.
In order to distinguish the impact on the budget balance of targeted government events, use the "full-time budget" - the state of the budget in the functioning of the economy in the natural level of unemployment.
Full employment budget deficit (structural deficit)it characterizes the difference between income and state budget expenditures at a given level of taxation and government costs and potential GNP (relevant natural level of unemployment). The deficit of the full employment budget eliminates (eliminates) economic cycle on the magnitude of the budget deficit.
The difference between the actual budget deficit and the budget deficit of full employment is called cyclic deficiency. The cyclic deficit is a deficit caused by a decline in production, excess of the actual unemployment of its natural level (Fig. 11.4).
Gross National Product
Fig. 11.4. Actual, structural and cyclic budget deficit
If in terms of complete employment, the GNP is equal Q, then with the existing tax system and this level of government spending budget deficit is equal aB. At the production level equal to the same taxation system and the same government expenditures the actual budget deficit will be equal to se including, cD - This is a structural deficit, a dE. - cyclic - the result of the drop in production volumes (q, less Q).
The growth of structural deficit means that the government conducts a stimulating policy: increases costs and reduces taxes, which causes an increase in total demand and has a positive effect on the production of products. Reducing the structural deficit, on the contrary, indicates a restraining fiscal policy.
With this magnitude of the budget deficit, its impact on the economy depends on the methods of financing the deficit, sources of costing costs exceeding income. Government spending that have no profitable base can be financed by:
Emissions of money;
Loans in the central bank;
Loans in the private sector.
The first two ways to finance budget deficit are inflationary in nature, i.e. They lead to a rise in prices, the third method is considered non-inflammony, but it generates "the effect of displacement". The essence of the latter is that placing loans in the money market, the government comes into competition with private entrepreneurs for financial resources. Increased money demand leads to an increase in interest rates and subsequent decline in investment. Government expenses, as a rule, carrying unproductive nature, "displacing" private investment in production.
The impact of various methods for financing the budget deficit on the economy is presented in Table. 11.5.
Table 11.5.
|
Financing method |
Short-term effect |
Long-term effect |
|||
|
Interest rate |
Investments |
Money mass |
Prices |
||
|
Private sector loans |
Height |
Reduction |
Not changeless |
Incognage |
Small growth of aggregate demand |
|
Loans at the Central Bank |
Reduction |
Height |
Height |
Height |
Growth of aggregate demand, inflation |
|
Money emission |
Reduction |
Height Roman jurisprudence leads its origin from practical activities |
|||
|
Economy. P. Samuelson. ECONOMY. Tom I. Circulation 25,000 copies. |
There is a close relationship between the state budget and the value of GDP. If you imagine that the amount of government procurement of goods and services is a constant value that does not depend on the level of income, then with a low level of income there will be a deficit, and with high - excess budget.
If the budget is balanced, then the amount of tax revenues coincides with the amount of government procurement. If the economy has an economic downturn, the amount of tax revenues to the budget with the unchanged level of public procurement is reduced, budget deficit arises. At the phase of economic recovery, the value of tax revenues is higher than the level of government procurement, budget excess (surplus) occurs. At a given level of government spending and this level of the tax rate, the size of the budget deficit or excess depends on the amount of income.
Fig.8.1. Cyclic balancing of the state budget
Proticiency - Exceeding income on expenses. If the surplus is found, it is reduced by: reducing revenues from the sale of state or municipal property, revenues from the sale of state reserves and resources; the direction of budget funds to repay debt obligations; transmission of part of income budgets of other levels.
If government expenses exceed income, the deficit of the state budget arises. If income is exceeded over costs, the state has a positive budget balance.
Budget deficit \u003d costs - income.
Clean taxes \u003d tax revenues - social benefits.
In this case, the budget deficit can be represented as follows:
Budget deficit \u003d Purchases of goods and services - net taxes.
or Bd \u003d G - T.
The size of the budget deficit is influenced by fluctuations in the volume of national issuance. During the periods of depression, when GDP decreases, the budget is usually reduced with a deficit, while during the lifting periods there is a positive budget balance.
The reasons for these changes the balance of the budget are in the fact that during the recession tax revenues from income tax And other direct taxes are decreasing, as the taxable base is reduced. At the same time, during periods of recession, some types of government expenditures increase (unemployment benefits and other social payments).
Suppose state expenses are 200 monetary units, and the tax rate t \u003d 0.2. Therefore, at y \u003d 0 Tax inclities T \u003d 0. When expenses increase to 1000 units, tax revenues become equal to state expenses (200 units). With income of 1500 units, government spending will amount to 300 units, etc.
Thus, at a low level of income, there is a deficit of the state budget, with a high - excess budget.
Studies of economists show that the growth of government spending leading to an increase in revenues does not ensure that taxes that "walked" increased costs. This means that the amount of tax revenues will always be less than the increase in government spending.
If there is an excess in the state budget, i.e. If the state is withdrawn with taxes more than gives, it means that seizures from macroeconomic turnover becomes more than injections. As a result, GDP reduction occurs.
On the contrary, if the state budget is lacking, i.e. Its costs exceed income, injections are becoming more than withdrawal. This means that purchasing power increases and GDP increases.
Thus, the budget deficit is not an indicator of bad management. Back in the 30s, J. Keynes and Swedish economists, Murdal and B. Walin offered to retreat from the traditional idea that the state budget should be balanced and go for some excess of income expenses for stimulating economic growth, especially during periods crises.
Indeed, if the state pays more money than getting, it increases the purchasing power in society - people are more buying, enterprises sell more, increasing the employment of resources.
therefore the deficit is useful during unemployment , but in the lifting phase it is dangerousSince it leads to inflation, since the growth of purchasing power is not accompanied by an adequate increase in production due to the exhaustion of resources.
To analyze the sources of education of the state budget deficit:
1) structural deficit;
Structural deficit The budget occurs during the periods of the indigenous breakdown of industry structures of economies, which are repeated with periodicity of 45-55 years. It is calculated as a difference between current government expenditures (G) and income that could enroll in the budget, subject to full employment with an existing tax system:
Second \u003d G - T * YF,
where the structure is a structural deficit of the state budget;
YF - GDP, subject to complete employment;
t - income tax rate.
Cyclic deficiency Represents the difference between the actual deficit and structural deficit:
WCTC \u003d T (YF - Y),
where WCTC is a cyclical deficit of the state budget;
Y - actual GDP for this year.
During the economic downturn, the state conducts policies of injection into the national economy and is forced to increase the amount of government spending. Initially, the level of increased government spending increases the volume of budget deficit. But the level of government spending and the tax rate can affect not only the magnitude of the budget deficit, but also to the level of aggregate demand, therefore, on the volume of GDP. The increased volume of government procurement increases the volume of income, thereby increases the total volume of tax revenues in the treasury, therefore, the level of budget deficit should, on the contrary, to be reduced.
However, taxes affect the amount of cumulative demand through the multiplier. Therefore, the change in equilibrium income (d'-d) is equal to the change in government spending (G'-G) multiplied by the multiplier value (MRC). Since the change in income level can be recorded as a change in the value of GDP (Y'-Y), then:
Y'-Y \u003d MPC (G'-G).
It is known that the change in the budget deficit (B'-b) is equal to changing the level of government spending minus changes in the amount of tax revenues T (y'-y), which took place as a result of changes in income level:
B'-B \u003d G'-G-T (Y'-Y).
Thus, the growth of government spending will be able to cause the revival of economic activity, in which the amount of taxes charged will exceed this increase in government spending. With a balanced budget, the sum of all savings (s) and net taxes (T) is equal to the amount of government procurement (G) and investments (I), and the Balanced Budget multiplier is 1:
During the economic recession, the state allows an increase in the deficit of the state budget. When analyzing foreign economists of stabilization fiscal events, it was found that an increase in the state budget deficit to an equal value has a different impact on the aggregate demand in the country - depending on whether the increase in the budget deficit is funded by reducing taxes or by changing public procurement. With tax reducing, households part of the increased disposable income are sent to savings, therefore the initial increase in consumption is less than the amount of tax reducing. As a result, the increase in the state budget deficit financed by taxes has a greater impact on the growth of aggregate demand. This phenomenon opened the laureate of the Nobel Prize T.
Havelmo. It received the name theorems Havelmo. Its essence is as follows.
If the growth of government spending is funded by income taxation, the final increase in national income is equal to the initial increase in government spending. The Balanced Budget multiplier is 1.
In the mechanism of actions to change taxes on the GDP level, the tax multiplier shows a net effect on the value of the GDP of the growth of tax fees per 1 dollar. Nevertheless, the change in taxes is accompanied by a change in the magnitude of government spending. Such a combined effect on GDP reflects the government spending multiplier.
The multiplier establishes that the increase in government expenditures D (G), accompanied by an increase in the increase in the increasing tax receipts D (T), has its result growth of production (GDP). Such a phenomenon occurs while simultaneously action of counter effects:
1. The increase in government expenditures (DG) leads to an increase in total demand (DAD) on the same value;
2. Tax growth (DT) reduces consumer demand for a much smaller value (including MRCs), the fall in total demand, taking into account the disposable income, will be equal to MRC (Y-DT) + A \u003d MPC * Y (1 - T) + a.
Let's try to display the value of the multiplier with a mathematical manner.
Imagine the function of aggregate demand in the form of
AD \u003d Y \u003d MPC * Y + A + I.
We introduce into its formula mathematical values \u200b\u200bof G, T, TR, characterizing the degree of state intervention in the country's economy. At the same time, net taxes are equal to T - TR (tax revenues minus social budget payments), and government purchases G are equal to state expenses minus transcribe payments tr:
Y \u003d MPC (Y - T + TR) + G + A + I.
We will open brackets and imagine tax revenues in the budget as
T \u003d Y * T, provided that these are proportional taxes:
Y \u003d MPC * Y - MPC * T * Y + MPC * TR + G + A + I.
We collect together the term functions that do not depend on Y, we denote them
(Autonomous consumption in the economy):
Y - mpc * y + mpc * y * t \u003d a + i, where A \u003d MRC * TR + A + I;
![]()
Expression 1/1-MRC (1-T) and is public spending multiplier.
The government spending multiplier has long been applied in macroeconomic modeling, in particular in the Hicksa-Samuelson business cycle model. The meaning of this model consists in leveling "waves" of cyclic fluctuations in the economy by regulating the amount of government spending by varying the tax rate of proportional tax and changes in government spending
(Neokeinsian approach).
There are three ways for financing budget deficit:
1) by additional emission of money;
2) at the expense of CB loans;
3) through the borrowing of the population and firms.
Each of these methods has its pros and cons. The advantages of the first two are that their use makes it possible to avoid providing private investment by state, so business spending and personal consumption will not decrease. However, their use is fraught with an increase in inflation.
There are three concepts budget balancing :
1. The concept of annual balancing (Ricardianism). Economic subjects They proceed from the belief that any debts need to be sent sooner or later. They increase the debt of states perceive as an increase in taxes in the future, because Other, except taxes, the source of income from the state is not. State budget restriction:
Tnat. + TBUD. / (1 + i) \u003d GNAST. + Gbud. / (1 + i).
The concept denies the positive effects of stabilization fiscal policy. Thus, the growth of government spending does not lead to stimulating the aggregate demand due to the effect of investment displacement. The decline in taxes does not lead to an increase in consumer spending, but leads to an increase in savings, since the subjects should be prepared for tax increases.
2. The concept of cyclic balancing. The admissibility of balancing the budget during the economic cycle is approved. Deficities during recession periods allow you to stimulate the cumulative demand, and excess during periods of lifts is to restrain the "overheating" of the economy. This policy allows you to smooth the amplitude of the cycle fluctuations by 30 - 35%.
3. The concept of functional finance. The problem of budget balance is considered as a secondary, the task of stabilization is put forward to the fore economic Development. High employment maintenance has priority. The growth of the public debt will not lead to the threat of bankruptcy of the state, subject to a well-established financial system and a high degree of confidence in state institutions.
Page 1.
Cyclic deficit (Cyclical Deficit) - deficit federal budgetcaused by a decline of business activity and caused by the reduction of tax revenues.
When GDP, structural deficiency is AB, a cyclic deficiency is zero. The state should increase Gili to cut G to destroy this deficit, but it may want to do it for several years so as not to bring the economy to the decline.
The budget deficit at full employment is also called a structural deficit in contrast to the cyclical deficit.
The deficit of the actual budget in any particular year consists of a deficit at full employment (or structural deficit] and cyclic deficit. In this case, this deficiency really exists, because when GDP, government spending exceeds tax revenues. When GDP, structural deficiency is AB, and cyclic - zero.
Once again, we emphasize: a discretionary fiscal policy is a targeted change in the deficit at full employment (or structural deficit), but not in the change in cyclic deficit. Since the deficit of the actual budget consists of structural and cyclic deficits, it is impossible to judge the fiscal policy of the government.
The main share of the deficit of the actual budget in the 80s and at the beginning of the 90s was not due to the cyclical deficit, which arises as a result of an automatic reduction in tax revenues for GDP below the level of complete employment.
It does not take into account the lack of tax revenues arising in connection with incomplete employment. Cyclic deficiency is the difference between G VL T, caused by the fact that tax revenues are below those that would be with complete employment.
The state that uses finance as a tool for regulating the economy can consciously make an increase in budgetary expenses or a decrease in tax burden on entrepreneurs. In this case, the emergence of structural budget deficit is inevitable. The cyclical budget deficit is brought primarily to the reduction of the tax base in terms of the decline in production in the phases of the economic crisis and depression and only in the second place - the desire of the government to compensate for the reduction of demand by increasing government spending. The inverse situation occurs in the phases of revitalization and lifting: with increasing production, the tax base is expanded and budget revenues increase, but the government reduces costs to level the increase in demand from entrepreneurs and the population.
The achieved automatically stability, that is, a change in the value of tax revenues in direct dependence on GDP, means that the excess or deficit of the current, or actual, budget in any particular year does not indicate the fiscal policy of the government. Now imagine that investment costs have decreased by causing a decline in production to the level of VVPG. Suppose the government does not accept any discretionary measures. Therefore, the G and T lines remain in the position that is shown on the graph. The emerging cyclic deficiency DC, named as it is associated with the economic cycle, is not the result of certain anticyclic fiscal measures of the government, but rather a by-product of fiscal inaction at that time when the economy rolled down to the decline.
The key problem of this budget concept is that the lifts and decals in the economic cycle may be unequal in depth and duration. Consequently, the task of stabilization comes into conflict with the task of the budget balance during the cycle. As a result, a new phenomenon occurs - a cyclic budget deficit.
Thus, the budget deficit, surplus associated with the production volume, which allows to distinguish structural and cyclic deficiencies. Real deficiency may be more structural. The main reason for such a phenomenon is the decline in production. It leads, on the one hand, to reduce the incomes of the population, entrepreneurs, which reduces tax revenues to the treasury, and on the other hand, to an increase in unemployment payments and other social programs, which increases government spending. The difference between the real and structural deficit is called cyclic budget deficit.
Pages: 1.
Budget deficit - This is the amount of excess budget expenditures over its income in every fiscal year.
Budget surplus - This is the amount of excess budget revenues over its expenses in every fiscal year.
Fully balanced state budget, that is, the budget without a balance is possible only theoretically. Even if the draft budget is balanced, in the process of its execution, equality is practically impossible. Allocate positive and negative aspects of the budget deficit.
Positive side - The policy of scarce financing leads to enhancing economic growth.
Negative side - Budget deficit leads to an increase in public debt, strengthening the tax burden, stimulates inflation processes.
The budget deficit may arise as a result:
1. The need to implement large state investments in economic development,
2. Emergency (war, large natural disasters and etc.).
3. Crisis phenomena in the economy, its collapse, ineffectiveness of financial and credit relations, etc. - the most dangerous and disturbing form of the budget deficit, when it is a reflection of crisis phenomena in the economy, its collapse, the government's inability to keep the financial situation in the country under control.
Functions of the budget deficit:
1. Distribution (redistribution),
2. Food-forming,
3. stimulating,
4. Control.
Distinguish the following types of budget deficit:
Structural deficit - The deficit embedded in the structure of income and expenses in the formation of the budget.
A deficiency or positive budget balance calculated for the economy in the face of the natural level of unemployment, with a natural level of GNP, as well as at the tax rates and the size of transfer payments defined by the current legislation. Usually the presence of a structural deficit is the result of a discretionary fiscal policy. Discretionary fiscal policy - a deliberate change in taxes (tax rates) and the volume of government spending (costs for goods and services and services and transfer payments) in order to ensure the production of non-inflationary GNP in full employment and stimulate economic growth.
It is a calculated difference between current government expenditures and income under the assumption of a certain fixed (natural) unemployment level.
Cyclic deficiency- A state budget deficit caused by a decline of business activity and a reduction in tax revenues.
The difference between the actually observed deficit and structural deficit. Such a deficit varies throughout the business cycle. If the actually observed budget deficit is less structural deficit, then the difference between the structural and real deficit is called cyclical bipling.
Operational deficiency - General deficit of the state budget minus the inflationary part of interest payments for public debt.
Quasi-fiscal (hidden) deficiency State budget accountability of the current (quasi-budgetary) activities of the Central Bank, as well as state enterprises and commercial banks.
The quasi-fiscal operations include:
a) financing by state excess employment enterprises and payroll rates above the market at the expense of bank loans or by accumulating mutual debt;
b) accumulation in commercial banks separated at the initial stages economic reforms from the Central Bank, a large portfolio of inactive loans (overdue debt obligations of state-owned enterprises, preferential loans to households, firms, etc.) these loans are paid mainly due to preferential loans of the Central Bank;
c) financing of the Central Bank (in transition) of losses from measures to stabilize the exchange rate of currency, interest-free and preferential loans to the government (for the purchase of wheat, rice, coffee, etc.) and refinancing loans to commercial banks for serving inactive loans, as well as refinancing Central Bank of Agricultural, Industrial and Housing Programs for Salad Rates, etc.
The hidden budget deficit lies the value of the actual budget deficit and public debt, which may be targeted (for example, before elections), as well as within the framework of the "hard" government course on the annually balanced budget.
Primary deficit - represents the difference between the value of the overall deficit and the amount of interest payments on debt. In case of debt financing of primary deficit, the main amount of debt and its service coefficient increases, i.e. The "burden of debt" in the economy increases.
The theory also distinguishes active and passive deficits.
Active deficit It occurs as a result of excess costs. It may be associated with an increase in investment in new production, which leads to the creation of jobs, increases the employment and level of income of the population.
Passive deficiency - in connection with a decrease in tax and other revenues (due to the slowdown in economic growth, misunderstanding).
Normal is the budget deficit approximately corresponding to the level of inflation in the country. Such a budget deficit is usually covered by low-cost or interest-free credits of the Central Bank. International Standards Assuming a possible budget deficit at 2 - 3% GNP. Usually, the budget deficit of up to 10% of the income amount is considered permissible, while a shortage of more than 20% is critical.
Most complex problem Is the problem of budget balance.
There are various methods of covering the budget deficit:
1. Credit and monetary emission (monetization).
First form - money emission. In the case of the monetization of the deficit, seniority often occurs - the income of the state from the printing of money. Senorage arises against the background of excess of the growth rate of the money supply over the growth rate of the real GNP, which leads to an increase in the average price level. The consequences of such emissions are as follows:
Developed uncontrollable inflation,
Incentives are undermined for long-term investment, investment activity is reduced,
Spiral price spiral is spiral - wages,
The lifetime of the population falls, depreciate the savings of the population,
The budget deficit is reproduced.
In order to preserve the economic and social, stability of the government of developed countries, an unnecessary emission of money is avoided.
Second form - credit emission. The monetization of the state budget deficit may not be accompanied directly by cash emissions, but to be carried out in other forms, for example, in the form of expanding the credits of the Central Bank to state enterprises at discount interests percent or in the form of deferred payments. In the latter case, the government buys goods and services without paying them on time. If purchases are carried out in the private sector, then manufacturers increase prices in advance to insure from possible non-payments. It gives impetus to raising general level Prices and inflation levels. If deferred payments accumulate against public sector enterprises, then these payments are often funded by the central bank or accumulate, increasing the general deficit of the state budget. Therefore, although deferred payments, unlike monetization, are officially considered a non-inflationary method for financing the budget deficit, in practice, this separation turns out to be very conditional.
2. Release loan.
Government loans can be carried out in various forms:
In the form of transferring state securities;
Loans for extrabudgetary funds;
Getting loans.
If the state budget deficit is funded by issuing state loans, then the average market rate The percentage, which leads to a decrease in investment in the private sector, falling net exports and partly to reduce consumer spending. As a result, the effect of displacement occurs, which significantly weakens the stimulating effect of the fiscal policy. Debt financing of the budget deficit is often considered as an anti-inflational alternative to the monetization of the deficit. However, the debt method of financing does not eliminate the threat of inflation growth, but only creates a temporary deferment for this growth, which is characteristic of many transitional economies. If the bonds of the state loan are posted among the population and commercial banks, the inflationary stress will be weaker than when placing them directly in the National Bank.
In the case of mandatory (forced) placement of government bonds in extrabudgetary funds under low (and even negative) interest rates, debt financing of the budget deficit turns into a substantially in the mechanism of additional taxation.
State loans are less dangerous, but they are in some extent undermine market economy If there is a compulsory placement of government securities or the possibilities of obtaining private loans, which increases the demand for loans in the loan capital market, contributes to the rise in the cost of the loan, i.e., the growth rate.
If the debt state accumulates, it turns into public debt. The concept of public debt and methods of management were considered above.
3. Increased tax revenues in the state budget.
The problem of increasing tax revenues to the state budget goes beyond own funding budget deficit because it is permitted in long term On the basis of comprehensive tax reform aimed at reducing rates and expanding the tax base.
4. Sequestration costs.
Its essence is in proportional reduction in government spending in all unprotected budget items.
The list of protected articles is usually included:
wage;
accrual by wages;
transfers to the population (scholarships, pensions, benefits, non-cash housing subsidies and other payments to the population in accordance with the legislative acts of the Republic of Belarus);
food;
medicines and dressings;
interest on public debt;
repayment of public debt;
payment of services of research organizations.
The reduction in the budget deficit should be carried out on a specially developed program. It should envisage the following measures:
Improving the efficiency of public reproduction, which will contribute to the growth of financial resources;
Further development and strengthening market relations, conducting market reforms; privatization and privatization of property (in order to reduce budget financing);
Expansion of the circle of payers should be carried out simultaneously with the optimization of taxation;
Development of territorial-regional economical (strengthening the independence of the regions);
Optimization of the volume and restructuring of the costs of the state budget as a whole and above all sent to the real sector of the economy;
Preservation of financing only the most important and reasonable adoption of new social programs;
Improving planning and system development paid services in the non-productive sphere;
Adjustment of transfer policies, involving a decrease in transfer payments to the industries real sectors economy, improving the efficiency of transfer payments;
Reforming the budget process as a whole. It is necessary to abandon the concept of priority budget expenditures and scarce financing;
Budgeting on a multivariate basis for the purpose of forming optimal structure income and expenses;
The development of the state securities market, which will make it possible to finance the expenses of the state without increasing the money supply in circulation;
Taking measures aimed at attracting foreign capital in the form of investments.
For achievement real Effect And the reduction in the budget deficit listed activities should be considered in their unity and apply comprehensively.
Budget Device, Construction Principles
Author - Matveeva Tatyana Yuryevna, Lecturer NIU-HSE
"Macroeconomics: a course of lectures for economists", 2001
State budget: the costs and income of the state
The state budget is the balance of income and state expenses for a certain period of time (usually a year), which is the main financial plan countries that after its adoption by the legislative authority (Parliament, state Duma, Congress, etc.) acquires the force of the law and is obligatory for execution.
When performing its functions, the state carries numerous costs. For purposes, state expenses can be divided into expenses:
On the political goals: 1) the cost of ensuring national defense and security, i.e. The content of the army, police, ships, etc.; 2) the cost of the maintenance of the state management apparatus
For economic purposes: 1) the cost of maintenance and ensuring the functioning of the public sector of the economy, 2) the cost of help (subsidizing) to the private sector of the economy
For social goals: 1) expenses on social Security (payment of pensions, scholarships, benefits); 2) Education costs, health care, development of fundamental science, environmental protection.
From a macroeconomic point of view, all government spending are divided into:
- government procurement of goods and services (their cost is included in GDP);
- transfers (their cost is not included in GDP);
- interest payments for government bonds (public debt service).
The main sources of state revenues are:
- taxes (including social insurance contributions);
- profit of state enterprises;
- senorage (income from money emissions);
- income from privatization.
Types of state budget states
The difference between incomes and expenses of the state is a balance (state) of the state budget. The state budget may be in three different states:
1) when budget revenues exceed the costs (T\u003e G), the budget balance is positive, which corresponds to the excess (or surplus) of the state budget;
2) when income is equal to expenses (G \u003d T), the budget balance is zero, i.e. Budget is balanced;
3) when budget revenues are smaller than expenses (t
At different phases of the economic cycle, the state budget is different. In decline, budget revenues are reduced (as the business activity is reduced and, therefore, the taxable base), therefore the budget deficit (if it existed initially) increases, and the surplus (if it was observed) is reduced. When the bug, on the contrary, the budget deficit decreases (as tax revenues increase, i.e. budget revenues), and the surplus increases.
Deficit of the state budget and its types
There are structural, cyclic and actual budget deficit. The structural deficit is the difference between government expenses and budget revenues, which would be accepted in the conditions of complete employment of resources at the existing tax system:
The cyclic deficit is the difference between the actual deficit and structural deficit:

During the recession, the actual deficit is larger than the structural, since cyclical is added to the structural deficit, since with the recession y y *. Structural deficit is a consequence of a stimulating discretionary fiscal policy, and a cyclic deficit is the result of an automatic fiscal policy, a consequence of the action of built-in stabilizers.
The current budget deficit and primary deficit are also distinguished. The current budget deficit is a general deficit of the state budget. The primary deficit is the difference between the total (current) deficit and the amount of payments to public debt.
Concepts of the state budget
Attitude towards the deficit of the state budget is usually negative. The most popular is the idea of \u200b\u200ba balanced budget. Historically, three concepts have been put forward in relation to the state budget: 1) the idea of \u200b\u200bannually balanced budget; 2) the idea of \u200b\u200bthe budget balanced by the phases of the economic cycle (on a cyclic basis); 3) the idea of \u200b\u200bbalance not budget, but the economy.
The concept of an annual balanced budget is that independently of the economic cycle phase every year the budget expenditures must be equal to income. This means that, for example, during the recession, when budget revenues (tax revenues) are minimal, the state to ensure the balance of the budget should reduce government spending (government procurement and transfers). And since the decline and public procurement, and transfers leads to a decrease in total demand, and, therefore, the volume of production, this measure will lead to even deeper recession. And, on the contrary, if in the economy boom, i.e. Maximum tax revenues, then for balancing budget costs with incomes, the state should increase government spending, provoking even greater overheating of the economy and, therefore, even higher inflation. Thus, the theoretical failure of such an approach to budget management is quite obvious.
The concept of the state budget balanced on a cyclic basis lies in the fact that it is not necessary to have a balanced budget annually. It is important that the budget is balanced in general during the economic cycle: budget surplus, increasing during the boom (highest business activity), when the budget revenues are maximal, should be used to finance the budget deficit with a place during the period of recession (minimum business), When budget revenues are sharply reduced. This concept also has a significant drawback. The fact is that the phases of boom and recession differ in duration and depth, therefore the amount of the budget surplus, which can be accumulated during the boom, and the deficit, which accumulates during the recession period, as a rule, do not coincide, therefore the balanced budget cannot be ensured.
The concept of which the goal of the state should not be balanced by the budget, but the stability of the economy, was the greatest distribution. This idea was put forward by Keynes in his work " General Theory Employment, interest and money "(1936) and was actively used in the economies of developed countries until the mid-70s. According to the views of Keynes, the tools of the state budget (government procurement, taxes and transfers) should be used as anticyclic regulators that stabilize the economy at different phases of the cycle. If the decline in the economy, the state in order to stimulate business activity and ensure economic recovery should increase its costs (government procurement and transfers) and reduce taxes, which will lead to an increase in total demand. And, on the contrary, if in the economy boom (overheating), the state should reduce costs and increase taxes (income), which restrains business activity and "cold" the economy leads to its stabilization. The state of the state budget does not matter. Since Keynes theory was aimed at developing recipes for the fight against recession, with a decline in the economy, which was proposed to be carried out using, first of all, the tools of budget regulation (an increase in government procurement and transfers, i.e. budget expenditures and tax cuts, i.e. . Budget revenues), then this theory is based on the idea of \u200b\u200b"scarce financing". As a result of use in most developed countries in the 50s - 60s of Keynesian recipes for the economy, the problem of chronic state budget deficit by the mid-70s became one of the main macroeconomic problemsthat served as one of the reasons for the strengthening of inflationary processes.
Methods for financing the deficit of the state budget
The deficit of the state budget can be financed by three ways: 1) due to the emission of money; 2) at the expense of the loan in the population of his country (internal debt); 3) at the expense of a loan from other countries or international financial organizations (external debt).
The first method is called emission or monetary method, and the second and third - debt method of financing the deficit of the state budget. Consider the advantages and disadvantages of each method.
Em session method of financing the deficit of the state budget. This method is that the state (Central Bank) increases the money supply, i.e. Releases additional money in appeal, with the help of which covers the excess of their income expenses. The advantages of the emission method of financing:
The growth of money supply is a factor in the increase in total demand and, therefore, the volume of production. The increase in the money supply causes a decline in the interest rate in the money market (depreciation of the loan price), which stimulates investments and ensures growth cumulative expenses and cumulative release. This measure, therefore, has a stimulating effect on the economy and can serve as a means of exiting a state of recession.
This is a measure that can be done quickly. The growth of the money supply occurs, or when the Central Bank conducts operations on the open market and buys government securities and, paying for sellers (households and firms) the cost of these securities, issues additional money (such a purchase it can be done at any time and in any The required amount), or at the expense of a direct emission of money (on any required amount).
Disadvantages:
The main disadvantage of the emission method of financing the deficit of the state budget is that in the long period, the increase in money supply leads to inflation, i.e. This is an inflationary method of financing.
This method can have a destabilizing effect on the economy during overheating. The decline in the interest rate as a result of the growth of the money supply stimulates an increase in total expenses (primarily investment) and leads to an even greater increase in business activity, increasing the inflation gap and accelerating inflation.
Financing the deficit of the state budget due to internal debt. This method lies in the fact that the state issues securities (government bonds and treasury bills), sells them to the population (households and firms) and the funds received uses to finance the excess of government spending over revenues.
The advantages of this funding method:
He does not lead to inflation because money mass does not change, i.e. This is a non-inflation method of financing.
This is quite an operational way, since the issue and placement (sale) of government securities can be provided quickly. Population B. developed countries I am pleased to buy government securities, because they are highly qualified (they can easily sell them - this is "almost money"), highly reliable (guaranteed by the state that enjoys trust) and enough incomes (percentage is paid).
Disadvantages:
On debts need to pay. Obviously, the population will not buy government bonds if they won't bring income, i.e. If the percentage will not be paid on them. The payment of interest on government bonds is called "public debt service." The more public debt (that is, the more government bonds issued), the greater the amounts should go to the service of debt. And the payment of interest on government bonds is part of the costs of the state budget, and what they are more, the more budget deficit. The vicious circle is obtained: the state issues bonds to finance the deficit of the state budget, the payment of interest on which it provokes even greater deficit.
Paradoxically, this method in the long term is not non-inflation. Two US economists Thomas Sarzent (laureate Nobel Prize) And Neil Wallace proved that debt financing of the state budget deficit in the long term can lead to even higher inflation than the emission. This idea got in economic literature The name "Theorem Sarzhen-Wallace". The fact is that the state by financing the budget deficit by internal loan (release of government bonds), as a rule, builds a financial pyramid (refinance debt), i.e. It pays with the past debts of the loan in the present, which will need to return in the future, and the return of debt includes both the amount of debt and interest on debt. If the state will use only this method of financing the state budget deficit, then the moment in the future can be used when the deficit is so large (i.e., such a number of government bonds and the costs of serving public debt will be so significant) that its financing is debt The way it will be impossible, and will have to use emission financing. But at the same time, the amount of emission will be much larger than if it is carried out in reasonable sizes (small portions) every year. This can lead to a burst of inflation and even determine high inflation.
As Sarjent and Wallace showed, to avoid high inflation, it is wiser not to abandon the emission method of financing, but to use it in combination with debt.
A significant disadvantage of the debt of financing is the "displacement effect" of private investment. We have already considered its mechanism when analyzing the shortcomings of fiscal policy from the point of view of the impact on the economy of increasing budget expenditures (public procurement and transfers) and reduce budget revenues (taxes), which generates a budget deficit. Now consider the economic meaning of the "displacement effect" in terms of financing this deficit. This effect is that an increase in the number of government bonds in the securities market leads to the fact that a portion of household savings is spent on the purchase of government securities (which ensures the financing of the state budget deficit, i.e. goes to non-production goals), and not on Purchase securities of private firms (which ensures the expansion of production and economic growth). This reduces the financial resources of private firms and, therefore, investments. As a result, the volume of production is reduced.
The economic mechanism of the "displacement effect" is as follows: an increase in the number of government bonds leads to an increase in the supply of bonds in the securities market. The growth of bond supply leads to a decrease in their market prices, and the price of the bond is in reverse Addiction With a percentage rate, therefore, the interest rate is growing. The growth rate of interest determines the reduction of private investment and reducing the volume of output.
The debt method of financing the state budget deficit can lead to a balance of payments shortage. Not by chance in the mid-80s, the term "twin deficits" appeared in the USA ("Twin-deficits"). These two types of deficits can be interconnected. Recall the identity of injection and seizures: I + G + EX \u003d S + T + IM, where I - Investments, G - Government Procurement, Ex - Export, S - Savings, T - Clean Taxes, IM - Import.
We regrure: (G - T) \u003d (S - I) + (IM - EX)
From this equality it follows that with the growth of the state budget deficit, there should be either to increase savings, or to reduce investments, or increase the trade deficit. The mechanism of exposure to the growth of the state budget deficit to the economy and financing it at the expense of internal debt has already been considered when analyzing the "effect of displacement" of private investments and issuing as a result of the growth rate of interest. However, along with the internal displacement, the growth rate of interest leads to the displacement of pure exports, i.e. Increases trading deficit.
The external displacement mechanism is as follows: The growth of the internal interest rate compared to the world makes the securities of the country more profitable, which increases the demand for them from foreign investors, this in turn increases the demand for the national currency of this country and leads to an increase in the national currency exchange rate , making goods of a given country relatively more expensive for foreigners (foreigners now have to exchange large quantity of its currency to buy the same amount of goods from this country as before), and imported goods become relatively cheaper for domestic buyers (which should now exchange fewer national currency to buy the same number of imported goods), which reduces exports and increases import, causing a reduction in pure exports, i.e. Determines the deficit of the trade balance.
Financing of the state budget deficit with external debt. In this case, the budget deficit is funded at the expense of loans from other countries or international financial institutions (international monetary Fund - IMF, World Bank, London Club, Paris Club, etc.). Those. It is also a type of debt financing, but by external borrowing.
The advantages of this method:
- The possibility of obtaining large sums
- Non-inflational nature
Disadvantages:
- The need to return debt and debt service (i.e. payments both the amount of debt and interest on debt)
- The impossibility of building a financial pyramid to pay external debt
- The need to distract funds from the country's economy to pay external debt and its service, which leads to a reduction in the internal production and decline in the economy
- With a balance of payments deficiency, the exhaustion of the country's gold reserves
So, all three ways to finance the state budget deficit have their advantages and disadvantages.
Public debt, its types and consequences
The public debt is the amount of accumulated budget deficits, adjusted for the magnitude of budget excess (if any). The state debt, therefore, is an indicator of the stock, since it is calculated at a certain point in time (for example, as of January 1, 2000), in contrast to the deficit of the state budget, which is a flow rate, since it is calculated for a certain period of time (per year). There are two types of public debt: 1) internal and 2) external. Both types of public debt were discussed above.
In the absolute value of public debt, it is impossible to determine its burden for the economy. For this purpose, an indicator of the ratio of the amount of public debt to the magnitude of national income or GDP, i.e. d \u003d d / y. If the growth rate of debt is less than GDP growth rates (economy), then the debt is not terrible. At low rates of economic growth, the national debt turns into a serious macroeconomic problem.
The danger of a large state debt is not related to the fact that the government can go bankrupt. This is impossible, because, as a rule, the government does not pay a debt, but refinance, i.e. Building a financial pyramid, releasing new state loans And making new debts to repay old. In addition, the government to finance its expenses can increase taxes or issue additional money into circulation.
Serious problems I. negative consequences Great public debt, are as follows:
- The efficiency of the economy is reduced, since the funds from the production sector of the economy are distracted both on the service of debt and the payment of the debt amount itself;
- Redistan revenue from the private sector to the state;
- Inequality in income is intensified;
- Definancing debt leads to an increase in interest rate, which causes investment in the short term, which in the long term can lead to a reduction in capital reserve and reducing the production potential of the country;
- The need to pay interest on debt may require increasing taxes, which will lead to the undermining of the economic incentives
- Created a threat of high inflation in the long term
- Lays the burden of debt payments for future generations, which can lead to a decrease in their welfare
- Payment of interest or principal amount of debt foreigners cause the translation of a certain part of GDP abroad
- A threat of debt and currency crisis may appear





