At the beginning of the VIII century. The Moors and Berbers, led by the Arabs, invaded and in a short time captured almost the entire peninsula. In the middle of the VIII century. as part of the Arab Caliphate, whose capital was located in, the Emirate of Cordoba was created, in the X century. which became an independent caliphate. Its architecture is close to that of the Maghreb, but also absorbed the architectural experience of Byzantium. One of the most significant works of this architecture is the Great Mosque in Cordoba, built in the 10th century. Despite the fact that in the XIII century. inside the Cordoba Mosque, the Cathedral of the Virgin Mary was built, and the minaret was turned into a bell tower, the entire interior of the mosque was preserved. It contains about 900 columns made of marble, jasper, agate, a fountain for ablutions and a courtyard planted with orange trees.
(Andalusia), located in the bend of the Guadalquivir River, at the time of its heyday in the X-XI centuries. its splendor competed with Constantinople, Damascus and Baghdad. Then the population of Cordoba was greater than in any other city in Europe, and the number of mosques, palaces, baths and public buildings was measured in hundreds. Unfortunately, the complex of the emir's palaces, decorated with 40 thousand columns, did not survive, but entire quarters of the snow-white buildings of the Muslim city have survived.
(Andalusia) is the former capital of the last and longest existing Moorish state in southern Spain. It was created in the XIII century. and survived until 1492, i.e. year of the discovery of America. Muslims during this period developed trade, science, arts, it was the heyday, the "golden age" of Granada. At this time, the architectural gems of Granada were created - the fortress palace, the Generalife summer palace, the oldest quarter of the city of Albacín. The Albassin district is a labyrinth of narrow streets surrounded by snow-white facades of houses and walls of courtyards, behind which are hidden flower beds and orchards. The country residence of the Generalife emirs was created in the middle of the 13th century. on a hill next to the Alhambra. Graceful pavilions with cascading pools, courtyards with orange trees, rose gardens and hedges - all this bears little resemblance to the palaces of European monarchs of that time.

("Al-hamra", ie "red", according to the color of the walls of red sandstone) - the residence of the Emir of Granada. This is the best preserved 9th century Alcazaba. Rising on a hill above the city, the Alhambra amazes with its proportions from afar, and from the inside - with the splendor of its interior decoration, reminiscent of the scenery for "Tales of 1001 Nights". One openwork hall follows another, with even more refined arabesques, with even more carved columns, even more whimsically decorated with vaults. The Hall of the Two Sisters is striking, the ceiling of which resembles a honeycomb pattern. In the Alhambra, the most famous is the Lion's Courtyard, surrounded by galleries with light openwork arcades, with a fountain in the center, the bowl of which is supported by marble statues of lions (late 14th century).

Similar to the Alhambra, surrounded by luxurious gardens, it was built in the 10th century. in the city of Zaragoza (Aragon). Despite a noticeable restructuring at the end of the 15th century, it is the largest monument of the Moorish style in the north of the country.

The Mauritanian heritage can be seen in various parts of Spain, with the exception of the far north of the country, which did not submit to the Arab conquerors. - the former palaces-fortresses of the rulers, preserved in many Spanish cities: (Andalusia), Segovia (Castile-Leon), Toledo (Castile-La Mancha), etc.

In the city (Extremadura) you can see the fortress walls built by the Moors with arches and 30 clock towers, the most famous of which is called Torre del Bujaco.

The monument of the Arab era belongs to the city of Elche (Valenciana). There are about 200 thousand palm trees here. Oasis Palmeral was created in the 10th century. by the Arabs thanks to a very complex irrigation system. There is no other such example of Arab farming in Europe. Many buildings of the Arab era have also survived in the town: the Altamir palace, a defensive tower, etc.

Moor - who is this? A representative of a cruel and willful people or someone who made an invaluable contribution to the development of cultures of different countries? Where is the truth and what is fiction?
The birth of an empire
Moors called the inhabitants of Mauritania, located in northern Africa. Their history is inextricably linked with the development of Islam.
In the XII century, the city of Medina was founded by the prophet Muhammad. After that, the people, who had previously adhered to a nomadic lifestyle, found a permanent place to live. Then they began their development, conquering new lands, preaching Islam to the east and west.
Thirst for knowledge
Moor - who for whom are conquests important? Contrary to the generally accepted attitude towards the Moors as to uneducated people, it must be said that this is a great delusion. For a Muslim, knowledge was essential. Due to the heat of the day, nomadic peoples moved around at night. The result of which was the emergence of such a science as astronomy. When meeting with representatives of other cultures, the Moors tried to get as much new knowledge as possible. They attached particular importance to books. Their value was very high and a large number of them were published.
Due to the fact that the crusaders created an unflattering glory for Muslims, many do not know for sure the Moor - who is this? Believing that it is a synonym for the word "barbarian".
In fact, Arab culture was open to new knowledge. After the capture of Egypt, the Moors gained access to which allowed them to seriously expand their horizons. Many works have been translated into Arabic. It should be noted that the Arabs and Berbers professing Islam were also called Moors.
She tried to protect herself as much as possible from new knowledge, which significantly hampered her development.

Moors in Europe
Having overcome Gibraltar in 711, the Moors came to For 4 years, capturing a large territory up to France. Considering the fact that Europe of those times was in deep crisis, many cities were only happy to receive a rather strong patron who could protect against wars and raids of tribes. Despite the fact that Islam was unknown to the population of the Iberian Peninsula, they quite easily began to accept the new religion. Many cities were rebuilt practically from scratch, Cordoba became the main one. Moor - who is he and what is his contribution to the development of Spain? New technologies were introduced: an irrigation system was used to water the gardens, and there was water supply and sewerage in the houses.
Of particular importance was paper, which was recognized in Europe thanks to the Arabs. Unsurprisingly, there were 10 libraries in Cordoba. The foundations of modern algebra and chemistry were born in Toledo, only here it was possible to study works on mathematics and astronomy.

The Crusades, which aimed to rid the countries of Europe from the invaders - the Moors, mercilessly destroyed them, buildings and all technical structures. People were forcibly forced, under pain of death and property seizure, to convert to Catholicism. Thus, a new but ambitious culture supplanted a more developed one, which gave Europe a lot over the XII centuries of influence.
Quite often you can hear the phrase: "The Moor has done his job, the Moor can leave." This is a quote from the play The Fiesco Conspiracy in Genoa, written by J. F. Schiller at the end of the 18th century. The phrase is a symbol of the unprincipled use of a person for their own purposes. The attitude to him was like a tool to achieve the goal, which was no longer needed after the action.
Modern Moors (Mauritians) are the descendants of brave warriors who managed to conquer many peoples. Now it is a large people living in several African countries, including the Republic of Mauritania.
History
The ancestors of the modern Moors include the Berbers, who included the Gethuls and Sanhajis. These tribes migrated frequently, which contributed to their spread across Northwest Africa. They were warlike, so they easily captured the peace-loving population. Military campaigns continued for a long time and in the 11th century they allowed the Berbers to create the Almoravid kingdom. It was characterized by general Islamization, which intensified significantly with the penetration of the Arabian tribes who came here in the 14th century. The migrants fought with the locals, but the Arabian tribes outnumbered the Berbers in battle, so they were forced to retreat to the Senegal River. As a result, there is a complete Arabization of the territory, the Moors acquire the gene pool from the Berbers and Arabians.
Where do they live (territory)
A significant proportion of the Mauritanians live near the Senegal River. This group is represented by the sedentary Moors who gravitate towards the right bank. Other Mauritanians lead a nomadic lifestyle and are on the move all the time, settling in the Sahara Desert, as well as various semi-deserts.
Life

The highest stratum in Moorish society were the Hasans. One step below were the marabouts who carried independence. The marabout class included civil servants, merchants, clergy, and teachers. The Hasans respected the Marabuts and willingly gave their daughters in marriage to their sons. The Zenaga, the main backbone of the Mauritanian population, were completely dependent on them.
Much of the behavior of the Mauritanian is determined by Islam. Unlike many Arab peoples, a lot of attention is paid to women. She has many rights and freedoms, monogamy reigns in marriage. A woman is allowed to file for divorce and enter into marriage unions on her own initiative. Interestingly, Mauritanians associate themselves with Arabs, although they are guided by the Berber family code. The way of life of nomads differs sharply from that of sedentary ones.
Language
In everyday life, Mauritanians use the Mauritanian language, which is classified as a sub-dialect of Arabic. French is also very common.
Religion
Most Mauritanians accept Sunni Islam. There is a small stratum that adheres to the cult of ancestors. Some are fetishists. A number of Moors are Catholic.
Culture

The Mauritans have become very famous people for their culture. Artisans who are famous all over the world work in Mauritania. The Mauritans mastered a special technique for processing fabric and leather. Skillful crafts made of silver, wood, patterned carpets delight the eye and find new owners. Silver has become the main precious metal from which various crafts are made, for example, chests, jewelry. Pottery flourishes, especially in the Tagant region.
The Mauritanians make artful leather goods for everyday use. The bags of the Tagant masters have gained recognition in many parts of the world, as have the shoes. In addition to Tagant, Atar became famous in Mauritania, where artisans are engaged in the manufacture of silver items, and in Alega they perform complex works from different types of wood. Gold is also known to Moorish jewelers. They prefer to combine it with coral. There are also very original works, for example, calabash - containers for storing things or liquids made of pumpkin.
Moorish music has also become famous all over the world. Musicians in Mauritania have always played a special role in conveying messages and valuable information from one village to another. Their songs were also motivational, performed for the warriors. The main musical instruments are:
- lute-like tidinite;
- ardin;
- table;
- ratchet.
The drum-like placard was usually used by men, and ardin (an exquisite variation of the African harp) by women.
Nomads cultivate date palms and cultivate land in the oasis. The presence of land suitable for pasture largely determines the life of a nomadic Mauritanian. With the onset of winter, it is time to move from the northern territories to the southern ones, but when summer comes, you can return to the north again. Drought gives way to a rainy period, which determines the way of life. The distances that have to be covered sometimes exceed hundreds of kilometers. Nomads travel by tribes, taking all their property with them. During long journeys, they cover over a thousand kilometers. For successful movement, camels are used, which can do without food and water for a long time. In a nomadic camp, up to 30 Mauritanians can be present, who are called nomads by the sedentary. All of them are united by excellent knowledge of the area, therefore there are many pathfinders among the nomads. This knowledge is essential when traveling long distances, as there are few sources of water in the desert. A few wells are scattered throughout the territory, every nomad knows that the more he can visit the wells, the more his camel can get drunk. You yourself also need to replenish water supplies. The Mauritanian nomads teach their children toponymy from an early age. There are already about 5 generations of experienced nomads who know the desert areas around Senegal like the back of their hand.

The Mauritans know 2 types of wells. The first one is called vir and is a deep hole that can reach 80 meters. Arkhans are relatively shallow wells. The latter are hardly known to anyone, although it is not easy to find the same vira without a special map. It is according to it that the Moors are guided, wandering in the desert. Knowledge of topography determines success, but it is not enough. It is necessary to know every landmark, even a small hill matters.
The most prestigious occupation among nomads is cattle breeding. The more heads of cattle, the richer a person is considered. Moreover, the Moors rarely sell their livestock and do not even always use it for cooking. Even those nomads who are transitioning to a sedentary lifestyle continue to replenish the number of livestock, trying to demonstrate their status to those around them. The most important animal is the camel. The dromedary, a one-humped camel, which many associate with a nomadic way of life, is especially honored.
Dwelling
Nomads live in tents, which are made of durable black linen. The fabric is sewn from coarse wool (camel or sheep). The fabric can be up to 10 meters long. The canvas is picked up with wooden poles, fixed with stakes. One such tent can accommodate about 8 people. Sometimes they use ordinary tents, the fabric of which is sewn from cotton. Goat skins are laid inside, bedding and pillows are laid. A kettle is usually placed in the center.
The sedentary Moorish people make their dwellings from sandstone. The life of the average Mauritanian is rather modest, wealthy people can afford rich utensils.
Traditions
The traditions of the Mauritanians can shock you. Until now, slavery is widespread in Mauritania, which has a massive character. This fact also influenced the marriage, because among women there are also many slaves. In general, the customs associated with wedding and marriage can be considered truly amazing.
Wedding
Black robes for a woman are a symbol of imminent marriage, which she, oddly enough, rejects. Bridesmaids should do their best to prevent marriage, literally blocking the path of the spouse. This is far from the most surprising custom, for example, the sahwa tradition requires newlyweds to be extremely modest at a wedding. The celebration itself does not look like a bright holiday, everything takes place with family and close friends.
However, one cannot but take into account current trends. The world is changing, which is clearly seen in the example of the Mauritanians. Many people try to arrange lavish weddings, emphasizing the status of the family. Now many Mauritanians say that the number of guests determines the status, which is due not so much to the desire to announce the wedding to the whole world, but to the desire to recoup it as soon as possible. After all, every guest must bring a gift.
A traditional wedding begins with the appearance of the bride and groom. Over the black robes, a white shawl is thrown over the girl. The groom, on the other hand, appears in a white robe and holds a black scarf in his hands. The most honored guest will be the one who gave the most money to the newlyweds. If the family of the bride and groom can afford a party, they will invite artists and dancers. After the celebration, the newlyweds go to the groom's house. The bride is supposed to hide in it so that the betrothed cannot find her for as long as possible.
Appearance
clothing

National costumes in Mauritania are bubu (derra). Few Mauritanians can afford such clothes. It is sewn from blue jacquard, the clothes fall to the ground. Both men and women wear it. A distinctive feature of the man's suit is the turban, which is necessary to protect the face and head. Women can wear melikhwa, which has no seams. Melikhwa is sewn from a large piece of fabric, which can reach a length of 5 meters. The fixation of clothes is carried out with the help of knots - there are no pins or buttons on the small ones. The meaning of this outfit is to hide the female body from prying eyes. The color of the melikhwa can be very diverse, and a variegated color is not excluded. Mauritanians are very fond of jewelry, accessories, beautiful shoes, glasses. This helps them create unique images, compensating for the closeness. In recent years, Mauritanian fashion has become one of the most famous on the African continent. Wearing a melikhwa requires some skill, as you can get confused in it.
Food

The food of the Mauritanians is unusual. They can combine flavors that may seem unusual to many. For example, sauces can have a bittersweet-salty flavor. Mayonnaise is sour, like almost all vegetables.
- Camel sour cream, which is eaten with dates, will seem very unusual.
- The oil in Mauritania is also difficult, it crumbles a lot when cut.
- The main meat dish is camel meat. They eat it with vegetables and couscous.
- All Moorish soups are thick.
- From drinks, the Moors prefer tea, coffee, camel milk.
The Moors for most people remain a mysterious people, whose culture is too exotic. At the same time, they are considered the descendants of a warlike people who influenced the history of Portugal and Spain. The difficulty of studying the Moors and Mauritania is caused by a special language that is difficult to learn. However, the high interest from tourists promises good prospects.
Video
This video shows a typical Moorish dance.
"Mavros" (μαῦρος) in Greek means "black." Today the Greeks refer to Negroes and sometimes Arabs as well.
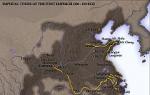
Arab conquest of the Iberian Peninsula
At the end of the 7th century, the Arabs, having made their stronghold in the city of Kairouan in the east of modern Tunisia, conquered North Africa, by 709 reached Tangier and the shores of the Atlantic Ocean.
In 711, Arabs and Berbers, led by Tariq ibn Ziyad, landed on the Iberian Peninsula. After defeating the Visigoths on July 19, 711 at Lake Khanda and defeating Ecija, the Arab troops took Cordoba, Toledo, the capital of the Visigothic kingdom, and other cities.
The army of Musa ibn Nusayr, who arrived in 712 from North Africa, occupied Medina-Sidonia, Carmona, Seville and Merida.
By 718, the Iberian Peninsula, with the exception of a small part in the north, passed into the hands of the Arabs. In 720 they invaded Gaul, occupied Septimania and Narbonne.
Their further advance into Europe was stopped after the defeat of the Arab troops by the Frankish cavalry and the infantry of Karl Martell near Poitiers on October 4, 732. In 759 Pepin the Short drove the Arabs out of Narbonne and Septimania.
In the conquered Spanish territories, the Arabs formed an emirate, which was part of the Umayyad Caliphate; in 756 the Umayyads founded the independent Emirate of Cordoba, and in 929 the Caliphate of Cordoba.
The local secular and ecclesiastical landowners, who expressed obedience to the conquerors, were left with part of the lands they had previously owned, along with the peasants.
A significant part of the land passed into the hands of the new land nobility from among the conquerors. The most fertile lands of the south and southeast were occupied by the Arabs themselves; in the central and northern parts of the country, the Arabs settled numerous Berber tribes that were part of their troops.
The Arab state reached its greatest power under Abdarrahman III (ruled 912-961). The development of feudal relations led at the end of the 10th century to a weakening of the central government. In 1031 the Caliphate of Cordoba split into many small emirates. This ultimately led to his downfall.
Reconquista
Centers of resistance to the Arab conquest arose as early as the 8th century. in the north of the peninsula:
- the Kingdom of Asturias (since 718), which laid the foundation for the Reconquista (the conquest of the territories captured by the Moors by the peoples of the Iberian Peninsula),
- Navarre, who achieved independence against the Arabs and Franks in the middle of the 9th century,
- Spanish brand, formed in the area between the Pyrenees and the river. Ebro, conquered by the Franks in 785-811. By the end of the 9th century, the counties that made up the Spanish mark had become virtually independent feudal states.
From 924 the expanded Kingdom of Asturias was called the Kingdom of León (after the new capital, León). In 1035, Castile formed as an independent kingdom.
In the same year, Aragon became an independent kingdom. The interests of the development of the Reconquista demanded the unification and centralization of the independent Spanish states formed in the north and east of the peninsula.
In 1037 (finally in 1230) they united into a single kingdom of Leon and Castile. In the northeast, political hegemony passed in the 11th century to Aragon.
The decisive stage of the Reconquista began after the collapse of the Cordoba Caliphate in 1031. In 1085, the Castilians took Toledo, which became the capital of the Leono-Castilian kingdom.
Small Arab states, faced with this threat, called for help from the Almoravids from North Africa, who, having won a victory in 1086 at Salak and halting the course of the Reconquista, subjugated all of Muslim Spain. However, in 1118 Aragon conquered Zaragoza from the Moors.
In 1212, at the battle of Las Navas de Tolosa, the combined forces of Castile, Aragon and Navarre won a decisive victory over the troops of the Almohads (who drove the Almoravids out of Spain in the middle of the 12th century).
In 1236 the Castilians took Cordoba, in 1248 - Seville; in1229-35 Aragon conquered the Balearic Islands, in 1238 - Valencia; the Portuguese liberated the territory of the Algarve (the south of modern Portugal) in 1249-50.
By the middle of the XIII century. the Moors had only a small area in the south - the Emirate of Granada.
In the west, the Reconquista was held by Portugal (in 1095-1139 a county, nominally dependent on León; from 1139 - a kingdom, recognized as independent by León in 1143).
In 1492 the Reconquista ended with the capture of Granada, the last Muslim stronghold on the Iberian Peninsula. The Arab-Berber population that remained in Spain was forcibly converted to Christianity. In 1492 the Jews were expelled from Spain, in 1502 - the Moors, who did not accept Christianity.
The descendants of the Muslim Moors who remained in the Iberian Peninsula were called Morisco ( moriscos). They constituted a significant part of the peasantry in some regions - such as Aragon, Valencia or Andalusia, but in 1609-1614 they were mostly expelled.
According to historians ( Henre lapeyre), 300 thousand of the total population of approximately 8 million were expelled. The exiles mostly moved to modern Morocco, Tunisia and Algeria, bringing their culture there. Some of them were engaged in sea piracy.
How often do we use words and don't even think about their meaning? Many of them become so familiar that over time they lose their original meaning. In literary sources of the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, the word "Moor" is used quite often. What nationality is this? Where did this name come from? And why is it so rare now? We will answer all your questions about this topic.
Moor - who is this?
To understand the meaning of a word, it is necessary to understand from which language it came to us. Scientists are still arguing about the origin of the name "Moor". This word has a fairly typical pronunciation for many language groups. But for the most part, the scientific community has come to the conclusion that the word "Moor" is a native of the Latin language. Literally translated, it means "Mauritian" or "Mauritanian". The Greek version of the origin of this word is also close, translated from the ancient Greek dialect it can sound like "dark" or "black".
Who were called the Moors?
The meaning of the word "Moor" gives some idea of who was attributed to this nationality. But in reality, not everything is so simple. Residents of different countries called Moors completely different nationalities. The only thing they had in common was their dark skin color.
For example, in the Middle Ages, this was the name given to the Muslim population of Spain, as well as the inhabitants of North Africa. For a medieval European, it was clear that the Moor was an Arab. They included in this category all black Muslims who came to the Iberian Peninsula.
The Spaniards, in turn, called the Moors the indigenous inhabitants of the Philippine Islands, which they discovered in the first half of the sixteenth century. Judging by the works of Russian classics, they had their own idea of the Moors. In the books and poems of the nineteenth century, all black Africans were classified as Moors. We can say that in Russian the words "Moor" and "Negro" were synonymous.
In the modern world, the word "Moor" is rarely used. It has a somewhat derogatory connotation. Most often, you can hear how the Moors are called Arab migrants who settled in Spain. In many languages of the world it is considered indecent to speak to a person - "Moor".

Moor: other meanings
It should be borne in mind that in modern language there is another meaning for this word. In the West, the word "Moor" refers to a simple card game, which is played mainly on vacation. It consists of several parties and can last for several hours. There are cases when it was played for more than two days. This is possible when a company of four or five people participates in the game process.
In Russia, this game is known as "101", it often brightens up a long and boring train journey or becomes entertainment in a children's camp. Apart from its two main names, this game has more than five more variants that it is known by. Every country in the world uses its own familiar name.

Knowing that Moor is not the simplest word that has several meanings, you yourself will decide whether to use it in everyday speech. The main thing is to apply it to the place and not be mistaken. After all, this is the approach that characterizes literate and educated people.