Why does a green coating appear on the tongue? The causes of this pathological phenomenon will be discussed below. You will also learn how to get rid of this unpleasant condition.
basic information
The color of plaque on the tongue can indicate the presence of many problems in the human body. It is not without reason that when visiting a doctor, the doctor very often asks to show him your tongue in order to confirm or refute the diagnosis. The color palette of such raids can be quite extensive. Therefore, only an experienced specialist can identify the true cause of their formation. By the way, it often relies on other existing symptoms.
Green coating on the tongue: reasons
The substance that appears on the tongue plate can vary significantly depending on the season, climate and other conditions. But if such a phenomenon is pronounced and unnatural, then, most likely, we're talking about about the symptoms of a serious illness.
So why does a green coating appear on the tongue? The reasons for this condition may be the following:
Who should I contact?
You should ask your therapist about why the coating on your tongue has changed color. A dentist and a gastroenterologist can also answer this question.
Symptoms
Now you know why a green coating may appear on the tongue. The reasons for this unpleasant phenomenon were listed above. When identifying them, the doctor is obliged to pay attention not only to the color scheme of the plaque, but also to its other features.
Also, during the examination of the patient, doctors identify the structure of the lesion. Thus, the substance that coats the tongue can be fatty or cheesy, wet or dry. An important role is also played by the presence various damages. (the causes and treatment of this pathology are presented in this article) indicate serious problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Color palette
As mentioned above, the cause of layering on the tongue plate is very often determined by its color scheme.
- a small thickness may indicate a person’s normal condition. This color may also be associated with heat.
If the intensity of the shade increases noticeably, the consistency of the substance and its thickness change, then this indicates problems in the gastrointestinal tract. Pathological changes in the digestive system can be associated with diseases of the biliary tract, malfunctions of the liver, bile ducts, etc. 
- White-green coating. This layering indicates normal functioning of the body. But if over time the plaque increases and begins to thicken, then this indicates problems with the intestines (for example, prolonged constipation).
If a dense whitish coating is observed against a background of high temperature and common features intoxication, it can be stated infection.
- Dark green color of the tongue. Such a non-standard color is quite rare. It manifests itself in people with severe pathology (for example, with impaired functioning of the bile ducts, pancreas or gall bladder).
Also, the dark green color of the tongue can indicate dehydration of the human body, increased blood acidity and Crohn's disease.
- Gray-green plaque also indicates organ damage digestive system, especially the stomach and intestines. Such symptoms are often found with peptic ulcer disease.
Diagnostics
How to diagnose an existing disease and identify the cause of the development of green plaque and cracks on the tongue? The causes and treatment of such pathological conditions should be determined and prescribed only by a doctor. The latter is obliged to examine the patient, assess his general condition, and also pay special attention to the shade, density and size of pathological layers. The doctor may also prescribe general tests, performing ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and FGDS. 
Treatment process
You can get rid of the green layer on the tongue only if you have installed the real reason its occurrence.
If no pathologies were identified during the medical examination, then most likely the problem arose due to improper or absent oral hygiene. In this case, the patient is advised to take good care of himself, constantly brush his teeth, tongue surface and gums, and also rinse his mouth after each meal.
If the reason for the development of a green layer on the tongue lies in disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, then you need to contact an experienced gastroenterologist. The same applies when observing cracks, wounds and ulcers on the oral mucosa.
For such pathologies, doctors very often prescribe antibacterial agents, as well as digestive enzymes.
If thrush and fungal diseases are detected, doctors recommend the use of antifungal medications.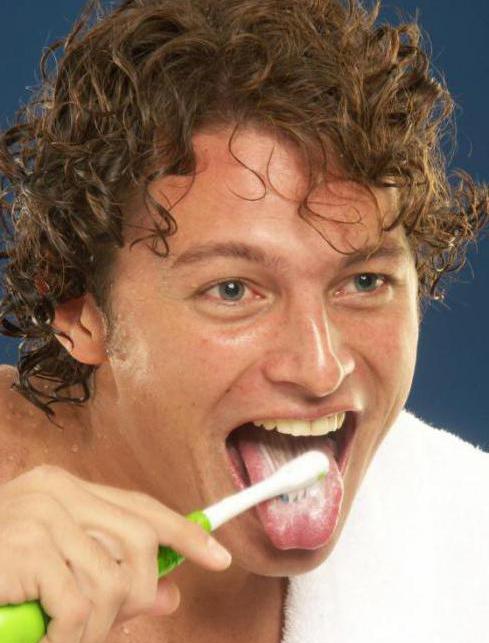 
If the body's defenses are reduced, the patient is prescribed multivitamin complexes, dietary supplements, etc. The patient may also be recommended a diet consuming large amounts of fresh vegetables and fruits. In addition, it is necessary to avoid fried, hot and spicy foods that have a detrimental effect on the digestive system.
If a green coating on the tongue occurs as a result of a bad habit, it is recommended to give up smoking and alcohol abuse.
In the presence of other diseases, including HIV infection, special therapy and medical supervision are required.
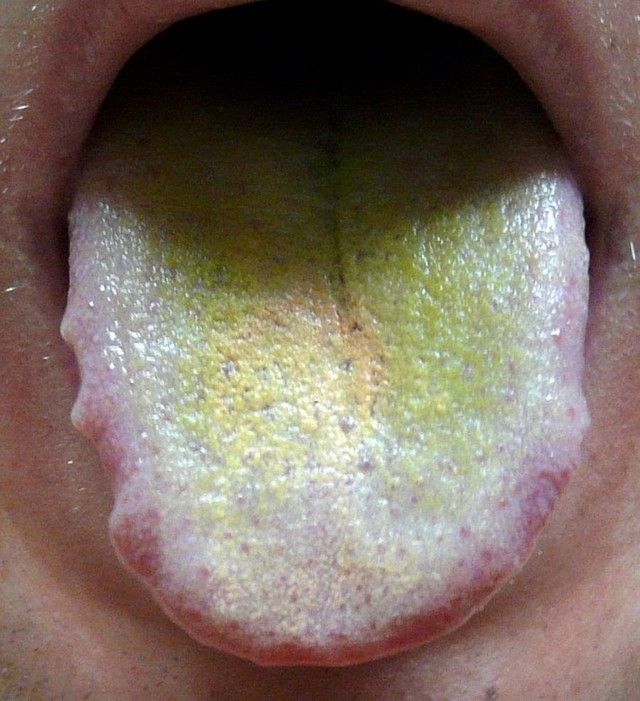
Green coating on the tongue
Quite often at a doctor’s appointment, the doctor asks to show your tongue. Why does he need this? It turns out that based on the shade of plaque on the patient’s tongue, an experienced specialist is able to determine which area’s pathology causes such changes? And the color palette, it turns out, can be quite extensive; for example, a green coating on the tongue can indicate the presence of a fungal infection in the patient’s body. A qualified doctor is able to determine the presence of many diseases based on the level of compaction of the neoplasm and its color.
If the tongue surface is covered with a slight coating, which easily disappears after morning procedures, then there is no need to worry. This is part of the normal functioning of the body. But if the tongue is coated with a green coating, this is already a reason to consult a doctor, because such a symptom can serve as an indicator of a number of diseases, including fungal origin. Even if the pathology has not yet been diagnosed, then a change in the shade of the “spraying” makes it possible to assume its presence and detect it even later. early. Therefore, the tongue can be perceived not only as an organ that is created by nature to participate in the process of speech communication, chewing food, and taste perception, but also as one of the diagnostic methods.
The general condition of the tongue can become the primary determining criterion on the diagnostic path. Even different colors of the tongue indicate the presence of a particular disease. For example:
- If the tongue is covered with a green coating, this may indicate one of the multiple fungal diseases.
- Blue – purple talks about problems respiratory system, in particular the lungs.
- A bright red color may indicate problems in the hematopoietic system or the functioning of the heart.
- The tongue may acquire a lilac hue due to kidney disease.
- A very pale color indicates vitamin deficiency and anemia, poor nutrition.
- If the raid white, it can be dangerous only in the case of increased density of the substance, which appears together with high temperature. This can indicate the fact that an infection has entered the human body.
The tongue of a healthy person should be uniformly pink in color with a firm, elastic structure. In addition to color, the doctor takes into account the thickness and density of applied substances. These parameters can change depending on the time of year (which should be taken into account by the doctor): in summer period the plaque is usually observed to be somewhat denser than in winter. However, with the onset of cold weather, it may acquire a yellowish tint.
An increased density of plaque may indicate infectious processes occurring in the patient’s body. If a coating of medium consistency is observed, this may indicate a serious illness that has affected the respiratory system. In this case, the lesion is sluggish, chronic in nature and viral etymology.
Somewhat less common than others is the green coating on the tongue, covering the central area of the tongue plate. Less commonly, only a certain area of the organ is coated. The plaque resembles mold and can remain on food during consumption.
Causes of green coating on the tongue
The substance that appears on the tongue plate may vary depending on climatic conditions residence of a person, as well as the time of year, but if it has a pronounced color, then, most likely, symptoms of a more serious disease are observed. What could be the reasons for a green coating on the tongue?
- Ignoring the rules of personal oral hygiene.
- Pathological changes in the digestive system (GIT). Especially if these symptoms are accompanied by cracks on the lingual surface. Consultation with a gastroenterologist is necessary.
- Poor nutrition, lack of vitamins in the patient’s body. If the problem does not go away after adjusting the diet, a consultation with a therapist is necessary (to determine the root cause of the symptoms).
- Thrush.
- Man uses a large number of spicy, fried or fatty foods - this significantly affects the functioning of the liver, which causes a green coating on the tongue. This disease is most likely if, along with a change in color, there is also increased dryness in the mouth. If these two symptoms are present, the likelihood of liver pathology increases significantly and becomes a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
- The green tint of sediment may indicate a decrease in the body's immune forces.
- Diseases whose root cause is fungal infections. With this aggression, the tongue may be completely covered with mold or in separate torn areas.
- The color change can also be catalyzed by antibiotics taken, against the background of which fungal flora can actively develop.
- HIV infection.
- A green tint can also appear as a result of taking drugs that suppress immune system.
- Bad habits: smoking, drugs, alcohol.
- The reason for the change in color of plaque on the tongue may be the change of seasons and climatic variations.
- Puberty in adolescents.
Therefore, if a precedent arises, it is worth making an appointment with a doctor. Only a specialist will be able to correctly determine the causes of green plaque on the tongue, make a diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. This doctor could be a therapist, gastroenterologist or dentist.
Symptoms of green coating on the tongue
Often, when describing the symptoms of a manifestation, they talk about a phenomenon that in itself is already a symptom of one or more diseases. It is very difficult to describe the symptoms of a green coating on the tongue, because this factor itself serves as an indicator of a large number of diseases. It can only be noted that the pathology of plaque is considered not only by color, but also by the thickness and structural density of the formation.
- Thickness distribution. If the layer is thin, this suggests an incipient pathology. This is how a respiratory or infectious disease can manifest itself. A thick layer indicates the chronic nature of the disease, the course of severe infection of the body.
- The location of the plaque can also be an important indicator: the tongue can be covered completely or in separate areas located in a certain place.
- A different shade allows an experienced specialist to talk about a particular disease. At the same time, the thicker the color and the darker the plaque, the more seriously the pathology affects the body.
- During the examination, the doctor also evaluates the ease with which the substance separates from the surface of the tongue. A soft, easily removable plaque (even if it quickly forms again) is either a sign of normality or characterizes a mild pathology (the decision is up to the attending physician). In case of aggravation of the pathology, the neoplasm becomes denser.
- A different structure of the lesion is also observed: the substance can be cheesy and fatty, as well as dry or moist.
Yellow-green coating on the tongue
A slight coating is present in almost any language. And if it has a small thickness and a pale yellow or white-grayish tint, then 90% we can talk about the normal state of human health, and a slight change in color may be associated, for example, with hot summer. But if the intensity of the shade increases, the thickness and consistency of the substance changes - this indicates that pathological changes in the patient’s digestive system have begun to progress. An intense yellow-green coating on the tongue may appear due to the following diseases:
- For diseases of the biliary tract, various abnormalities in the functioning of the liver and intrahepatic bile ducts (the so-called increased bilirubin).
- A change in the color of the plaque on the lower part of the tongue (to yellow-green) can be seen at the initial stage of the spread of jaundice.
- Such symptoms can also indicate congestion in the gallbladder, excess bile in it, as well as pathology in the digestive system. In this situation, the plaque may be red.
- A yellow-green coating on the tongue, with a slightly brown tint, most often appears in people who smoke a lot or abuse alcohol. This coloration is also possible due to severe lung disease.
- This shade can also appear after taking a specific product. And if such a plaque appears immediately after eating and goes away after some time, then there is nothing wrong with it.
- Increased bilirubin, which turns the tongue yellow, may be caused by adrenal dysfunction.
- Acute intestinal infections can also lead to this coloration of the tongue.
- The cause can be any acute respiratory disease.
- Taking, for example, drugs such as furazolidone, cardiac glycosides, quinine or enterofuril can make the tongue yellow.
- Glossitis (catarrhal inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tongue) caused by bacterial or fungal flora.
White-green coating on the tongue
If, when brushing your teeth, a person sees a small whitish coating on the tongue, then you should not be upset - this is a normal functioning of the human body. But if, over time, the layer of neoplasm begins to progressively increase, this fact should alert you and cause you to seek advice from a qualified specialist. In the mirror you can see a white-green coating on the tongue - the cause of this phenomenon could well be prolonged constipation. In the case when a dense whitish coating is visible against the background of high temperature, as well as obvious signs of intoxication of the body, it is almost unmistakably possible to ascertain an infectious disease developing in the body.
The root localization of a white-green coating on the tongue often indicates pathological changes occurring in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Diseases such as stomach ulcers and duodenum, intestines, gastritis or enterocolitis. But its lateral predisposition (on both sides of the front part) may indicate lung or kidney diseases.
Dark green coating on the tongue
Doctors rarely observe this non-standard shade of plaque. An intense dark green coating on the tongue usually appears in patients with fairly severe pathology, often burdened by a “bouquet” of various diseases. But mainly this:
- Severe disturbance in the structure and function of the pancreas, bile ducts and gallbladder.
- In case of severe dehydration of the human body. In this case, the patient experiences an increase in blood acidity, which is the catalyst for these symptoms.
- Crohn's disease, which is caused by a decrease in the level of certain hormones produced by the adrenal glands, can also provoke such a plaque. In this situation, an increased amount of melanin is produced. It is this substance that gives the tongue such an unusual color.
- An almost black - dark green coating on the tongue gives rise to such a terrible infectious disease as cholera.
Gray-green coating on the tongue
Any deviation from the norm frightens a person very much. And what feelings might arise when you see a gray-green coating on your tongue in the mirror? Just awful! But what can this color of the speech organ indicate? It turns out that if during an examination the doctor sees a tongue of such a color scheme, then his decision is clear - consultation and diagnostic studies which the patient will have to undergo under the guidance of a gastroenterologist, since a gray-green coating on the tongue clearly indicates damage problems associated with the organs of the digestive system: the stomach or intestines. Such symptoms can be caused by their ulcerative lesions.
Diagnosis of green plaque on the tongue
To effectively eliminate pathological change the color of the plaque covering the tongue, and, if possible, to prevent its recurrence, it is necessary to establish the reason why such a change occurred. To do this, a green coating on the tongue is diagnosed. First of all, it would not hurt to exclude changes in the color of the tongue, which can occur after eating. A person can do this test independently. If after eating the plaque disappears after some time, then there is no need to worry - this is a normal physiological process.
If the process does not reverse, you need to seek help from a specialist. This could be a therapist, dentist or gastroenterologist. You can start with a therapist, after an examination he will write a referral to a more specialized specialist, or make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment yourself.
Primary and mandatory item Diagnosis of green plaque on the tongue is its examination, which will allow the doctor to assess its general condition: shade, size of pathological deposits and their density. At the same time, in order to get an idea and a more complete clinical picture of the pathological deviation, it is worth adhering to a number of simple rules:
- A visual inspection should be carried out only in a well-lit room, preferably in natural daylight. If there is a shortage of such lighting, it can be replenished with additional lamps. The auxiliary light source must have high brightness and be in the spectrum of white, white-yellow or yellow. Blue and white-blue shades are unacceptable. With their use, a distortion of the color of the tongue occurs, which can lead to difficulty in making a correct diagnosis.
- The doctor asks the patient to stick out his tongue strongly. For ease of examination, health workers use a spatula. The procedure should be carried out carefully, sequentially examining all parts of the organ: from tip to root, including the side walls and its inner part.
For a reasonable diagnosis, when examining the tongue, the doctor must pay attention to deviations from the physiological and anatomical form. He evaluates:
- Geometric parameters and shape.
- His mobility (normal, partial or complete limitation).
- Anatomical deviations: condition of the papillae and type of relief.
- Color of the tongue plate.
- Evaluates whether the tongue is wet or dry.
- And without fail, visually determines changes in the shade of plaque, its density (which is assessed using a spatula), and thickness of plaque. Visualizes the localization of pathological plaque. Eastern medicine believes that different areas of the tongue are responsible for different organs.
Treatment of green plaque on the tongue
Previously, questions about the reasons that cause the pathology we are interested in and methods for diagnosing it were clarified; it remains to understand the principles of treating green plaque on the tongue. Although this question has already been partially answered. Treatment methods for any symptomatology come down to relieving the root cause that causes it. If you do not completely eliminate the cause of the pathology, you will not be able to get rid of the green coating on the tongue. Therefore, before starting therapy, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics and determine the disease.
If no pathology was identified during the examination, the most likely problem is improper or completely absent oral hygiene. You just need to take more careful care of your oral cavity: properly and constantly brush your gums, teeth, and tongue surface, and rinse your mouth after the next meal. If you have any questions, you should consult a dentist. He will tell you how to carry out these procedures correctly, recommend the most effective toothpaste and a comfortable, non-hazardous toothbrush. When plaque appears, it may come from the mouth. bad smell, which can be eliminated with specially formulated antiseptic rinses. They cope well with pathogenic flora of the oral cavity.
Miramistin. Using this solution is quite simple. It is necessary to rinse the mouth for one minute. If the drug is presented in spray form, then it is sprayed in the mouth three to four times throughout the day. The course of treatment is up to seven days. Miramistin is not able to penetrate the skin and cellular barriers, therefore, if you do not swallow the drug, it can be used during pregnancy.
Forest balm. This rinse has a beneficial effect on inflammatory processes occurring in the oral cavity. Its basis is natural oils with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties: essential oils fir, pine nut, pine needles, aloe juice and extracts from herbs yarrow, sage and St. John's wort. The use of Forest Balsam has a detrimental effect on pathogenic flora, having a beneficial effect on the rotten smell. This product is used after each brushing of teeth (at least twice a day). The drug is taken into the mouth (without diluting, unless this is indicated in the attached instructions), without swallowing, rinse the cavity for a minute or more. After completing the procedure, spit out all the liquid and do not drink or eat anything for another hour so that the antiseptic works better.
Chlorophyllipt solution. A herbal preparation created on the basis of essential oils obtained from eucalyptus leaves, which have pronounced fungicidal, antibactericidal, antiprotozoal, antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties. Before rinsing, dilute a teaspoon of 1% alcohol solution with a glass of warm boiled water. Rinse for at least a minute.
There are many traditional medicines:
- In this case, essential oils that have antibactericidal properties are effectively used. It is worth remembering that you should not just swallow such a composition. Place a teaspoon of oil into the oral cavity and keep it there for 10-15 minutes. The effectiveness of the procedure is assessed by the change in the color of the essential oil. After completing the procedure, spit out the used oil and rinse your mouth.
- In such cases, decoctions of herbs with antiseptic properties (mint, St. John's wort, calendula, chamomile, oak bark, sage, chicory) have proven themselves to be excellent.
- You can prepare the following solution: dissolve two teaspoons of soda in 200 ml of warm water. Soak gauze in the resulting mixture and wipe your tongue with it, removing plaque. It is worth repeating two to four such procedures throughout the day. This event should be performed for ten days.
If more thorough oral hygiene does not produce positive results, the doctor tries to find the underlying causes of these symptoms. If a diagnosis is made, treatment for green plaque on the tongue is selected based on this knowledge. After all, the symptoms will go away only if the cause that causes them is eliminated.
If the problem is the pathology of bile secretion and its stagnation, choleretic agents (choleretics: cholenzim, lyobil, vigeratin) are prescribed.
Allohol. The diuretic is drunk immediately after meals three to four times throughout the day, one to two tablets. The duration of the course is one to two months. You should not use this drug in case of increased intolerance to the drug, in case of concomitant cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis or hepatitis, ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, acute and subacute liver dystrophy, as well as in children under three years of age.
Tanacehol. The medicine is taken after finishing meals, two tablets three times a day. In case of acute medical necessity the number of techniques can be increased to four. The duration of treatment is up to a month. Patients who suffer from hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, who have a history of gastroduodenitis and peptic ulcers of the digestive system should not take this drug.
In the treatment of a particular disease, antispasmodics can also be used: atropine, duspatalin.
No-shpa. The drug is taken 40–80 mg two to three times a day. This drug is contraindicated for use in cases of prostatic hypertrophy, individual intolerance to the components, as well as glaucoma.
Drotaverine. The tablets are administered orally, without being tied to meals. The dose of the drug and duration of treatment are prescribed by the attending physician individually. The dose usually prescribed is 40-80 mg of the drug (this corresponds to one or two tablets), taken in two to three doses. You should not exceed the dosage of 240 mg per day. In children aged 6-12 years, the dosage is slightly lower and is 20 mg one to two doses per day. Children from two to six are prescribed 10–20 mg of the drug administered once or twice a day.
Hepatoprotectors are also used that promote the regeneration of liver cells:
Karsil. The dosage of this drug is purely individual and, depending on the severity of the pathology, the number of pills taken can vary from one to four pieces throughout the day. Before the age of five, this drug is usually not prescribed, and for older children, the dosage is calculated as 5 mg taken per kilogram of the child’s weight and divided into three doses. The duration of treatment is at least three months. You shouldn't accept this medicine in cases where the patient has a tendency to allergic reactions. No side effects have been identified while taking Karsil.
Legal. If a severe form of liver failure is diagnosed, the patient is initially prescribed Legalon-140 (in the capsule active substance silymarin is included in the dosage of 140 mg). At the first stage of treatment, the patient receives one unit of the drug three times a day, subsequently one capsule twice a day. If the patient’s condition is moderate, then the doctor prescribes Legalon-70, one or two units three times a day. The drug is taken orally whole, without crushing, with a small volume of water. Usually the drug is well tolerated and does not cause side effects. However, it should not be prescribed to patients who are hypersensitive to the components of the drug.
Antiviral drugs: roferon A, intron, welferon.
Reaferon. The drug is used locally or intramuscularly. The injected solution is prepared just before use: one ampoule of the drug is diluted with 1 ml of physiological sodium chloride solution. The number of appointments and duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician. Reaferon is contraindicated for use: if the patient is pregnant or has a history of cardiovascular disease.
If necessary, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, and, depending on the disease, the drug taken may be related to various groups: macrolides, tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins.
Ampicillin. The method of administration of the drug is selected individually by the attending physician: intravenously, intramuscularly or orally. The dosage used is also purely individual and depends on the severity of the disease. Ampicillin is administered orally once in an amount of 250–500 mg (the daily amount should not exceed 2–3 g). When medium shape pathologies, the drug is taken several times a day with an interval of six to eight hours. If a severe stage of the disease is diagnosed, the drug is taken in 1-2 g doses. In this case, the intervals between administrations of the drug must be maintained within four to six hours. In the acute period, the doctor may prescribe medication into a vein - 500 mg, the IV interval is six hours. Ampicillin is not prescribed for infants under one year of age, and for older children - at the rate of 100 - 200 mg per kilogram of the baby's weight. The resulting amount is divided into four to six injections. The duration of taking the drug depends on the patient’s condition, the progressive effectiveness of treatment and can range from five days to three weeks.
Patients suffering from hypersensitivity to penicillin derivatives, lymphocytic leukemia, liver dysfunction, and gastrointestinal diseases should not take this drug.
Antifungal drugs: fluconazole, mycosist and others.
Griseofulvin. Medicine administered orally, with food or after finishing a meal. The drug is most effective when used together with vegetable oil. Depending on the disease and the form of the infecting fungus, the dosage of the drug may vary significantly. For example, for trichophytosis and favus in children, the dosage is calculated using the formula 18 mg per kilogram of the child’s weight. Dosage regimen: initially, daily, after obtaining a therapeutic effect, the dosage is left the same, but taken every other day (this lasts two weeks), after that twice a week (the same two weeks). For microsporia, the calculation is based on other figures: 21 -22 mg per kilogram of the child’s weight is the daily dosage. For an adult patient, the amount of griseofulvin varies from 0.5 to 1 g. The dosage regimen is similar. If onychomycosis is diagnosed, then an adult is prescribed 625 mg – if the patient’s weight does not exceed 50 kg. The permissible daily amount is 1 g of the drug, which corresponds to eight tablets. For children and adolescents, the daily volume of the drug is calculated based on 16 mg per kilogram of the small patient’s weight. The course of treatment is quite long and can last up to eight months.
Griseofulvin is contraindicated for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as in the case of concomitant diseases: porphyria, liver and kidney dysfunction, hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, cancer, disorders cerebral circulation, in case of bleeding of various origins, for children under two years of age.
Adsorbents and central dopamine blockers are used quite actively.
Reglan (metoclopramide, cerucal) - blockers. The drug is administered orally, before meals. Adult patients - 0.005 - 0.01 g (or one to two teaspoons) of the composition three times a day. In the case of an acute period of the disease, the amount increases to 2 ml (intravenously or intramuscularly). The dosage administered to babies is 0.0025 - 0.005 g orally or 1 ml intravenously or intramuscularly. The drug is contraindicated when internal bleeding, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Enterosgel (activated carbon, polyphepane) – adsorbents. The composition is drunk one to two hours before meals, washed down with a small amount of water or before use, diluting the contents of the sachet with a small amount of liquid.
Adults are prescribed one packet three times during the day. You should not take more than three packets (67.5 g) per day. Children from five years old and adolescents up to 14 years old - 15 g of the drug (two teaspoons) three times a day. No more than two packets per day. For toddlers under five – one teaspoon of enterosgel three times a day. No more than one package per day. It is advisable for infants not to exceed a dosage of half a teaspoon. In this case, the drug must be diluted in breast milk(or boiled water) at the rate of one part enterosgel and three milk (water).
In case of acute intoxication, the doctor has the right to double the dosage.
When taking this drug, side symptoms are observed quite rarely and boil down to nausea, gag reflexes, and constipation. It is contraindicated only in cases of increased intolerance to the components of the drug by the patient’s body.
- Daily hygiene of the body, including the oral cavity. If you have any questions, you should contact your doctor or any dentist for answers, who will clearly explain how to properly care for your gums, teeth and tongue, which toothpaste to choose, which toothbrush to choose.
- Remove bad habits: smoking, drugs, alcohol.
- Do not ignore preventive visits to specialized specialists.
- Rooms in the house must be systematically wet cleaned and ventilated daily.
- You should not self-medicate, because this can only worsen the situation, and the use of antibiotics can also cause a green coating on the tongue.
- If any symptoms appear, you should not let the disease take its course. It must be diagnosed in time and adequately treated, and this can only be done by a qualified specialist.
- Review your diet, balancing it and removing “harmful” foods.
- Try your best to maintain your immune system at the proper level.
If a green coating on the tongue, despite all your efforts, still appears, you should not self-medicate - leave it to your attending physician - the result will be much more effective.
Forecast of green coating on the tongue
The tongue is, in fact, an indicator of the state of health of the body. And the appearance of some deviation from the norm in its physiological and anatomical manifestation directly depends on one or another malfunction in the body. Therefore, the prognosis of a green coating on the tongue largely depends on many factors. If hygiene measures could be stopped this problem, then there is no need to worry at all - this is just a temporary reaction of the body to some external stimulus. If the pathology is deeper and more severe, then a positive prognosis for a green coating on the tongue consists of such parameters as the area of the diagnosed disease, the severity of its pathology, the time of treatment (how early the disease is diagnosed) and the effectiveness of the therapeutic measures taken.
When you get up in front of the mirror in the morning and see a green coating on your tongue, you shouldn’t immediately panic and faint. After all, the reason may be quite banal - the tongue was tinted with one of the food products. But you shouldn’t relax either. It would be correct to observe the color of the plaque over some time, and if the intensity of the shade does not go away (or increases), then it is imperative to undergo an examination by a specialist who will determine the reason for the change in the color of the plaque on the tongue plate, and based on this will be able to prescribe an adequate course of therapy.
With obvious signs of intoxication and an increase in temperature with a white gap in the tongue, one can conclude that an infectious disease is developing.
If plaque is localized at the root of the tongue, this indicates problems with the gastrointestinal tract. In case of pathology of the kidneys or lungs, it is concentrated in the lateral part.
The presence of a dark green coating indicates severe pathology. This mainly indicates problems with the pancreas or gallbladder.
Formations on the surface of the tongue with a dark greenish tint are one of the signs of Crohn's disease. At the same time, melanin production increases. The substance gives the tongue this color.
If the reason for the change in the color of the tongue is related to a malfunction of the internal organs, then you should consult a doctor.
Yellow-green plaque in a child
Parents are attentive to everyone's appearance external signs in a child, because in early age It is difficult to independently determine the disease. It is important to establish the cause of the change in tongue color. To do this, you need to pay attention not only to plaque, but also to other symptoms.
It is important to remember that some baby foods contain dyes. Then, when they are used, a coating of the corresponding color may appear on the tongue; it can be easily removed with a brush. If formations on the surface appear again, then the reason is related to the work of the internal organs.
The main reason for the appearance of plaque in children is the accumulation of various substances on the surface of the tongue. Most of concentrated in the back.
The appearance of plaque in children is usually associated with infectious processes in the oral cavity. It could be a sore throat or stomatitis. In addition to plaque, the child experiences symptoms of intoxication, fever, problems with bowel movements and abdominal pain. All this indicates disturbances in the functioning of certain organs.

With local inflammation, a sore throat is observed and the tonsils become inflamed. It is important to pay attention to the manifestation of these symptoms and consult a pediatrician.
Survey
If the plaque does not correspond to the norm, then a clinical examination is prescribed to establish the disease. The patient must undergo the following tests:
- Blood test (general and biochemical)
- Blood on
- Scraping from mucous membrane
Based on the results of a blood test, the inflammatory process can be determined. Antibody tests are performed to determine the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the body.
Other research methods may also be needed: corpogram and ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
A corpogram is prescribed to exclude intestinal disease, and an ultrasound is performed to diagnose pathology of internal organs.
How to get rid of plaque
Before starting treatment, the cause of the plaque should be determined.

If it is associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, then you need to limit the consumption of smoked, fried, fatty foods, as well as alcoholic beverages.
It is important to practice good oral hygiene. It is necessary to brush not only your teeth, but also your tongue, twice a day. After every meal, be sure to rinse your mouth. It is recommended to use an antibacterial cleaning paste.
When the tongue is inflamed, antiseptic drugs are used for treatment: Furacilin or Chlorhexidine. Dense plaque is removed using Trypsin or Chemotrypsin.
Forest balm effectively helps with inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. It is based on natural oils that have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. The balm is used 2 times a day after each brushing of teeth.
Chlorophyllipt solution will help remove plaque on the tongue. The composition includes essential oils with antibactericidal, antiviral and antiprotozoal properties. To rinse, dilute a teaspoon of alcohol solution in a glass of warm water. The mouth should be rinsed for about a minute.
If rinsing with antiseptic agents does not bring positive results, then other drugs are used. It will be possible to get rid of plaque only if the cause of its appearance is eliminated.
If plaque is a sign of pathology of the biliary tract, then Lyobil, Cholenzym, Vigeratin, etc. are prescribed.
To improve the digestive system, take appropriate medications (Mezim, Pancreatin, etc.).
For fungal diseases, Mikosist and Fluconazole are used. If necessary, the doctor prescribes hepatoprotectors, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, adsorbents, etc.

For prevention purposes, you can use decoctions and infusions to remove plaque. Before using them, you need to make sure that you are not allergic to herbs.
Self-medication is not recommended, as it can cause harm and aggravate the situation. If conventional methods do not help eliminate plaque, then a comprehensive examination should be carried out to identify and establish the cause. In this case, you will need to consult not only a therapist for adults and a pediatrician for children, but also other specialists: a gastroenterologist, etc.
Traditional methods of treatment
An infusion using sage, chamomile, and mint will help eliminate plaque and support the intestinal microflora. All components must be taken in equal quantities, pour hot water and leave for 2 hours. The resulting infusion should be used to rinse your mouth 3-4 times a day.
A decoction of oak bark has a bactericidal effect. Brew a tablespoon in a glass of boiling water and heat in a water bath for 40 minutes. When rinsing with a decoction of oak bark, you can not only remove plaque, but also get rid of the unpleasant odor.
To stabilize the functioning of all organs, it is useful to take a decoction based on flax seeds on an empty stomach.
An effective remedy for plaque is a soda solution. Dissolve a tablespoon of soda in a glass of warm boiled water, stir and rinse your mouth twice a day.
You can wipe the tongue with a soda solution or an antiseptic. To do this, wrap a sterile gauze bandage around your finger, then dip it into the solution and collect plaque from the surface of the tongue.
An effective way to eliminate green or yellow formation– treatment using vegetable oil. Take a small spoon of oil and suck, rather than swallow, for 10-15 minutes. After finishing, you need to rinse your mouth with water. If the procedure is performed correctly, the oil will change color.
The condition of the mucous membranes of the tongue indicates the state of human health and warns of various ailments of the internal organs and oral cavity. It is important to pay attention to the presence of bacterial plaque, its color, swelling and unpleasant odor. What does green coating on the tongue mean, what causes its appearance?
Why does green plaque form?
What are the main reasons that cause the appearance of a greenish coating on the tongue?
A green coating on the tongue of an adult or child can be caused by serious pathologies of internal organs that require treatment under the supervision of a doctor, and an incorrect lifestyle. If such deposits are eliminated after cleaning the surface of the mucous membrane, then there is no cause for concern. More attention should be paid to hygiene and avoid bad habits. If the deposits are persistent or other symptoms are present, you should seek medical help.
Oral diseases
If a green coating appears on the tongue, the cause may be advanced fungal stomatitis (thrush). It is caused by yeast-like microorganisms, which are always present in the body of every person. While creating favorable conditions bacteria begin to multiply rapidly and damage the tissues of the mucous membranes, forming erosions, ulcers or aphthae. Causes of thrush:
- mucous membrane injuries;
- weak immunity in children and elderly people;
- wearing dentures;
- hormonal imbalance;
- taking antibiotics, oral contraceptives.
 In the initial stages of stomatitis, spots appear on the mucous membranes, covered with a white cheesy coating. After its removal, bleeding erosion remains. Ulcers can be single or affect a large area, sometimes merging into continuous films, affecting inner side lips, cheeks, gums and tongue.
In the initial stages of stomatitis, spots appear on the mucous membranes, covered with a white cheesy coating. After its removal, bleeding erosion remains. Ulcers can be single or affect a large area, sometimes merging into continuous films, affecting inner side lips, cheeks, gums and tongue.
If treatment is not carried out on time, the wounds can become infected and inflamed. The disease becomes necrotic. In this case, ulcers are formed, covered with yellow-green crusts.
Why does a yellow-green coating form on the tongue of an adult or child? Damage to the membranes of the tongue is called glossitis. Patients are concerned about pain, burning during eating and talking, putrid odor, and increased body temperature. Treatment of fungal stomatitis in adults is carried out by a dentist. The child should be shown to a pediatrician and pediatric dentist.
Diseases of internal organs
Why is the surface of the tongue green? Diseases of the stomach and intestines cause disruption of the natural microflora in the oral cavity. The surface of the teeth and tongue is covered with a persistent green coating. In this case, patients are worried about pain, heaviness in the abdomen, flatulence, heartburn, belching, and bad breath when speaking. In the initial stages, such plaque is removed after morning cleaning, but during the day it forms again. In more severe forms of the disease, deposits become denser and difficult to remove. With such symptoms, treatment by a gastroenterologist is necessary.
Disturbances in the functioning of the liver, gallbladder and its ducts cause the formation of a greenish coating on the tongue, which is not removed during brushing.
Additionally, there is a feeling of dryness in the mouth, and cracks appear on the tongue. Patients complain of heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium, a bitter taste in the mouth, stool disorders, nausea or vomiting. Symptoms worsen after eating spicy, fried, fatty foods or alcoholic beverages. The thickness of the green coating indicates the stage of the disease.
Plaque color and consistency
When diagnosing diseases, doctors pay attention to the consistency, thickness and color of plaque. A thin layer indicates the beginning of the development of the disease, a thick layer indicates severe forms or a chronic course. The consistency of deposits can be curdled, dry or wet. By color they are:
The condition of the tongue and mucous membranes of the oral cavity can promptly warn of the development of a serious illness in an adult or child. Therefore, if a green coating appears that is difficult to remove, or your breath becomes stale, you should consult a doctor.
Everyone knows what a healthy human tongue looks like. As a rule, this is a visually moderately moist organ of a pale pink color. However, various diseases, conditions, disorders or habits can make it yellow, green, orange, blue, white, and even brown, black, or purple. A qualified doctor, based on the appearance and nature of the coated tongue alone, will assume the presence of one or another disease. Green color of the tongue (pale, dark, yellow-green, greenish-white, etc.) - a common problem for people of all ages, including seniors, adults and children.
What does a green coating on the tongue look like?
Normally, the tongue has an even pale pink or reddish-pink color, covered with stratified epithelium and mucous membrane. In the morning, a thin white translucent coating may appear on its surface, which can be easily removed by brushing your teeth in the morning. These exfoliating horny scales have a whitish tint. In case of digestive disorders, the separation of keratinized epithelial cells is inhibited, which is why a white layer (“coated” tongue) forms on the tongue.
A healthy tongue is pink in color and has a velvety texture.
When a coating on the tongue appears and lasts throughout the day, is difficult to wash off, has characteristic color or a specific smell - this indicates a problem in the body.
The tongue becomes green when a coating (film, mucus, substance, dirt) of the corresponding color appears on it. Plaque is actually the growth of bacteria and microscopic fungi on food debris. It can envelop the organ completely or partially, and also occur with reverse side language.
For effective treatment For problems with the gastrointestinal tract, our readers recommend GASTRO TEA. . The collection contains only natural ingredients with maximum effectiveness. The product has no contraindications, the effectiveness and safety of the drug has been confirmed by many doctors. Today the collection is sold at a 50% discount.
Types of raid
The shade also varies depending on the underlying cause as well as individual characteristics of a particular organism, it can be: pure green or pale green, yellow-green, dark green, blue-green, greenish-white.
Oral thrush is the most common cause of a white, yellow, or greenish coating on the tongue in babies and toddlers.
Some adults have this problem all the time if the underlying cause is not diagnosed or treated. For others, a green layer on the tongue predominates in the morning after sleep (for a short time).
Associated symptoms
In addition to the discomfort from green appearance tongue, a person may experience a number of other signs and symptoms that depend on the underlying cause. Common symptoms of this condition include:
Specific symptoms are very important for diagnosis; they help determine what the plaque, which at times can be quite dense, may mean.
Causes and factors of green plaque
There are many possible factors and causes of a greenish tongue, ranging from diseases and conditions, certain habits, to other underlying medical circumstances. Typical causes of this problem include:
These may be local or systemic problems.
Oral candidiasis or oral thrush
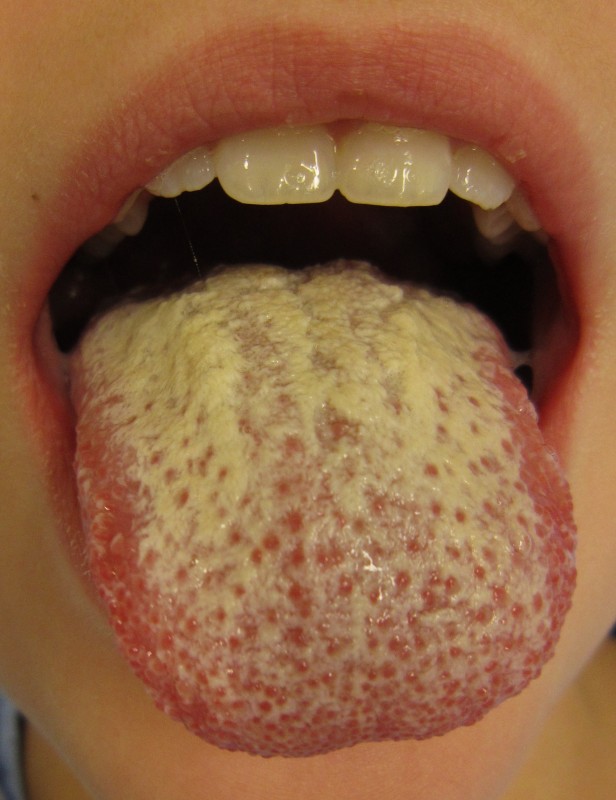
Light green coating on the tongue caused by oral candidiasis
Oral candidiasis or thrush is a fungal infection of the throat and mouth, it is caused by the overgrowth of opportunistic fungi - conditionally pathogenic microorganisms, which under normal conditions do not lead to the development of infection in healthy people(without immune system disorders). This is a yeast-like fungus of the species Candida albicans (Latin “candida albicans”), it is characterized by white, yellow or green mold on the tongue.
Often it is distinguished by white spots on the mucous membrane, on inner surface cheeks, throat, palate and tongue, as well as soreness and pain in the mouth. However, after eating certain foods, as well as taking certain antibiotics, the tongue becomes covered with a film. green shades: yellow-green, dark green, pale or whitish green substance.
Anyone can suffer from oral thrush. It is common among infants and toddlers, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems, especially those whose immune systems are weakened by HIV infection, cancer, or uncontrolled diabetes.
Other causes of oral candidiasis include:
Please note that oral candidiasis should not be confused with genital candidiasis, which is a sexually transmitted disease (STD).
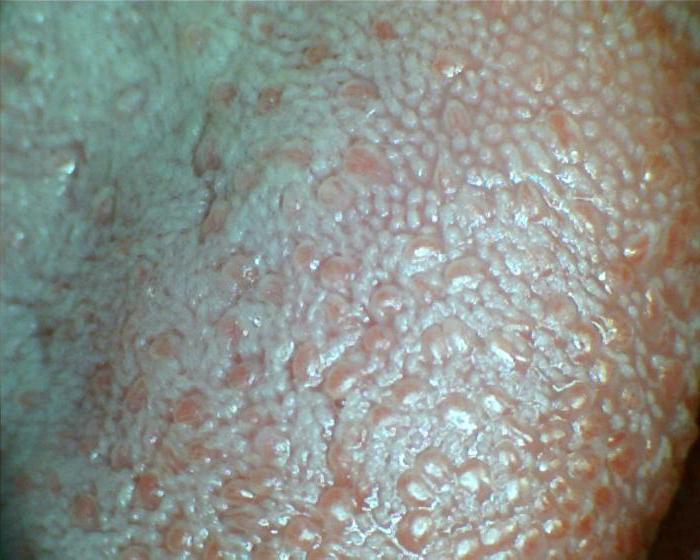
Villous tongue syndrome ("black hairy tongue")

Villous tongue syndrome causes changes in its color, including green or black
Hairy tongue syndrome is the second most common cause of a loose, hairy, rough, and often green-appearing organ. Although this condition is most often referred to as “black hairy tongue,” the actual color can be brown, white, green, pink, or any other color (depending on the specific etiology and secondary factors). In this case, even the tongue may become intensely stained food products, depending on your eating habits, your tongue will tend to be one color or another.
According to medical classification, hairy tongue syndrome refers to an abnormal covering on the upper (dorsal) surface of the tongue. The filiform papillae of the tongue become keratinized and increase in size. In some cases, the papillae can be very long, forming a kind of hair. This often occurs when keratin proteins accumulate on the tongue, due to lack of abrasion or stimulation of the surface of the tongue. Food, bacteria, yeast accumulation, and papillae that are not properly saturated can cause a hairy tongue. As a rule, the causes of this condition are:
The disease occurs predominantly in middle-aged and elderly men.
Other causes of green tongue
In addition to the most common reasons described above, there are other possible prerequisites for the occurrence of this anomaly. Among them are:

Chewing tobacco causes colored coating on the tongue
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
A correct diagnosis is of utmost importance if you are to successfully treat the underlying cause, especially when that cause is serious.
How is the examination and diagnosis carried out?

The color and shape of the tongue tell the doctor a lot about the patient's health status.
The initial appointment is carried out by a general practitioner, who will certainly interview you for additional complaints and assess the condition of the tongue, examining the necessary parameters:
Differential diagnosis of oral candidiasis is carried out with such diseases as:
When diagnosing oral thrush, it is based on typical complaints of patients, clinical picture, laboratory research data.
The following tests are prescribed:
According to the results visual inspection state skin and nails, if necessary, are referred to specialized specialists - a dermatologist, gastroenterologist, gynecologist, or endocrinologist.
Candidiasis is confirmed based on the detection of an increased number of Candida fungi in the scraping. Material for microscopic examination should be collected on an empty stomach, without brushing your teeth, at least 4–5 hours after the last meal. It is forbidden to even rinse your mouth before taking a smear, as this may distort the result. After completing the course of therapy and the disappearance of clinical symptoms, the patient is prescribed a second smear sampling.
If there are additional symptoms, the doctor will rule out a possible disease associated with inflammatory process upper respiratory tract, as well as pathologies of the liver, gall bladder and ducts.
Green tongue and sore throat
If a green tongue is combined with a sore throat, the doctor will suspect the patient has an upper respiratory tract infection. The most common cause of which is streptococcal throat (acute pharyngitis, bacterial tonsillitis). Other possible infections include a cold, sinusitis, or rhinitis. With bacterial sore throat, whitish or green pus is present in the throat, especially on the surface of the tonsils. Sometimes the disease may appear green tongue, sore throat, as well as small dark red, almost purple pimply spots on the back of the roof of the mouth and the base of the tongue.
Greenish plaque and diseases of the liver and bile ducts
If a greenish-yellow plaque is combined in a patient with pain in the upper abdomen, dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, vomiting), digestive disorders, then he should be sent for additional examination to a gastroenterologist for the purpose of detailed diagnosis for pathologies of the hepatobiliary system (bile stagnation, sand, stones, etc.)
In most cases green color language does not indicate serious problem health related. However, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment if the problem does not go away on its own after a few days.
What to do and how to treat it?
Treatment of oral candidiasis is carried out by increasing the body's natural immune defense, acting on the pathogen with antimycotic drugs. Sanitation of the oral cavity is mandatory - treatment of all chronic infections, including caries and tonsillitis. Diet is also important. Patients with recurrent forms of candidiasis are subject to additional examination, which will be prescribed by a therapist. Therapy of deep mycosis affecting internal organs, conducted by a specialist mycologist.
A detailed examination and treatment of underlying diseases plays a leading role in successful recovery, especially for chronic infections, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine or immune system.
Drug therapy
Treatment with medications involves taking the following drugs:

Nystatin is an effective antifungal drug
It is important to exclude any injuries to the mucous membrane. Sanitation should begin 3–4 days after the start of antifungal therapy.
If villous tongue syndrome is recognized as the cause of green plaque in the mouth, the doctor will recommend cleaning the tongue along with brushing the teeth. The procedure is performed using a specialized tongue scraper brush and antiseptic gel or paste. It is done 2 times a day. Oral baths based on hydrogen peroxide and chlorhexidine are also indicated. For rapid tissue regeneration, applications of keratolytics (Salicylic alcohol, Resorcinol) are used, which help exfoliate dead cells from the surface of the tongue.
Diet
Persistent course or frequent relapses of oral thrush indicate immune deficiency. Therefore, the first step to take is to support the immune system through a healthy diet. Patients with oral thrush should good nutrition with limiting the amount of easily digestible carbohydrates.

Sugar in case of candidiasis should be eliminated from the diet in any form as much as possible.
Candida fungus feeds on sugar, which is one of the reasons why uncontrolled diabetes and chronic high level glucose can cause frequent mycotic infections. Eliminate as possible more sugar will starve the yeast microorganisms and stop their population growth. The term "sugar" refers to everything that the body can easily convert into glucose - not only confectionery- but also all types of products containing natural sugar, such as fruit, honey or syrup, as well as all refined cereals and starchy vegetables. Food doesn't have to be tasty to quickly turn into sugar and feed the fungus.
Other dietary changes
In addition to simple sugars, you may need to eliminate yeast, mold, and fungi, which the body can mistake for Candida and trigger an immune system response. Therefore, you should limit or try to avoid foods and ingredients such as:
Instead, the bulk of your diet should consist of:
Probiotics
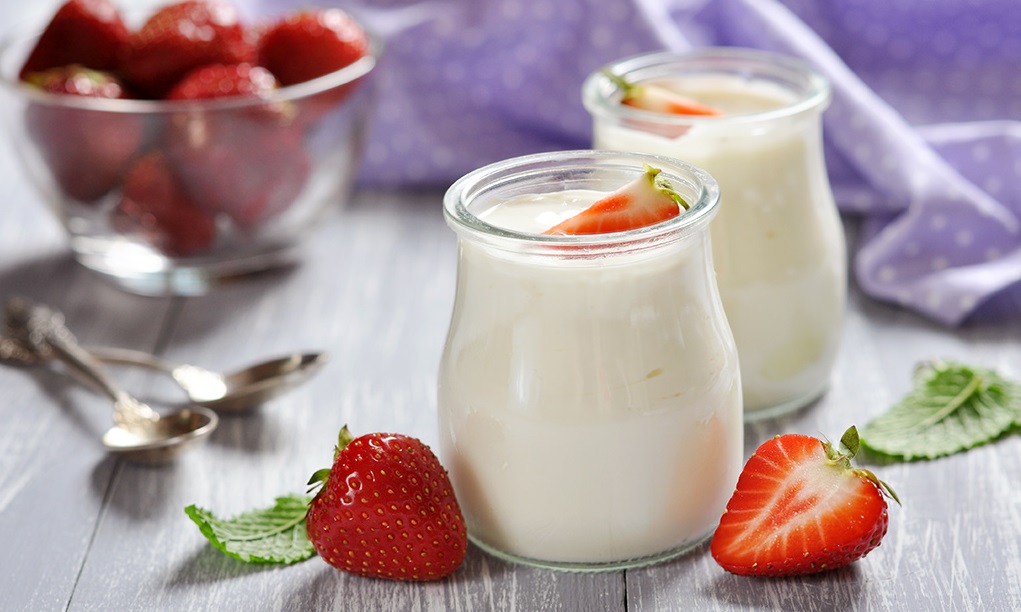

Natural yogurt is an excellent source of probiotics
Supplementing with probiotics—both as supplements and in natural foods—is an important part of the fungal diet. Probiotics are friendly bacteria that keep the yeast population under control. Often the fungus is activated when something destroys the good bacteria in your body's system, allowing Candida albicans to multiply rapidly. Lactobacillus acidophilus, found and cultivated in dairy products such as yogurt and kefir acidophilus, can help treat thrush, doctors say. You need to choose an unpasteurized product - heating kills both bad and good bacteria. The labels - worth studying in detail - talk about living or active cultures.
Folk remedies
In addition to a balanced diet, it is important to maintain good hygiene oral cavity, lead an active lifestyle, rest properly and get a good night's sleep. Additionally, some simple home remedies are available to fight the infection and reduce symptoms.
- Salt - the best remedy for the treatment of oral thrush. It creates an inhospitable environment for fungus. In addition, salt helps to quickly relieve symptoms.
- Mix 1 teaspoon of salt in 1 glass of warm water. Rinse your mouth thoroughly with a sip of the solution, then spit it out. So use all the solution. Repeat this procedure several times a day until you get good results.
- The second method is to spray a little saline solution on your tongue and inside your mouth, then rub lightly with your finger for a few seconds. Then rinse your mouth thoroughly with warm water. Use this remedy 2 times a day for several days.
- Apple cider vinegar contains enzymes that can control candida infection. It also restores the body's pH levels, which helps fight yeast overgrowth that causes infection. In addition, it stimulates the immune system, giving the body the ability to more intensively fight candidiasis. According to recent medical research, apple cider vinegar has shown antifungal properties against Candida fungus.
- Stir 2 teaspoons apple cider vinegar and 0.5 teaspoon salt in a cup of warm water. Use this mouth rinse several times a day until improvement occurs.
- Another way is this: add 2 tablespoons of apple cider vinegar and a little honey to 1 glass of warm water. Drink this water 2 times a day.
- Tea tree oil is effective against oral candidiasis. Its powerful antifungal properties help inhibit yeast growth and provide fast recovery. Scientists have found that the antifungal properties of tea tree oil and its components against Candida are highly effective.
- Add 4 or 5 drops of tea tree oil to 1 glass of warm water. Squeeze the solution into your mouth in small portions and rinse it for several minutes. Use this remedy 2 times a day until improvement occurs.
- Note: Remember not to ingest tea tree oil as it may cause unwanted side effects.
- Baking soda is an effective and affordable remedy for oral thrush. It destroys the fungus that causes the infection. According to scientific experiments, a 5% sodium bicarbonate solution is effective against Candida albicans. In addition, it helps maintain required level pH in the mouth, neutralizing acids.
- Mix 1 – 2 teaspoons of baking soda with enough water to form a paste. Using a cotton swab, apply this paste on your tongue and inner area cheeks Wait a few minutes, then rinse your mouth with warm water. The procedure should be carried out in the morning and evening for several days.
- As a second method, dissolve 0.5 teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of water. Rinse your mouth with this solution 2 times a day until improvement occurs.
Folk remedies - gallery
Regular salt- the worst enemy of oral candidiasis Apple cider vinegar helps restore healthy pH levels in the body Baking soda - cheap, but effective remedy against fungus Tea tree essential oil should be used carefully and should not be swallowed
Treatment prognosis, complications
The treatment prognosis for mild forms of oral thrush is favorable; recurrence of the disease is unlikely. With a moderate form, there is a possibility of relapse. A severe course can develop into a chronic infection, which is dangerous by the development of a generalized form of the disease - candidal sepsis.
The outcome of villous tongue syndrome is also favorable, provided that the causative factors are eliminated and complex therapy is performed. Strict adherence to medical recommendations promises the restoration of a healthy surface of the tongue.
Prevention
These measures will help reduce the risk of developing candida infections and developing villous tongue syndrome:
Following these simple rules will significantly reduce the risk of an unpleasant green coating on your tongue.
Microalbumin kidney disease indicator analysis




