The wisdom tooth (dentists call it "eight") got its name due to the fact that it germinates only by the age of 20, by the time a person becomes wiser. There is an opinion that this is an absolutely useless tooth, since in the process of evolution there was no need to chew too hard, unprocessed food, but this is not so. In old age, it may be needed, for example, for the installation of a bridge. Unfortunately, very often various reasons wisdom teeth have to be removed, and many people are concerned about the question: "What complications can arise after tooth extraction?"
Indications for removal
- the figure eight is located incorrectly and rests on other teeth;
- the tooth is affected by caries, and due to its characteristics (it fits too tightly to the adjacent tooth) it is impossible to fill it;
- recurring pericoronitis (inflammation of the gums with a partially erupted tooth);
- pain in the trigeminal nerve;
- pain in the area of the wisdom tooth (if it is accompanied by a general painful condition, headaches and pain when swallowing);
- due to its incorrect location, the mucous membrane is injured oral cavity.
Soreness of the process
"Is it painful to remove a wisdom tooth" is a question of interest to many. But there is no definite answer to it, since everything depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. How painful it is to do this procedure depends on four factors: the threshold of personal pain sensitivity, the presence of various complications (cyst, suppuration, etc.), the peculiarity of the location of the roots and the structure of the tooth itself.
Illustration of the location of the wisdom teeth.
Varieties of consequences
Even if your wisdom tooth was removed the most the best specialists unfortunately, one cannot be 100% sure that there are no complications. This is due to the fact that each person has individual characteristics the body, as well as how carefully the patient monitors his health after the operation. So, what complications after tooth extraction can lie in wait for a person?
Temperature increase
An increase is more likely not a complication, but a normal reaction of the body. The temperature can last for two to three days, increasing in the evening. Take antipyretics and follow your doctor's orders. If the temperature rises for more than three days, contact your dentist.
Alveolitis is an inflammatory process that forms at the site of an extracted tooth. True signs this complication is pain in the gums, swelling, unpleasant taste and odor from the mouth, the formation of a rough clot in the hole of the tooth (instead of the necessary smooth one).
![]()
Alveolitis is a very undesirable consequence of tooth extraction.
There are a number of aspects that cause alveolitis. If you avoid them, then the consequences will not threaten you:
- reduced immunity (drink a complex of vitamins before the operation, prepare your body for stress, strengthen its protective functions);
- the presence of caries on other teeth;
- poorly performed operation (a piece of the root remained in the gum);
- Availability infectious diseases in the oral cavity, such as tonsillitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis;
- the presence of any chronic infectious diseases.
It is very simple to treat alveolitis in the early stages: the doctor removes the festering clot, treats the wound and applies medicine. In more advanced cases, a gum incision and drainage may be needed. Alveolitis treatment is always accompanied by a course of antibiotics.
Hematoma
The word "hematoma" familiar to our hearing has a slightly different meaning when it comes about the consequences after the procedure for removing a wisdom tooth. The danger of a hematoma is that it begins to be asymptomatic. Only after a while the gums swell.
If you do not immediately take action, then suppuration will appear and, as a result, severe pain and fever. You can protect yourself if you know what factors can cause a hematoma:
- damage to a small vessel during local anesthesia;
- increased pressure in the patient (which often happens due to strong excitement);
- increased capillary fragility.
Very often, patients themselves aggravate the situation, starting independent treatment of a frivolous, in their opinion, hematoma. Baths, lotions and warming up will not lead to good, and the latter will even contribute to the development of the suppurative process!

Alas, but the intervention of a specialist is indispensable here.
The only effective treatment for this complication is to cut the gums and install a drain to drain the pus. But immediately after the procedure, the patient feels relief, despite the fact that the entire healing process lasts 4-5 days.
Bleeding
Bleeding after the removal of wisdom teeth has the same prerequisites as a hematoma. If it started while still in the dentist's chair, then the doctor stops the blood with a special sponge, and then sutures it. There are things that should not be done by those who have been stitched. They should remember the following rules:
- you cannot smile too widely, and even more so open your mouth;
- do not touch the wound (neither with a finger, nor with foreign objects), this will not only open the wound, but can also infect;
- you cannot smoke, spit and make any suction movements with your mouth (this will create a "vacuum" in the mouth);
- alcohol should be avoided, as it promotes vasodilation;
- don't let your blood pressure rise: avoid heavy physical labor and bending;
- people with hypertension should take appropriate medications on time.
The peculiarity of such a complication as bleeding is that, as a rule, it begins already outside of dentistry. Therefore, be prepared to give yourself first aid.
You need to make a sterile swab, for example, from a bandage and apply it to the bleeding, pressing down firmly. In the meantime, measure your blood pressure. If it is elevated, then take the medicine. Apply ice or any frozen food wrapped in a towel to the cheek on the side of the tooth that has been removed. Keep the cold for no more than five minutes, then take a ten minute break.
If you could not stop the bleeding on your own, then you need to urgently go to the hospital. You can safely call ambulance, because the treatment is urgent. At the hospital, you will be stitched and given the necessary injections.
Dry hole
A few days after you have your wisdom tooth removed, another unpleasant complication, called a "dry socket", may occur.
The fact is that a blood clot should form at the site of the extracted tooth, but with this complication, it either does not form at all, or falls off after formation. And this clot - the most important thing during wound healing, accordingly, its absence significantly slows down the healing process.

If after tooth extraction long time the pain does not go away, you should contact your dentist.
A dry socket has two signs - "dull" pain and bad smell from mouth. The doctor puts a medicine on the place of the extracted tooth, which needs to be changed once a day, until complete recovery.
Please note that such a consequence, after tooth extraction, occurs most often in smokers.
Paresthesia
The last but not the least unpleasant complication is paresthesia. It occurs if the removed wisdom tooth was located too close to the jaw nerves and they were damaged or simply touched during surgery.
You can easily diagnose yourself with paresthesia. The sensations with her are very similar to those when the oral cavity is anesthetized: numbness in the lips, tongue, chin. Moreover, these symptoms remain for a very long time (sometimes up to several months), but eventually disappear. However, you can speed up the healing process with a course of physiotherapy and a complex of multi-vitamin preparations.
The likelihood of paresthesia is much lower if a wisdom tooth is removed at a young age, when it does not sit too tightly in its hole.
Prevention of complications
Prevention of complications after wisdom tooth extraction begins even before the operation. Consider the following three tips carefully to make the procedure as painless and less traumatic as possible:
- before removing a tooth, treat all diseases of the oral cavity, not only caries, but also diseases of the gums, as well as of the mucous membrane;
- carefully approach the choice of anesthesia and be sure to warn the doctor about the presence of any allergic reactions;
- it is not necessary to remove more than one tooth in one procedure.
It often happens that patients ask for general anesthesia rather than local anesthesia and to remove several teeth at once. This is big mistake and the likelihood of complications in this case increases several times. After tooth extraction, swelling always forms and this is normal. But just imagine what kind of swelling will be after removing four teeth.
What to do after the tooth has already been removed? First, take one pain reliever tablet and apply ice to your cheek. This will help relieve pain and swelling. Secondly, avoid any rinsing of the mouth, and brush your teeth very gently and carefully - you cannot damage the blood clot in the hole, as this is directly related to the healing process. Third, remove hot liquid foods and drinks from your diet for a while. And fourthly, exclude any physical activity for a few days after the operation.
Around the topic of wisdom teeth extraction, myths and legends have been circulating for centuries. Some are sure that they should be removed immediately, because they do not even have time to push their way out, as they immediately begin to hurt. Others believe that they only cut through smart people as a symbol of wisdom. It is these teeth that never hurt and can successfully serve the owner for many years. So what can actually be an indication that a wisdom tooth needs to be removed, how does this procedure take place and what can be the consequences after its removal?
Indications for the extraction of a wisdom tooth
Wisdom teeth in dentistry are called third molars, and among the people - eights. In fact, it is they who cause a lot of trouble, and these problems are of various kinds: they do not erupt completely and cause unpleasant sensations, sometimes they are not at all able to push over the gum, in some cases, immediately after their appearance, caries begins, which is almost impossible to treat. It should be especially noted that there are many defects in the development and position of molars, the vast majority of which are considered a direct indication that a wisdom tooth should be removed immediately. This explains the reason why there are so many questions around the teeth, each of which has several answers. What is the mystery of this tooth, and is it really mysterious? Should a wisdom tooth be preserved when the dentist insists on it?
The wisdom tooth, the third molar, or "figure eight" in dentistry is perceived as a rudimentary organ - without it you can live peacefully as without appendicitis, because it does not perform a special chewing function. Often not erupted, impacted tooth causes suffering to its owners. In dentistry, two types of immersion of wisdom teeth are distinguished: bone, when the tooth is not even able to pass through the tissues of the jaw, and tissue - a hood is formed above it. Based on this, the following factors are indications for its removal:

The dentist assesses the severity of the problem on the basis of an x-ray or a visiography result. The surgical technique is selected taking into account the location of the wisdom tooth and the degree of its immersion. Tooth extraction is carried out under local anesthesia.
Description of the procedure and the complexity of its implementation
Depending on the location of the wisdom tooth, dentists also assess the complexity of the operation to extract it. Easier to remove the eight of the top row. They are stronger, and after removal, only in isolated cases can give minor complications.
This is due to the fact that the bone tissue of the upper jaw is quite malleable, and the tooth becomes more accessible for dental instruments. Moreover, the roots of the upper third molars are less curved and often accrete, which simplifies the removal process itself. The operation is carried out with extreme caution, because there is a fairly high risk of mechanical trauma to the tooth. For the procedure, the surgeon uses special dental instruments. In a situation where the third molar is completely located in the gum, before removal, it is dissected to open access to the operating field. Upon completion of the manipulation, the incision is sutured using a self-absorbable suture material.
Dental surgery to remove molars is considered more difficult when there is bone tissue above them. This occurs if the tooth cannot erupt or partially came out to the surface. The level of difficulty in removing such a tooth largely depends on how wide the patient can open his mouth, providing access for dental instruments to the operating field. This kind of surgery is performed under general anesthesia. A prerequisite is the crushing of the tooth, followed by the extraction of all its fragments. Upon completion of the operation, a visiographic procedure is performed to identify the remains of the tooth.
The consequences of removing the figure eight and how to eliminate them
 The consequences after surgical removal of the third molar are not favorable in every case, and should not be underestimated. possible risks... Sometimes more problems can arise if you ignore such a surgical intervention, especially when there are all indications for its implementation. One of the unpleasant moments can be called a rather serious course inflammatory process, which can pose a threat to the patient's life in case of untimely access to the dentist. Based on the foregoing, it is necessary to understand all the complications that a third molar can lead to.
The consequences after surgical removal of the third molar are not favorable in every case, and should not be underestimated. possible risks... Sometimes more problems can arise if you ignore such a surgical intervention, especially when there are all indications for its implementation. One of the unpleasant moments can be called a rather serious course inflammatory process, which can pose a threat to the patient's life in case of untimely access to the dentist. Based on the foregoing, it is necessary to understand all the complications that a third molar can lead to.
The wisdom tooth on the upper and lower jaws erupts much later than all other molars and premolars. This is the main reason why the figure eight, having initially the correct structure, can deform during its pushing over the gum. This concerns the roots of the tooth, which can be deformed in the jaw so that the crown can come out and fit into the dentition.
In the photo for the article, you can see the stages of the operation to remove the impacted wisdom tooth. When preparing for a tooth extraction procedure, the surgeon professionally evaluates possible obstacles that may arise during its extraction from the socket. The following situations are called risk factors:
- pronounced inclination of the tooth to the side;
- low location of the coronal part;
- deformed root part;
- the roots are located near the maxillary sinuses.
The above factors can be foreseen, appropriate measures can be taken in a timely manner, choosing the correct direction for the removal of the molar. Almost all unpleasant moments arise from the doctor's mistake, and the more experienced the dentist, the lower the risk of their occurrence. Let's consider the most common consequences that arise in practice as a result of the extraction of a wisdom tooth.
Temperature increase
A slight increase in body temperature can be observed within three days after the extraction of a wisdom tooth. At the same time, there is a slight swelling on the corresponding side and pain. If the scale of the thermometer does not rise above 37.5 ° C, and by the morning it decreases, then this situation in dentistry is considered as a normal reaction to the operation. Gradual decline temperature, along with which the swelling and pain in the socket area decreases, indicates that the healing process is proceeding normally. With more high temperature you should contact your dentist for an accurate diagnosis. A similar reaction of the body can occur in the following cases:

Painful sensations
Pain is a normal response to injury or inflammation. Despite the fact that it is quite difficult to pull out a wisdom tooth, and during the procedure minimal injuries are not excluded, you should not panic about pain for several hours after the effect of anesthesia has passed. It is not excluded that the pain will be present during the day, especially if a complex removal of the impacted tooth was carried out.
Bleeding
No dentist should let his client leave the clinic until he is sure that the bleeding from the hole will not stop. Normally, blood after tooth extraction should coagulate quickly, up to a maximum of 2 minutes. If she continues to walk, then the patient is measured blood pressure and check the operating field for damage to a large vessel. When a problem is found, the dentist will suture the wound or place a hemostatic sponge in the hole to stop the bleeding.
 Options are not excluded when wound bleeding can resume after the patient leaves the clinic. To prevent such a situation, dentists apply suture material to the wound in advance, which contributes to its quickest healing. Experts note several factors that can provoke bleeding by the hands of the patients themselves, who do not follow the dentist's recommendations. The most common of these are smoking and drinking alcohol soon after tooth extraction, sharp facial movements or increased exercise stress, hot shower or bath.
Options are not excluded when wound bleeding can resume after the patient leaves the clinic. To prevent such a situation, dentists apply suture material to the wound in advance, which contributes to its quickest healing. Experts note several factors that can provoke bleeding by the hands of the patients themselves, who do not follow the dentist's recommendations. The most common of these are smoking and drinking alcohol soon after tooth extraction, sharp facial movements or increased exercise stress, hot shower or bath.
Swelling and bruising on the face
Complications that can occur after tooth extraction are extremely unpleasant, but sometimes it is considered the norm. In particular, the formation of puffiness. Many women are also at a loss - why does a bruise appear on her face after she has removed a tooth? The fact is that during the procedure, a soft tissue vessel trauma took place. You do not need to immediately blame the doctor for this, because such an unpleasant moment can be provoked even by a needle from an injection when anesthesia is administered.
Cheek swelling should be a concern, especially if accompanied by chills, soreness, and swelling of the gums. In such a situation, you should immediately consult a doctor who will prescribe adequate antibiotic treatment, based on the current situation.
Severe swelling, especially after removal upper tooth, appears almost always. In some cases, it can be accompanied by an enlargement of the lymph nodes that are located below the jaw.
Dry hole
 After the removal of a wisdom tooth, in almost half of the cases, dry socket syndrome is observed. This pathology is due to anatomical feature jaw, which provokes the loss of the formed blood clot after surgery. As a result, the cavity is exposed, where the bone is visible. This is a rather dangerous complication, which is called alveolitis in dentistry. Symptoms can include twitching or aching pain in the face, especially in the lower part of the face, increased sensitivity of the teeth, putrid breath, and a bitter taste. The patient's appetite decreases, weakness and swelling of the facial area develops. With such symptoms, you should immediately contact your dentist, who will carry out all the necessary procedures to prevent the development of complications. With timely treatment for professional help, alveolitis can be eliminated in a few days.
After the removal of a wisdom tooth, in almost half of the cases, dry socket syndrome is observed. This pathology is due to anatomical feature jaw, which provokes the loss of the formed blood clot after surgery. As a result, the cavity is exposed, where the bone is visible. This is a rather dangerous complication, which is called alveolitis in dentistry. Symptoms can include twitching or aching pain in the face, especially in the lower part of the face, increased sensitivity of the teeth, putrid breath, and a bitter taste. The patient's appetite decreases, weakness and swelling of the facial area develops. With such symptoms, you should immediately contact your dentist, who will carry out all the necessary procedures to prevent the development of complications. With timely treatment for professional help, alveolitis can be eliminated in a few days.
Other consequences
The consequences of removing a diseased wisdom tooth can be different. It all depends on the patient's immune system and the experience of the dentist. It is worth noting that many of them are considered the norm, and there is no need to sound the alarm. If the symptomatology is suspicious, then you should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
Questions remain about the direct fault of the dentist in the development of such a complication as paresthesia, which causes numbness in the areas of the face, cheeks, lips, tongue and even chin. This abnormality can occur as a result of a pinched nerve during a tooth extraction procedure. To avoid such an unpleasant consequence, dentists recommend timely contacting the issue of removing a wisdom tooth. It is possible that the earlier the third molar is removed, the lower the likelihood of developing paresthesia. It should be noted that in isolated cases, a significant degree of nerve damage is observed, which can cause permanent numbness.
A condition is considered quite dangerous when a hematoma occurs at the site of the wound of the removed molar, which is quite difficult to diagnose at an early stage. Only a few days later, the swelling of the gums is clearly manifested, and if no measures are taken in a timely manner, then pus may form in the wound.
When is it worth sounding the alarm?
 The consequences of the extraction of the impacted wisdom tooth most often cause complications that require the intervention of specialists. It is necessary to sound the alarm immediately if, a few days after the dental procedure, the patient experiences severe pain, which is accompanied by an increase in temperature. Such symptoms may indicate the development of serious complications. In particular, a hematoma requires immediate installation of a drainage, which will facilitate the free removal of the resulting pus in the wound. No less serious is numbness of the face, the formation of a flux (periostitis), as well as the resumption of bleeding from the hole.
The consequences of the extraction of the impacted wisdom tooth most often cause complications that require the intervention of specialists. It is necessary to sound the alarm immediately if, a few days after the dental procedure, the patient experiences severe pain, which is accompanied by an increase in temperature. Such symptoms may indicate the development of serious complications. In particular, a hematoma requires immediate installation of a drainage, which will facilitate the free removal of the resulting pus in the wound. No less serious is numbness of the face, the formation of a flux (periostitis), as well as the resumption of bleeding from the hole.
What can not be done after deletion?
The results after the extraction of the third molar can be very different depending on the level of complexity of the operation and the patient's immunity. More complex consequences of removing an injured wisdom tooth bottom row: bleeding, hyperthermia, chills, edema, etc.
In addition, wisdom tooth extraction during pregnancy and during menstruation is carried out only in exceptional cases. If all the dentist's recommendations are followed, many unpleasant moments can be avoided, so each patient should understand what is not allowed to do after the removal of the third molar:
- eat hot food, as well as spicy foods;
- smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- take a hot shower, visit a bathhouse;
- to carry out hygienic care of the oral cavity within 24 hours after the operation;
- make warm compresses.
Prevention of complications after the procedure
In order to prevent complications that the third molar can cause, especially after extraction of the lower molar, the doctor recommends adhering to the basic rules for caring for the wound on an individual basis. The basic rules are as follows:
- Remove the swab from the well 20 minutes after the extraction. Make sure that a blood clot forms in the hole. A dry hole is a reason for a second visit to the dentist.
- Rinse the mouth with chamomile infusion and saline. Such procedures prevent the development of the inflammatory process and promote the outflow of pus from the wound.
- If a strong flux forms, immediately apply ice for 15 minutes and consult a dentist.
- After the complex operation to drink full course antibiotics according to all prescriptions and recommendations of the dentist.
- Take pain relievers if the patient's condition is unsatisfactory and he is in severe pain.
Knowing the symptoms of complications after surgical removal of the third molar (wisdom tooth), you can prevent many of them by following all the recommendations of dentists and promptly contacting the clinic for professional help. Do not ignore any suspicious symptoms; you need to immediately take all adequate measures to eliminate them. This is the only way to minimize the risk of side effects and carry out the extraction of a wisdom tooth without serious complications.
The wisdom tooth got its name because of the late eruption (at the age of 18-23 years), when the ripening of the rest of the organs has already ended. This is due to the fact that in the course of evolution, humans switched to softer and thermally processed foods. There are isolated cases of wisdom teeth eruption by the age of 40. There are four of them - one on each side of the jaw from below and from above. It so happens that not all wisdom teeth erupt, more often one or two. If by the age of 27 they have not erupted, then the probability of their growth in the future is minimal.
Complications of erupting a wisdom tooth
In the course of evolution, the size of the human upper and lower jaw has decreased slightly. In this regard, there is not enough space for the normal eruption of the last teeth, which can lead to complications such as: 
- The formation of a "hood" - due to insufficient space for growth between the 7th tooth and the angle of the lower jaw, when a wisdom tooth erupts, a tubercle is formed from the gum tissue, which becomes inflamed and sore. Treatment in this case consists in surgical excision of the "hood".
- The pressure of the wisdom tooth on the adjacent tooth is the same reason as with the "hood". There is pain in the corner of the jaw, it can spread to the cheek, neck. Treatment - wisdom tooth extraction.
- Formation of a jaw cyst - due to the slow growth of a wisdom tooth, a cavity formation filled with fluid is formed in the jaw tissue - a cyst. In the absence of its growth for a long time, there may be no symptoms. But with its continued growth and accession bacterial infection there is pain, swelling in the area of the growing tooth, local (local) and general increase in temperature, pus accumulates in the cyst. Treatment is only surgical - removal of a wisdom tooth and drainage of the cyst cavity.
- Incorrect tooth growth is a fairly common complication in which a wisdom tooth can grow into the mucous membrane of the cheek, with constant trauma. Treatment consists only in tooth extraction.
- Malocclusion - if there is not enough space for growth, the wisdom tooth displaces adjacent teeth, this disrupts their normal position. In this case, in addition to the removal of a wisdom tooth, orthopedic correction of the location of the remaining teeth is also necessary.
- Caries - wisdom teeth are located in the corner of the jaw, which makes them difficult to access for hygienic treatment, as a result of which caries is actively developing. It is also possible to erupt a tooth with damaged enamel. Usually, therapeutic methods and filling are not used for treatment, but only removal.
- Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve - can occur due to the destruction of the wisdom tooth, the formation of a "hood" or jaw cyst. It is manifested by pain in the area of the face from the side of the lesion. After the removal of the wisdom tooth, the inflammation subsides and the pain stops.
Wisdom tooth extraction technique
Removal is carried out by a dental surgeon under local anesthesia (anesthesia) with a solution of lidocaine or novocaine. An anesthetic allergy test is mandatory beforehand in order to avoid possible allergic reactions and complications of anesthesia. The removal procedure itself includes several stages:
- anesthesia;
- dissection of the gum surrounding the tooth for sufficient access to it, is especially important when it is incomplete erupting;
- dissection of the ligaments that attach the tooth to the jaw socket - performed with a special surgical instrument;
- direct extraction of a wisdom tooth with special dental forceps;
- if necessary, the gums are sutured for its speedy healing.
If there is a cyst in the jaw, then it is drained, to remove the liquid outside, special rubber bands are used, which are inserted into the cyst after the extraction of the tooth for several days. Through them, fluid or pus from the cyst goes out, and it heals.
In case of incorrect or incomplete growth of a wisdom tooth, a complex tooth extraction is performed, with a wide dissection of the gums above it. Before such a procedure, an X-ray examination of the jaw is required to avoid complications during the operation. 
Contraindications to removal
The only contraindication to removal is pronounced allergic reaction for the administration of anesthetics. In this case, general anesthesia is used.
Consequences and complications after wisdom tooth extraction
Depending on the time of development, early and late symptoms can be distinguished. Early consequences develop immediately after the removal of a wisdom tooth within 24 hours, these include:
- Pain that increases in intensity as the local anesthetic wears off. To reduce pain, it is recommended to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with an analgesic effect for 3 days after the operation (nimesil, ketanov, analgin). These medications are best taken after meals.
- Bleeding occurs immediately after removal, as the vessels are damaged. To stop it, the doctor puts a tight cotton-gauze swab on the wound. Also, if the recommendations are not followed, re-bleeding is possible, in this case it is necessary to apply cold to the cheek in the projection of the extracted tooth and seek medical help.
- Paresthesia is a feeling of numbness on the face in the area of an extracted tooth, similar to local anesthesia. The cause is damage to the branches of the trigeminal nerve adjacent to the wisdom tooth. Usually, paresthesia goes away on its own, sensitivity can return only after a few weeks or even months (it takes time for the damaged nerves to recover).
Late complications can develop several days or weeks after surgery:
- "Dry socket" - a late complication associated with a violation of the formation of a clot that closes the wound after tooth extraction, manifests itself as a re-emerging dull pain, while the healing time increases.
- Hematoma - is formed as a result of the accumulation of blood in the tissues, a tumor appears, it can be painful when pressed.
- Infection of the wound. When a bacterial infection enters, inflammation of the soft tissues develops in the area of the removed wisdom tooth, manifested by the fact that the body temperature rises, edema forms on the tissues, and regional lymph nodes become inflamed. Antibiotics are used for treatment wide range actions (cephalosporins, augmentin, amoxiclav).
- immediately after removal, the doctor applies a cotton-gauze swab to the well to stop bleeding, it must be kept for at least 20 minutes;
- for 3 hours after the operation, you must not eat, alcohol and smoke;
- during the first day, it is advisable to take painkillers (nimesil, ketanov);
- to reduce swelling and reduce the likelihood of re-bleeding, applying cold to the area of the extracted tooth will help;
- rinsing with an antiseptic solution to avoid infection of the wound is performed only on the recommendation of a doctor, furacilin, Dimexide is used.
Removing a wisdom tooth from above and below is an unpleasant procedure and not every dentist undertakes for it. As a rule, the removal of a wisdom tooth in the upper and lower jaw is a task for the dentist-surgeon. This procedure has a lot of complications, probable complications and consequences of wisdom tooth extraction, which we will talk about later.
general information
The third molars above and below appear the last of all - at the age of 20-25, when the jaw bone (lower and upper) is already fully formed and any violations of its integrity are quite painful. Statistics report that in 80% of cases, this process does not occur correctly, causing numerous problems. This can be caries, misalignment of the bite, disruption of the temporomandibular joint, and so on. Therefore, doctors tend to believe that the removal of the wisdom teeth of the upper and lower jaw should be done as early as possible, before they become the source of numerous problems in the oral cavity.
Removing a tooth seems like a good way out of the situation, but often even after it, patients develop health problems and complications.
In addition, how severe the complications will be and how they will be expressed depends on the complexity of removal. Naturally, a simple deletion leaves less deletion consequences than a complex one. With a simple extraction, a partially erupted or completely erupted tooth is removed quickly and almost painlessly. Complex extraction involves the extraction of the impacted (hidden under the gum, bone) tooth.
Complications during removal
This procedure is the cause of the development of a wide variety of complications and it itself is quite complicated. ![]() For example, it is much more difficult to pull out a tooth in the lower jaw than in the upper one. It will not be possible to work with forceps in 80-90% of cases.
For example, it is much more difficult to pull out a tooth in the lower jaw than in the upper one. It will not be possible to work with forceps in 80-90% of cases.
Removal with forceps consists in grasping the crown of the tooth, loosening and extracting the tooth from the mechanically enlarged hole. The lower jaw has a denser bone tissue, so this procedure is meaningless. Even if the molar has erupted strongly enough and has a crown intact by caries, remove it from the dense bone without having accurate information about the number and location of roots is very problematic.
To avoid some complications during the procedure, an X-ray should first be taken to see how the roots of the third large molar are located in the jaw.
The consequences of deletion
The consequences and complications after the removal of a wisdom tooth in the lower and upper jaw are very diverse. In particular, because after extraction, a large wound with torn tissues around it remains in the oral cavity, and in the case of difficult removal, also damaged bone and gums.
The most common complications after removal of the third molar are alveolitis, pain, swelling, bleeding from the socket. The body of each person reacts individually to this serious intervention. Someone may almost immediately feel as vigorous as before, and in some people, painful symptoms remain even after 3-5 days.
You should pay attention to the choice of a doctor who will carry out the extraction of a wisdom tooth in the lower jaw and will be responsible for all the consequences of such a procedure. It often happens that the doctor provokes a dislocation of the adjacent molar, damages the organs of the oral cavity with a jumping off instrument, breaks the lower jaw . has a variety of consequences.
Pain after the procedure
 After removing a tooth from above or below, painful symptoms will certainly appear, because pain is a normal reaction of the human body to any violation of the integrity of tissues. The more difficult the extraction was, the more painful the pain will become over time.
After removing a tooth from above or below, painful symptoms will certainly appear, because pain is a normal reaction of the human body to any violation of the integrity of tissues. The more difficult the extraction was, the more painful the pain will become over time.
A person who has decided to pull out a wisdom tooth should be prepared for such consequences.
When removing the 8th tooth, as a rule, abundant anesthesia is used, therefore, for the first time hours after the procedure, the patient will not feel anything. After a complex tooth extraction, a person may not feel pain even after 4-5 hours.
To relieve suffering, you must use pain relievers in powders or tablets. The well ceases to be a source of pain after a few days, because the tissues in the mouth area tend to regenerate very quickly.
Bleeding from a wound
Naturally, when blood flows from the wound, this indicates the normal functioning of the body. But bleeding must stop, because blood loss is always stressful for the human body. When removing a wisdom tooth  this is a classic complication.
this is a classic complication.
The flow of blood from the hole is necessary so that the place of the extracted tooth heals faster, so that foreign bodies that can cause diseases and suppuration do not enter the body.
Bleeding after the procedure should stop normally within a few hours. If this does not happen, then you should consult a doctor as soon as possible to get medical assistance... Otherwise, consequences such as drowsiness, weakness, in rare cases- loss of consciousness.
However, when the hole is not filled with a blood clot, it is also an alarming signal. Dry hole is a direct road to wound inflammation, which is called alveolitis.
Any surgical intervention forces the body to activate immune system in order to protect the body from negative influences external factors... That is why in the first days after surgery on the lower or upper jaw, patients may observe an increase in temperature. It can rise up to 38 degrees - this is normal. Also, the temperature can rise to 39 degrees, but by the end of the day it should subside.
If you have a fever after the intervention of a doctor, then do not panic, take these days more attentively to your body in order to recognize the beginning problems in time.
In the case when the temperature lasts more than three days, you should pay attention to the condition of the hole, to painful sensations. Putrid odor from the mouth, elevated temperature and pain that does not disappear after a few days are faithful companions of alveolitis.
Alveolitis
Suppuration of the hole, and scientifically alveolitis, can occur as a consequence of the removal of the eighth tooth. There are many causes of alveolitis, it is worth mentioning the most common of them:

The suppuration of the hole is accompanied by a number of unpleasant symptoms, in particular, pain, impaired chewing function, swelling, putrid breath, fever.
It is necessary to treat alveolitis, because a neglected or incorrectly cured disease can lead to acute osteolmyelitis, phlegmon, lymphadenitis, abscesses that are dangerous to human health and life.
Facial hematoma
Simply put - a bruise. There are several reasons for the occurrence of hematoma:

After the removal of the eighth tooth, quite formidable bruises may appear on the lower or upper jaw, but you should not focus on this. As a rule, after 4-5 days, not a trace remains of it. In order to avoid such an unpleasant consequence of the removal of 8 tooth, it is worth applying cold to the cheek in the first hours after the operation. This will reduce hematoma and potential swelling.
It is much more important to monitor how the healing is proceeding and, at the slightest suspicion of complications, to rush to the doctor.
Paresthesia
Another complication that the patient may have in connection with the removal of the figure eight in the lower jaw. The essence of this consequence is that a person loses the sensitivity of such areas of the face as lips, cheeks, chin, as well as the organs of the oral cavity - the tongue. Paresthesia occurs due to trauma to the mandibular nerve, which lies just in the area of occurrence of the roots of the third molars.
Such a consequence of pulling out a wisdom tooth, such as paresthesia, can occur if following factors risk:
- a special arrangement of the roots of the tooth or a strong inflammatory process. The closer anatomically the roots of a tooth are to the nerves, the higher the likelihood that they may be damaged;
- ineptness of the surgeon or negligence in planning surgery. The surgeon is obliged to examine the location of the roots of the tooth before removing it.
Over time, this condition disappears. Paresthesia can last for one to two weeks, but rarely forever.
Special medications and physiotherapy can help a patient with paresthesia.
Not every dentist agrees to treat wisdom teeth. After all, the complexity of therapy lies in their distant location in the oral cavity, and they often grow incorrectly.
Regardless of the type of surgical intervention, the operation is always stressful for the body. Removing a wisdom tooth is no exception. As a result of this manipulation, complications can arise both during its implementation and after the operation.
The adverse course of surgery can be influenced by:
- perpendicular position of the roots or the body of the tooth regarding the dentition;
- finding the body of the molar above the gum at a lower level compared to the neighboring seven;
- presence of crooked roots;
- location of the eighth molar close to the mandibular canal or maxillary sinus.
Complications during surgery can also be caused by medical error... Therefore, it is very important to seek help only from experienced and highly qualified specialists.
During manipulation, dislocation or destruction of the adjacent molar, damage to the gums, perforation of the maxillary sinus and others can occur. Let's consider each complication individually.
Dislocation or fracture of an adjacent molar
This complication is a consequence of an uncalculated load on the seventh molar. Inexperienced specialists use the adjacent tooth as a support for the elevator - a tool designed to remove the figure eight.
As a result, the molar involved in the process begins to wobble or, in the worst case, breaks down altogether.
A medical error can lead to the loss of another tooth or to the need for its restoration.
Damage to the gums or other soft tissues of the mouth
Absence correct technique Extraction of teeth can result in a significant cut in the gums or rupture of the soft tissues surrounding the molar.
This consequence is often the result of accidental slipping of the instrument and results in prolonged bleeding.
The situation can be corrected only by suturing.
Breaking off a site of the alveolar process
Deep grip of the body of the tooth with the instrument leads to a breakdown of the part of the alveolar ridge that holds the molar. As a result, the victim, again from an inexperienced specialist, can feel the sharp edges of the bone in the area of the tooth socket.
This consequence can lead to long-term wound healing.
The patient will need additional conservative treatment.
Dislocation of the lower jaw
Some dental surgeons believe that maximum effort is the key to quick extraction of a tooth, especially when it is firmly attached to the bone. However, such actions can lead to dislocation of the jaw, in particular, when the lower molar is eliminated.
In fact, modern dentistry allows you to remove teeth without physical effort.
Elimination of dislocation of the jaw is carried out by means of its reduction, which must be carried out by a qualified specialist.
Maxillary sinus perforation
Sometimes between the bottom of the maxillary sinus and the root of the wisdom tooth there is a relatively thin layer bone tissue, less than 1 cm. The reason for this may be gum disease or congenital facial features.
When a tooth is removed, the bone layer is sometimes damaged by the root or the whole tooth. As a result, nosebleeds may open and even the timbre of the voice may change.
However, the most unpleasant likely situation is the remainder of the molar in the sinus.
Subsequently, the foreign object is removed through the hole in the bone, and the patient is prescribed antibiotic therapy.
Aggravation after the procedure
The factors listed above can provoke complications not only during the operation, but also some time after its completion. In addition, the patient can create problems for well-being on his own, without following certain rules for caring for the oral cavity after surgery.
Be that as it may, during the rehabilitation period you can face not only the characteristic pain, fever and bleeding, but also a number of other consequences.
Pain
The effect of anesthesia, depending on the complexity of the operation, ends after 1 - 3 hours. Then the patient is faced with aching pain, which can be relieved by taking a pain reliever pill.
This phenomenon is considered normal for two days after any type of surgical intervention. However, what if 3 days have passed and the pain only gets worse?
The presence of increasing pulsating, tearing sensations may indicate the onset of an inflammatory process, especially if they are accompanied by a temperature. In addition, persistent pain is also a sign of the remnants of a part of the tooth in the hole.
Therefore, you should contact your doctor if, 10 hours after the operation, the nature of the sensations does not change in any way or the symptom does not go away for 2 to 3 days.
An exception is the presence of processes parallel to the extraction of a wisdom tooth - separation of bone tissue or suture. In these cases, it takes longer for the wound to heal (from 7 to 10 days).
Alveolitis
This consequence is an inflammation of the socket as a result of its infection after tooth extraction. The provoking factor of the process may be incomplete removal of the molar. A variety of concomitant chronic inflammation of the gums and soft tissues of the oral cavity, as well as a dry socket, can also cause a serious complication.
Symptoms of the consequences occur 1 to 3 days after the operation. Patients experience pain in the wound area, bad breath, gray plaque in the hole.
Only a dentist can eliminate alveolitis by performing a number of specific manipulations.
Hematoma
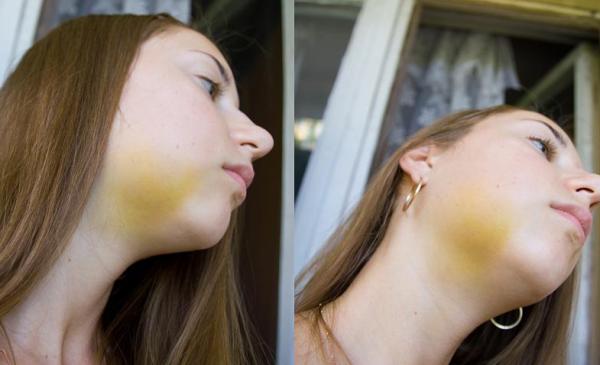
Damage to blood vessels and soft tissues, which is an integral part of tooth extraction, can cause a hematoma. Sometimes it is accompanied by a blue discoloration of the facial skin in the area of the operation. However, after 2 to 3 days, the symptoms described disappear on their own. Often, patients suffering from diabetes mellitus, and hypertensive patients.
If the hematoma is accompanied by increased pain and temperature, and the swelling continues to grow, you should immediately consult a doctor.
In the office, the dentist can cut the gum and rinse the wound with an antiseptic. In difficult cases, it is also required to install a drainage system for the disposal of purulent accumulations.
Temperature increase
If, after the removal of the wisdom tooth, the patient's temperature rises in the range of 37.2 - 37.5, this is the norm. Usually this phenomenon is a sign of wound healing and can be observed in the evening for 2 to 3 days.
If the temperature rises above these limits and decreases only when taking an antipyretic drug, immediately contact a specialist for appropriate wound treatment.
You are most likely developing an infection. The harbingers of serious consequences can be the absence of a protective blood clot in the hole, headache, reddening of the gums.
Bleeding
Removing a wisdom tooth is rarely accompanied by severe bleeding. Normally, blood clots within 1 to 2 minutes after the operation. Slight discharge of red fluid can be observed for another 1 to 3 days after the completion of the manipulation.
After the specified time, postoperative symptoms disappear by themselves. However, if this phenomenon does not fade away, it is worth seeking help from a specialist. It is possible that a large vessel was damaged during the extraction of a wisdom tooth.
Bleeding is eliminated by applying a special sponge. Suturing of the wound may sometimes be required.
It should be noted that this complication is observed most often in hypertensive patients. Therefore, it is not recommended to carry out the operation without first lowering the blood pressure.
In addition, a qualified specialist should not let go of the patient until the bleeding has completely stopped.
Paresthesia
This complication manifests itself in the form of numbness of the tongue, lips or chin and is a consequence of damage to the facial nerves.
The duration of such a phenomenon can be observed in a patient for 1 - 2 weeks, and in some, paresthesia becomes a companion of the whole life.
Treatment in this case is rational to discuss with a neurologist.
Periostitis
Popularly, this consequence is called a flux, which is formed as a result of an outbreak of the inflammatory process after the removal of a wisdom tooth.
The characteristic symptoms of periostitis are general weakness of the body, fever, swelling of the cheeks, and acute pain.
Dentists in this case prescribe antibiotic therapy for a course of 5 to 20 days.
The most common consequence of surgery is pain. To reduce its intensity and prevent the development of the inflammatory process, it is recommended:
- At the end of the operation, the tooth socket should be closed with a sterile swab. At the same time, you need to hold it, clenching the upper and lower jaw, for 30 - 40 minutes. This will prevent bleeding.
- 2 - 3 hours after the removal of a wisdom tooth, you should refrain from eating. It is necessary to allow time for the formation of a protective layer on a fresh wound.
- To reduce the likelihood of edema formation, as well as to prevent increased pain after the end of anesthesia it is advisable to apply ice or moistened cold water napkin... It is necessary to renew the compress every hour and keep it for 10 - 15 minutes.
- For the first few days, chew food with molars. located on the side opposite to the wound to avoid injury.
- When severe pain it is recommended to take an anti-inflammatory pain reliever, for example, nimesil, ketanov or tempalgin. These drugs are contraindicated in the presence of stomach ulcers and allergies to active ingredients.
Categorical prohibitions

During the rehabilitation period, it is prohibited:
- Eating hot food and drinks for 2 to 3 days after surgery. Ignoring the rule can increase pain and cause the development of the inflammatory process.
- During the first day, it is not recommended to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth. due to possible damage to the wound and its infection.
- It is worth refraining from drinking and smoking. Bad habits can provoke the development of the inflammatory process.
- Warming up the cheeks or going to the sauna is also unacceptable. All this can cause the appearance of flux or swelling in the area of the wound.