03.05.2013
A hundred years ago, countries strived to become the most powerful and developed powers in the world, capturing more and more territories and spreading their influence. This is the top 10 most great empires world in history. They are considered the most important and longest lasting, they were powerful and played a lot important role in history. Didn't make it into the top 10 Russian empire and even the great Macedonian empire created by Alexander the Great, but it was the first European empire that advanced into Asia and defeated the Persian empire, and perhaps one of the most powerful in the ancient world. But it is believed that these 10 great empires were more important in history, made a greater contribution.
Mayan Empire (c.2000 BC-1540 AD)
This empire is distinguished by its longevity, its cycle lasted almost 3500 years! This is twice the life of the Roman Empire. So far, scientists know very little about the first 3,000 years, as well as about the mysterious pyramid-like structures scattered throughout the Yucatan Peninsula. Well, is it worth mentioning the famous doomsday calendar?
French Empire (1534-1962)
 Second largest in history great empire- French colonial empire, occupied 4.9 million square miles and covered almost 1/10 of total area Earth. Her influence made French one of the most widespread at that time, brought fashion to French architecture, culture, cuisine, etc. to all corners globe. However, she gradually lost influence, and two world wars completely deprived her of her last strength.
Second largest in history great empire- French colonial empire, occupied 4.9 million square miles and covered almost 1/10 of total area Earth. Her influence made French one of the most widespread at that time, brought fashion to French architecture, culture, cuisine, etc. to all corners globe. However, she gradually lost influence, and two world wars completely deprived her of her last strength.
Spanish Empire (1492-1976)
 One of the first large empires that seized territories in Europe, America, Africa, Asia and Oceania, creating colonies. For hundreds of years it remained one of the most important political and economic forces in the world. The main contribution to history is undoubtedly the discovery of the New World in 1492 and the spread of Christianity in the Western world.
One of the first large empires that seized territories in Europe, America, Africa, Asia and Oceania, creating colonies. For hundreds of years it remained one of the most important political and economic forces in the world. The main contribution to history is undoubtedly the discovery of the New World in 1492 and the spread of Christianity in the Western world.
Qing Dynasty (1644-1912)
 The last ruling dynasty of China in its imperial past. It was founded by the Manchu clan Aisin Gioro in the territory of modern Manchuria in 1644, quickly grew and developed and eventually covered all the territories of modern China, Mongolia and even parts of Siberia by the 18th century. The empire covered an area of more than 5,700,000 square miles. The dynasty was overthrown during the Xinhai Revolution.
The last ruling dynasty of China in its imperial past. It was founded by the Manchu clan Aisin Gioro in the territory of modern Manchuria in 1644, quickly grew and developed and eventually covered all the territories of modern China, Mongolia and even parts of Siberia by the 18th century. The empire covered an area of more than 5,700,000 square miles. The dynasty was overthrown during the Xinhai Revolution.
Umayyad Caliphate (661-750)
 One of the fastest growing great empires in history, whose life, however, was just as short. It was founded by one of the four caliphates - the Umayyad Caliphate, after the death of the Prophet Muhammad and served to spread Islam throughout the Middle East and North Africa. Sweeping away everything in its path, Islam seized power in the region and retains it to this day.
One of the fastest growing great empires in history, whose life, however, was just as short. It was founded by one of the four caliphates - the Umayyad Caliphate, after the death of the Prophet Muhammad and served to spread Islam throughout the Middle East and North Africa. Sweeping away everything in its path, Islam seized power in the region and retains it to this day.
Achaemenid Empire (c. 550-330 BC)
 Most often it is called the Medo-Persian Empire. Stretching from the Indus Valley of modern Pakistan to Libya and the Balkans, this empire is the largest Asian empire in ancient history. The founder was Cyrus the Great, best known today as an enemy of the Greek city-states during the Greco-Persian Wars, who was killed by Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC. After his death, the empire split into two large parts and several independent territories. The model of state and bureaucracy invented in this empire still works today.
Most often it is called the Medo-Persian Empire. Stretching from the Indus Valley of modern Pakistan to Libya and the Balkans, this empire is the largest Asian empire in ancient history. The founder was Cyrus the Great, best known today as an enemy of the Greek city-states during the Greco-Persian Wars, who was killed by Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC. After his death, the empire split into two large parts and several independent territories. The model of state and bureaucracy invented in this empire still works today.
Great Ottoman Empire (1299-1922)
 Became one of the largest and longest-lived great empires of the world in history. At its height (under the rule of Suleiman the Magnificent) in the 16th century, it extended from southern borders Holy Roman Empire to the Persian Gulf, and from the Caspian Sea to Algeria, effectively holding control over for the most part southeastern Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. At the beginning of the 17th century, the empire included no fewer than 32 provinces, along with numerous vassal states. Unfortunately, ethnic and religious tensions and competition from other powers led to a gradual disintegration in the 19th century.
Became one of the largest and longest-lived great empires of the world in history. At its height (under the rule of Suleiman the Magnificent) in the 16th century, it extended from southern borders Holy Roman Empire to the Persian Gulf, and from the Caspian Sea to Algeria, effectively holding control over for the most part southeastern Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. At the beginning of the 17th century, the empire included no fewer than 32 provinces, along with numerous vassal states. Unfortunately, ethnic and religious tensions and competition from other powers led to a gradual disintegration in the 19th century.
Mongol Empire (1206-1368)
 Despite the fact that the empire lasted only 162 years, the pace at which it grew is frightening. Under the leadership of Genghis Khan (1163-1227), the entire territory from of Eastern Europe before Sea of Japan. At its peak, it covered an area of 9,000,000 square miles. Perhaps the empire would have been able to capture Japan if the ships had not been destroyed by the tsunamis of 1274 and 1281. By the mid-14th century the empire was in the process of internal conflicts began to gradually disintegrate and eventually split into several states.
Despite the fact that the empire lasted only 162 years, the pace at which it grew is frightening. Under the leadership of Genghis Khan (1163-1227), the entire territory from of Eastern Europe before Sea of Japan. At its peak, it covered an area of 9,000,000 square miles. Perhaps the empire would have been able to capture Japan if the ships had not been destroyed by the tsunamis of 1274 and 1281. By the mid-14th century the empire was in the process of internal conflicts began to gradually disintegrate and eventually split into several states.
British Empire (1603 to 1997)
 Despite the short life span - only 400 years, British Empire(essentially several British Isles) managed to become the largest in history. At its peak in 1922, the empire dominated almost 500 million people (1/5 of the world's population at that time) and covered more than 13 million square meters. miles (1/4 of the Earth's area)! That empire had colonies on all continents of the world. Alas, everything must come to an end. After two world wars, Britain was financially devastated and, after the loss of India in 1947, gradually began to lose influence and colonies.
Despite the short life span - only 400 years, British Empire(essentially several British Isles) managed to become the largest in history. At its peak in 1922, the empire dominated almost 500 million people (1/5 of the world's population at that time) and covered more than 13 million square meters. miles (1/4 of the Earth's area)! That empire had colonies on all continents of the world. Alas, everything must come to an end. After two world wars, Britain was financially devastated and, after the loss of India in 1947, gradually began to lose influence and colonies.
Greater Roman Empire (27 BC to 1453)
 Founded in 27 BC. Octavian Augustus it existed for 1500 years! And it was eventually overthrown by the Turks under the leadership of Mehmed II, who destroyed Constantinople in 1453. For 117 AD. heyday came great empire. At this time she was the most powerful on earth, although not the largest in history. The population was 56.8 million people, the territory under its rule was 2,750,000 km². Influence on modern Western culture, language, literature, science is difficult to evaluate because it is incredibly large.
Founded in 27 BC. Octavian Augustus it existed for 1500 years! And it was eventually overthrown by the Turks under the leadership of Mehmed II, who destroyed Constantinople in 1453. For 117 AD. heyday came great empire. At this time she was the most powerful on earth, although not the largest in history. The population was 56.8 million people, the territory under its rule was 2,750,000 km². Influence on modern Western culture, language, literature, science is difficult to evaluate because it is incredibly large.
Over the past 3 thousand years old light I saw the rise and fall of powerful empires, and their history and past glory could not but influence the culture of the countries and peoples that today occupy the spaces where they dominated. The ruins of large cities, majestic palaces and temples, remaining after the collapse of great civilizations - Persia and the Mediterranean - eloquently testify to the wealth, splendor and power of great empires. The remains of fortresses and roads, palaces and canals, codes of laws carved on rocks and written down on paper, and praises of triumphants tell how they achieved military power, with the help of which they subjugated more and more new territories and maintained control and administration over vast colonies. Ancient empires are significantly distant from each other in terms of their existence, differ in size and cultural traditions, but they all have some common features.
What is an empire
Which ancient states can be called empires? Of course, not only the title of the ruler and the official, declared name of the country can serve as the basis for such a division. But still, let’s try to look deeper into the essence of things and understand how they differ from other states. And it doesn’t matter who is in power: the emperor, the senate, the national assembly or a religious figure. The main thing that distinguishes the empire is its supranational character. A republic, despotism, or kingdom become an empire only when they go beyond the state formation of any one people or tribe and unite many cultures and peoples at different stages of development.
Map of the Old World in the 1st century. BC.

It is no coincidence that their era began in the countries of the Old World at approximately the same time, and it is no coincidence that this time is usually called the era of axial civilizations.
It begins at the turn of the 2nd and 1st millennia BC. e. and covers the period before the start of the Great Migration, which put an end to the greatest of. Of course, this provision is quite conditional. The first empires arose earlier than this designated period of time, and some of them survived its end.
It is enough to give just two examples. Egypt of the era of the New Kingdom, i.e. the second half of the 2nd millennium BC. e., can rightfully open long list greatest empires antiquities. It was during this period that the country of the pharaohs stepped over the boundaries of its national civilization. During this era, Nubia, the legendary “country of Punt” in the south, the flourishing cities and palaces of the Levant were conquered, and the nomadic tribes of the Libyan Desert were conquered and pacified. All these areas were not only forced to recognize, but were included in economic system, the administrative structure of the country of the pharaohs, experienced cultural influences on its part. Later rulers of Nubia and even Ethiopia traced their ancestry back to the godlike rulers of the Nile.

The Byzantine Empire is a direct successor ancient Rome, which continued officially, and the people were called Romans, that is, Romans, retained the attributes of empire and multinational character until its death in the middle of the 15th century. And the one who took her place Ottoman Empire for all its dissimilarity from Rome and Byzantium, it inherited and preserved many of their traditions and, first of all, remained faithful to the imperial idea for many centuries.
But still, we will dwell on the era when they were just emerging, gaining strength and were at the zenith of their strength.
During this period, i.e. in the 1st millennium BC. e., powerful empires stretched in a wide strip along the geographical latitude from Strait of Gibraltar in the west to the shores of the Yellow Sea in the east. The strip along which the power of empires spread was limited from the north and south by natural barriers: deserts, forests, seas and mountains.
But not only these barriers caused their formation along this axis. This is where the Old World is: Cretan-Mycenaean, Egyptian, Sumerian, Indus, Chinese. They paved the way for future empires: they created city network, built the first roads and laid out the first sea routes that connected the cities together. created and improved writing, the administrative apparatus, and the army. They discovered new ways of accumulating wealth and improved old ones. It was in this zone that all the achievements of mankind were concentrated, necessary for the emergence of a full-fledged state, their successful growth and development.
In this series of predecessors and heirs stands the Phoenician colonies of the Mediterranean, on the foundation of which arose the Roman Empire, the powers of the Assyrians, Babylonians, Medes and Persians of the Middle East, the Buddhist empires of the Indo-Aryans of the Ganges Valley and the Kushans, the empires of China.
The New World later, but also went this way from the “classical” urban civilizations of Teotihuacan to the Aztec empire and from the ancient prosperous cultures of the Andean highlands.
Having rallied many tribes and peoples around themselves, they not only successfully applied all the achievements of past centuries, but also created many new things, which distinguishes them from earlier civilizations. Of course, the great empires of antiquity were very different from each other in terms of traditions, forms of expression of their imperial spirit, and destinies. But there is also something that allows you to put them side by side. It was this “something” that gave us the right to call them all in one word - empires. What is this?
Firstly, as already said, all empires- These are supranational entities. And for the effective management of vast spaces with different cultural traditions, religions and ways of life, appropriate institutions and means are needed. With all the variety of approaches to solving the problem of management, they were all based on the same principles: a rigid hierarchy, the inviolability of central authority and, of course, uninterrupted communication between the center and the periphery.
Secondly, it must effectively defend its extensive borders from external enemies, and moreover, in order to confirm its exclusive right to rule many peoples, it must constantly grow. That is why in all empires war and military affairs received exceptional development and occupied a significant place in Everyday life and ideology. As it turns out, militarization has become weak point almost all empires: changes of rulers, rebellions and the fall of provinces rarely took place without the participation of the military, both in Rome, in the extreme west of the civilized world of the Old World, and in China, in its extreme east.
And thirdly, neither effective management, nor military power are capable of ensuring the stability of any empire without ideological support. It could be new religion, a real or legendary historical tradition or, finally, a certain unification of culture, which allows one to contrast oneself, one’s belonging to a civilized empire, with the surrounding barbarians. But the latter soon became the same.
Map of the Roman Empire

10
- Square: 13 million km 2
- Highest bloom: 720 – 750
A feudal state that existed from 661 to 750. The ruling dynasty is the Umayyads. The capital was in Damascus. The head of state is the caliph. Spiritual and secular power was concentrated in his hands, which was passed on by inheritance. The Umayyad Caliphate continued the aggressive policy of the Righteous Caliphate and conquered North Africa, part of the Iberian Peninsula, Central Asia, Sindh, Tabaristan and Jurjan.
9
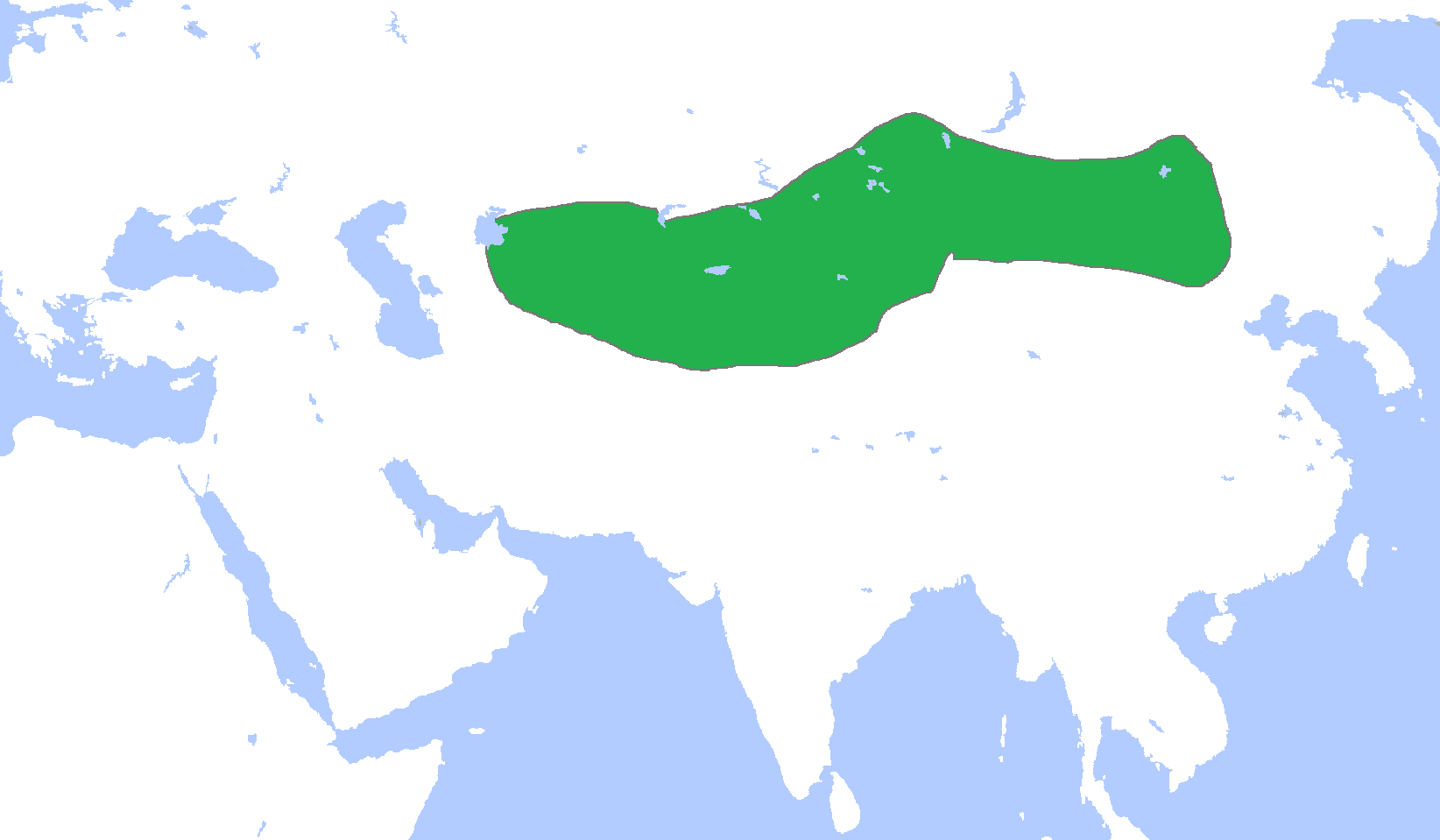
- Square: 13 million km 2
- Highest bloom: 557
One of the largest ancient states in Asia in the history of mankind, created by Turkic tribes led by rulers from the Ashina clan. During the period of greatest expansion (end of the 6th century) it controlled the territories of China (Manchuria), Mongolia, Altai, East Turkestan, West Turkestan (Central Asia), Kazakhstan and North Caucasus. In addition, the tributaries of the Kaganate were Sasanian Iran, the Chinese states of Northern Zhou, Northern Qi from 576, and from the same year the Turkic Kaganate seized the Northern Caucasus and Crimea from Byzantium.
8

- Square: 14 million km 2
- Highest bloom: 1310
Mongol state, the main part of whose territory was China (1271-1368). Founded by the grandson of Genghis Khan, Mongol Khan Kublai Kublai, who completed the conquest of China in 1279. The dynasty fell as a result of the Red Turban Rebellion of 1351-1368.
7

- Square: 14.5 million km 2
- Highest bloom: 1721
The official name of the Russian state in the period from 1547 to 1721. The predecessor of the Russian kingdom was Appanage Rus', as well as the Moscow principality. In 1547, Prince Ivan IV (the Terrible) was crowned the first Russian Tsar. He dissolved all fiefs and declared himself the only king. The Russian kingdom thus received centralized control and hope for stability in the country.
6

- Square: 14.7 million km 2
- Highest bloom: 1790
Was the last imperial dynasty of China. She ruled the country from 1644 to 1912, with a brief restoration in 1917 (the latter lasting only 11 days). The Qing era was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China. The multicultural Qing Empire existed for almost three centuries and formed the territorial base for the modern Chinese state. Qing China reached largest sizes in the 18th century, when he extended his power to 18 traditional provinces, as well as the territories of modern Northeast China, Inner Mongolia, Outer Mongolia, Xinjiang and Tibet.
5

- Square: 20 million km 2
- Highest bloom: 1790
The set of territories and colonies that were under the direct control of Spain in Europe, America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. The Spanish Empire at the height of its power was one of largest empires in world history. Its creation is associated with the beginning of the era of the Great geographical discoveries, during which she became one of the first colonial empires. The Spanish Empire existed from the 15th century until the end of the 20th century.
4

- Square: 22.4 million km 2
- Highest bloom: 1945 – 1991
A state that existed from 1922 to 1991 on the territory of Eastern Europe, Northern, part of Central and East Asia. The USSR occupied almost 1/6 of the Earth's inhabited landmass; at the time of its collapse it was the largest country in the world by area. It was formed on the territory that by 1917 was occupied by the Russian Empire without Finland, part of the Polish Kingdom and some other territories.
3

- Square: 23.7 million km 2
- Highest bloom: 1866
Was the largest continental monarchy that ever existed. According to the general census of 1897, the population was 129 million people. During February Revolution 1917 The monarchy collapses. During Civil War 1918-1921 there is a general collapse of statehood, up to 80 short-lived states are formed on the territory of the former Russian Empire, by 1924 most of this territory is united in the USSR.
2

- Square: 38 million km 2
- Highest bloom: 1265 – 1361
A state that emerged in the 13th century as a result of the conquests of Genghis Khan and his successors and included the largest contiguous territory in world history from the Danube to the Sea of Japan and from Novgorod to South-East Asia. During its heyday it included vast territories Central Asia, Southern Siberia, Eastern Europe, Middle East, China and Tibet. In the second half of the 13th century, the empire began to disintegrate into uluses, headed by the Chingizids. The largest fragments of Great Mongolia were the Yuan Empire, Ulus Jochi ( Golden Horde), the Hulaguid state and the Chagatai ulus.
1

- Square: 42.75 million km 2
- Highest bloom: 1918
The largest state that has ever existed in the history of mankind, with colonies on all inhabited continents. The total population of the empire was approximately 480 million people. Currently, the United Kingdom retains sovereignty over 14 territories outside the British Isles. In 2002 they received the status of British overseas territories. Some of these areas are uninhabited. The rest have self-government varying degrees and depend on Britain for foreign affairs and defence.
Created by a union of Turkic tribes and headed by rulers from the noble Ashinov family, this state was one of the largest in the history of medieval Asia. During the period of greatest expansion (at the end of the 6th century), the Kaganate controlled the territory of Mongolia, China, Altai, Central Asia, East Turkestan, the North Caucasus and Kazakhstan. In addition, such Chinese states as Northern Zhou and Northern Qi, Sassanian Iran, and, from 576, Crimea, depended on the Turkic empire.

Created in the thirteenth century as a result of the aggressive policies of Genghis Khan and then his successors. It became the largest in world history, occupying the territory from Novgorod to Southeast Asia and from the Danube to the Sea of Japan. The area of the state was approximately 38 million km2. In its heyday Mongol Empire it included vast areas of Central Asia, Eastern Europe, Southern Siberia, the Middle East, Tibet and China.

China's first and oldest unified state, Qin, laid a solid foundation for the subsequent Han Empire. She became one of the most powerful state entities Ancient world. For more than four centuries of its existence, the Han Empire represented an important era in the development of East Asia. To this day, the inhabitants of the Middle Kingdom call themselves Han Chinese - an ethnic self-name that comes from the empire that has sunk into oblivion.

During the Chinese Ming era, a standing army was created and a navy was built. The total number of soldiers in the empire reached a million. Representatives of the Ming dynasty were the last rulers who belonged to ethnic Chinese. After their fall, the Manchu Qing dynasty came to power in the empire.

The state was formed on the territory of modern Iran and Iraq after the overthrow of the Arsacids, representatives of the Parthian dynasty. Power in the empire passed to the Sassanid Persians. Their empire existed from the 3rd to the 7th centuries. It reached its peak during the reign of Khosrow I Anushirvan, and during the reign of Khosrow II Parviz, the borders of the state expanded significantly. At that time, the Sassanid Empire included the lands of present-day Iran, Azerbaijan, Iraq, Afghanistan, Armenia, the eastern part of present-day Turkey, parts of modern-day India, Pakistan and Syria. In addition, the Sasanian state partially captured the Caucasus, the Arabian Peninsula, Central Asia, Egypt, the lands of modern Israel, and Jordan, expanding its borders, although not for long, almost to the limits of the ancient Achaemenid power. In the mid-seventh century, the Sasanian Empire was invaded and absorbed into the powerful Arab Caliphate.

A monarchical state proclaimed on January 3, 1868 and lasting until May 3, 1947. After the restoration of imperial rule in 1868, the new government of Japan began to modernize the country under the slogan “A rich country is strong army" As a result of imperial policies, by 1942 Japan had become the largest maritime power on the planet. However, after the end of World War II, this empire ceased to exist.

After Portugal and Spain, France in the 15th-17th centuries. was third European state, engaged in the colonization of overseas territories. The French were equally interested in the development of tropical and temperate latitudes. For example, after exploring the mouth of the St. Lawrence River in 1535, Jacques Cartier founded a colony New France, which once occupied central part territory of the North American continent. In the 18th century, that is, in its heyday, French colonies occupied an area of 9 million km2.

As a result of Napoleon's occupation of Portugal, the royal family went to Brazil, the most important and largest of the Portuguese colonies. From that time on, the country began to be ruled by the Braganza dynasty. After Napoleon's troops left Portugal, Brazil became independent from the mother country, although it continued to be under the rule of royal family. Thus began the history of an empire that lasted more than seventy years and occupied a significant part of South America.

It was the largest continental monarchy. Thus, in 1914, the Russian Empire occupied a huge area (about 22 million km2). It was the third largest power that ever existed and extended from Baltic Sea in the west to Pacific Ocean in the east, from North Arctic Ocean to the Black Sea in the south. The head of the empire, the tsar, had unlimited absolute power until 1905.

Her possessions were in Asia, Europe and Africa. Turkish army for a long time was considered almost invincible. Power in the state belonged to the sultans, who owned countless treasures. The Ottoman dynasty ruled for more than six centuries, from 1299 to 1922, when the monarchy was overthrown. The area of the Ottoman Empire at the time of its greatest prosperity reached 5,200,000 km2.





