Increased salivation - acts as a manifestation of a physiological or pathological nature, which is not limited to a person’s gender and age. This means that it also develops in infants and pregnant women.
Many diseases can cause excessive salivation, and not only from the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, there are situations in which such a sign acts as a physiological manifestation.
If drooling is pathological in nature, then it will be supplemented by other clinical signs. The most common of them are pain syndrome, defecation disorder and manifestations of intoxication of the body.
Establishing the cause of such a specific symptom requires large quantity laboratory and instrumental examinations and consultation of several specialists from narrow fields of medicine.
Treatment directly depends on the provoking factor, but is often limited to conservative methods.
Etiology
Excessive salivation can be formed against the background of a wide range of various predisposing factors, which are usually divided into two large groups– physiological and pathological.
- the process of food consumption - in such cases, increased salivation is necessary to facilitate the passage of the food bolus through the esophagus, and this also ensures normal digestion;
- feeling the smell of appetizing food - salivation occurs when a person feels hungry. This is also explained by the appearance of some ingredients, for example, when people see a lemon, they secrete a lot of saliva at a reflex level;
- addiction to such a bad habit as smoking cigarettes - nicotine acts as an irritant that affects the receptor apparatus;
- period of puberty – in this case, such a sign is a physiological norm;
- menopause - in addition to increased salivation, women experience increased sweating;
- unsuitable dentures that irritate the oral mucosa and receptor apparatus;
- period of intrauterine development of the fetus. Increased salivation during pregnancy is normal due to hormonal changes in the female body. It is noteworthy that such a sign disappears as imperceptibly as it appears. However, its appearance can be provoked by pathological conditions.
Increased secretion of saliva in women, men and children can be caused by the following gastroenterological pathologies:
- or narrowing of the lumen of this organ - this may be a consequence of the inflammatory process, the influence of chemical and thermal burns;
- inflammatory process localized in the mucous layer of the stomach - salivation is observed both with and with low levels of hydrochloric acid;
- or ;
- acute or chronic course.

Excessive salivation in a person can also be caused by a number of dental problems, including:
- stomatitis or susceptibility to inflammation of the oral mucosa;
- gingivitis or the development of inflammation in the gums;
- inflammatory damage to the tissues of the salivary glands of an infectious nature, which is also called sialadenitis.
Often such a manifestation occurs due to the occurrence of diseases from the outside nervous system. This category of reasons is presented;
- stroke and vagotonia;
- Parkinson's disease;
- bulbar palsy;
- some forms of schizophrenia;
- inflammation of the trigeminal or facial nerve;
- neuroses and psychoses;
- malignant or benign brain tumors;
- mental retardation, idiocy and cretinism.
It should be noted that increased salivation in adults and children can also be caused by:
It is worth highlighting the reasons for the development of the main symptom in infants:
- a banal inability to swallow saliva - this condition is typical for children under two years of age. This disorder goes away on its own when the child reaches four years of age. If this does not happen for some reason, then the child should be shown to a pediatrician or ENT doctor. This need is due to the fact that excessive salivation can negatively affect speech activity;
- eruption of baby teeth is the most common factor that leads to increased production of saliva and children. It is noteworthy that in such cases, salivation will be observed during sleep.
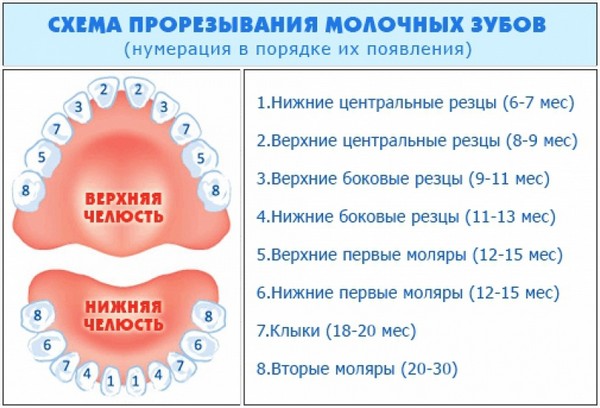
Classification
Specialists in the field of otolaryngology identify several forms of strong salivation in people:
- true– copious secretion of saliva occurs against the background of one of the above pathological processes;
- false– differs in that it is formed when the swallowing process is disrupted. This is normal for children, but in adults it is observed with brain damage. The second reason is muscle dysfunction oral cavity. The third factor is the destruction of the lips, for example, during tuberculosis.
Separation of such a trait according to the mechanism of its development:
- appearance due to disruption of the normal functioning of the salivary glands directly;
- occurrence against the background of dysfunction of the brain or spinal cord;
- formation due to damage to any internal organ.
According to the time of its occurrence, excessive salivation is divided into:
Due to the fact that children and adults often experience the development of increased salivation due to the occurrence of a pathological process, this sign will be supplemented by other symptoms. These include:
- attacks of nausea leading to vomiting;
In addition to the above main manifestations, which complement the symptoms of increased salivation, clinicians identify several specific manifestations, which are expressed in:
- frequent swallowing;
- secretion of saliva from the oral cavity - can be constant or periodic. This is the norm for babies at 2 months, and in women and men it is observed with various pathologies;
- violation of the integrity of that area of the skin that is constantly exposed to the influence of saliva;
- the formation of pustules in the area of damaged skin.
Diagnostics
To find out the factors in the development of the main clinical sign, several laboratory and instrumental studies will be required, but before this, the otolaryngologist should independently carry out the necessary manipulations.
The first stage of diagnosis in newborns and adults includes:
- familiarization with the medical history and life history of a person - to identify the most characteristic etiological factor that caused increased secretion of saliva;
- Conducting a physical examination to determine the presence of additional symptoms;
- a detailed survey of the patient or his parents - to find out the first time of appearance of the main symptom and the severity of accompanying symptoms;
- functional examination of the salivary glands and measurement of the volume of saliva produced.

After this, additional consultation with specialists from the following areas of medicine may be necessary:
- dentistry;
- gastroenterology;
- psychiatry;
- neurology;
- pediatrics;
- obstetrics and gynecology.
Treatment
Only the attending physician can decide how to reduce increased salivation after studying the results of all diagnostic measures and establishing the cause.
There are no specially designed preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of increased salivation in men, women and children. To avoid the development of such a symptom, it is recommended:
- completely abandon bad habits;
- avoid emotional stress;
- promptly treat any gastroenterological, dental and other ailments that in their clinical picture have increased salivation;
- Have a full examination at the clinic several times a year.
Increased salivation does not pose a threat to human life, but can lead to psychological discomfort, sleep disturbances, exhaustion and dehydration.
Also, the possibility of complications developing due to the diseases that caused the appearance of the main symptom cannot be ruled out. It is worth noting that some of them can be fatal.
The reasons for excessive salivation in humans can be very different: from diseases of the digestive system to inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, neurological and endocrine diseases. Children salivate excessively  may be physiological in nature, but may also be a sign of a disease.
may be physiological in nature, but may also be a sign of a disease.
Cause of excessive salivation in adults
Salivation (salivation) is a physiological process aimed at maintaining the cleanliness of the oral cavity, as well as wetting and digesting food. The salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, sublingual, minor salivary glands) are innervated by the autonomic nervous system, mainly by its parasympathetic branch. In adults, increased salivation (hypersalivation) cannot be the norm. She talks about some kind of pathology either in the oral cavity or throughout the body.
The most common cause of increased salivation in adults is increased acidity of gastric juice. High acidity can develop in the initial stages of chronic gastritis, gastric ulcer, as well as some diseases of the pancreas. For example, with a tumor of the islet apparatus of the pancreas (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome), the acidity of gastric juice increases, and multiple stomach ulcers and duodenum. At the same time, the salivary glands reflexively begin to produce an increased volume of saliva, which partially dilutes gastric juice and reduces acidity.
Increased acidity in the mouth may be associated with some kind of infection in the oral cavity, for example, inflammation of the oral mucosa, gums, periodontal tissues, or carious teeth. Increased salivation in this case is a protective reaction - it helps flush out the infection and tissue decay products from the oral cavity. If a person regularly consumes large amounts of acidic foods or certain medications (for example, ascorbic acid), the reaction of the salivary glands may be exactly the same.
The neuroendocrine system has a significant impact on the function of the salivary glands. Increased salivation may be a result of stress  or some endocrine disease, such as a disease of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
or some endocrine disease, such as a disease of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
In case of violations cerebral circulation(including in conditions after suffered a stroke), Parkinson's disease and some other diseases, the functioning of the salivary regulation centers located in the brain is disrupted. This can lead to increased salivation.
Causes of excessive salivation at night
Some people have increased salivation  appears at night when they are sleeping. The reasons for excessive salivation during sleep may lie in the predominance during sleep of the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), which innervates the salivary glands. Under the influence of the PNS, liquid saliva is released. Excessive night salivation is most often a sign of some kind of pathology. For example, increased salivation at night can occur due to impaired nasal breathing, helminthic infestation, increased acidity of gastric juice, neuroendocrine or neurological pathology.
appears at night when they are sleeping. The reasons for excessive salivation during sleep may lie in the predominance during sleep of the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), which innervates the salivary glands. Under the influence of the PNS, liquid saliva is released. Excessive night salivation is most often a sign of some kind of pathology. For example, increased salivation at night can occur due to impaired nasal breathing, helminthic infestation, increased acidity of gastric juice, neuroendocrine or neurological pathology.
During pregnancy, increased salivation can also be a consequence of the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system, which is typical for this condition.
Pathological hypersalivation accompanies early pregnancy toxicosis and can cause dehydration, which is very dangerous.
Causes of excessive salivation in a child
The salivary glands in a child begin to function from the age of three months. This is a new condition for the child, and he does not yet know how to swallow saliva. This skill comes to the baby after 6 months. Therefore, from 3 to 6 months, the child begins to show signs of false hypersalivation: there is no increased salivation, but saliva constantly flows from the mouth.
During teething, true hypersalivation appears - this is how the body cleanses the oral cavity of infection and inflammatory products. In preschool and school age hypersalivation can occur due to helminthic infestations, diseases of the digestive system, stress, and neuroses. In addition, increased salivation can occur with some neurological diseases, for example, with cerebral palsy.
The salivary glands secrete a multicomponent fluid, which consists mainly of water. About 5% of saliva is represented by enzyme compounds, proteins, acidic salt residues and many trace elements. Maltase and amylase contained in the oral cavity, being organic enzymes, are involved in the process of breaking down polysaccharides immediately after eating. Thanks to lysozyme, the growth of pathogenic bacteria is controlled.
General information
Why does a person sometimes experience foamy and overly thick saliva? It's all about high molecular weight glycoprotein-mucin, which is responsible for the formation and envelopment of the food bolus. A disruption in the functioning of this mechanism creates difficulties with swallowing food and moving it along the esophagus. From which we can conclude that thick saliva is important attribute the initial stage of the digestive process. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for how much saliva is released. In this regard, people who are asleep or under the influence of anesthesia experience dry mouth. Exposure to different smells and tastes triggers a dramatic increase in saliva production.
The appearance of excessive thickness and white saliva causes wide range reasons. Activation of the actions of irritants present in the oral cavity and triggering pulses in the sympathetic part of the nervous system, increase salivation. To prescribe the correct treatment, it is necessary to diagnose the underlying provoking disease.
Saliva may become thick for the following reasons:
In addition to a sharp reduction in the volume of secreted saliva and, as a result, an increase in viscosity, patients may experience additional symptoms:
- Impaired taste perception
- Sore throat
- Foul odor from the mouth
- Cracks on the lips and corners of the mouth, dry mucous membranes
- Burning sensation in the palate and tongue
- Hardening muscle fibers language
It is possible that saliva becomes thick due to temporary hormonal imbalances. In such cases, medication is not required, and the natural secretion of saliva is restored after some time. To understand the causes of impaired salivation, an in-person consultation with a dentist is necessary. He will interview the patient, give directions for tests, and only then select the appropriate course of treatment. As a rule, an accurate diagnosis of the underlying cause allows one to prescribe the correct treatment method, which will lead to a gradual normalization of the functioning of the salivary glands.
The first thing that needs to be done is to stabilize the level of moisture in the oral mucosa. They can help with this the following treatment procedures:
- Rinsing the mouth with anti-inflammatory herbal decoctions and soda-salt solution. To eliminate the symptoms of laryngitis, it is advisable to use antiseptics, for example, Hexoral.
- Use of artificial saliva. Used in the form of drops or spray.
- Spray moisturizers and gel substitutes. Well-known manufacturers produce drugs in the form of gel and spray, which instantly help eliminate dry mouth. In addition, they contain antibacterial components designed to eliminate unpleasant odors.
- Mucolytics. A group of medications to increase the production and thinning of saliva. Bromlane and acetylsteine have proven themselves well.
- Inhalations. They help those who have problems with the lungs and bronchi. Both pharmaceutical preparations and herbal infusions, for example, St. John's wort or sage, are suitable for inhalation.
- Chewing gum with sugar substitute. Excellent stimulation of the salivary glands.
Folk remedies to reduce saliva viscosity
- A decoction of pine needles and pine bark. Pour 4 tablespoons of ingredients with a liter of boiling water. Keep on low heat for 10 minutes, and then leave to infuse for an hour. Take the strained drink on an empty stomach three times a day, 2 tablespoons.
- A mixture of aloe and honey. Take a tablespoon orally no more than twice a day.
- Propolis with peach oil. Lubricate the oral cavity with the mixture in the morning and evening.
Preventive measures
Daily preventive measures will reduce the risk of thick saliva. Costs follow the following recommendations:
In contact with
Classmates
Hypersalivation or excessive salivation is a symptom of a person’s internal health, in particular, irritation of the mucous membrane of one or more organs. Most often, saliva “runs” if there are changes in the functioning of the kidneys, liver, pancreas, gall bladder, genitourinary system and gastrointestinal tract.
Why does salivation increase?
Normally, saliva levels should be up to 2 mg every 10 minutes. U healthy person saliva is secreted as a response to the smell of food; taste analyzers also have nerve endings in the oral mucosa. Maximum irritation is caused by excessive salivation: the more pleasant the smell, the more the appetite flares up, i.e. the gastrointestinal tract tells us that it is ready to work - we just need to start eating.
The salivary glands work continuously; they are designed to moisturize the oral cavity, protecting the tongue, nasopharynx, larynx and tonsils from drying out. They produce up to 2 liters of saliva per day. A decrease in salivation occurs during sleep, during dehydration, and also during stress.
What are the causes of increased salivation?
In addition to irritation of the mucous membrane internal organs, hypersalivation can occur from side effect drugs such as: muscarine, pilocarpine and physostigmine, if the body is oversaturated with iodine, in case of poisoning with mercury vapor and pesticides, with myasthenia gravis and auditory neuroma, with glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Almost all diseases associated with central nervous system disorders are accompanied by hypersalivation. But the most common disorder in the functioning of the body as a whole is increased work of the digestive glands (this is directly related to increased acidity). All deviations in the functioning of the salivary glands are divided into several groups: the first includes diseases of the oral cavity, the second includes deviations in the activity of the central nervous system, and the third includes irritation of the vagus nerve.
Oral diseases
All infections entering our body through the mouth are accompanied by hypersalivation. Saliva runs, it must either be spat out or swallowed (in the latter case it causes pain).
Bacteria settle not only on the mucous membrane, they also enter the salivary canals, so the glands can become inflamed and swollen. Any foreign body, which gets inside, including a denture, will initially cause increased salivation. Diseases of the teeth, gums and throat (stomatitis, gingivitis, tonsillitis), as a rule, are accompanied by frequent and profuse salivation.

Gastrointestinal diseases
Disturbances in the functioning of the gastric mucosa are caused by sharp and hot foods, diseases such as gastritis, ulcers, benign tumors, etc. Saliva is secreted reflexively if there is dysfunction in the liver and pancreas.
Vagus nerve irritation
This deviation in the functioning of the body can be provoked by frequent vomiting or nausea. This happens with acute gastritis, gallbladder diseases, climate change in women, pregnancy, in the early stages of Parkinson's disease, as well as with trigeminal neuralgia.
During menopause, salivation will be periodic: during hot flashes, hypersalivation is observed in 60% of women.
Involuntary secretion of saliva occurs with facial paralysis (this can also be a symptom after a stroke); in this case, the person cannot swallow at all, even liquid food.

If you have drool on your pillow after a night's sleep, there is no need to worry: sometimes drooling occurs before you wake up. People then say that a person slept soundly, which means he slept soundly. But if you are bothered by strong discharge, it is better to consult a doctor who, after a saliva test, will determine the real reason hypersalivation.
Any change in the amount of saliva, either towards its increase or decrease, causes a person to feel discomfort. But it is impossible to be inattentive to this phenomenon, especially to increased salivation, or hypersalivation, because it indicates serious health disorders.
Hypersalivation is a disease in which a person significantly increases the secretion of the salivary glands, resulting in increased salivation in the oral cavity.
Hypersalivation is considered normal only in children aged 3 to 6 months, in any other age childhood and in adults, excessive salivation indicates the presence of problems in the body.
Causes of excessive salivation in adults
Increased salivation can be a symptom of general ill health of a person, as well as irritation or inflammatory processes in some organs, as well as a symptom of an infectious or neuralgic disease.
There are many reasons why saliva “runs”, and only a doctor can determine what hypersalivation is a sign of.
Inflammation in the mouth
Acute inflammatory processes in the oral cavity (stomatitis, gingivitis, sore throat, etc.) can provoke excessive salivation due to unconditioned reflexes body.
Bacteria that enter the body through the oral cavity can settle on the mucous membrane and enter the salivary canals, causing the salivary glands to become inflamed and swollen.
Hypersalivation becomes a protective reaction to irritation of the mucous membrane, although an excessive amount of saliva on the mucous membrane itself negative impact cannot provide.
Pathologies of the digestive system
If there are disturbances in the functioning of the gastric mucosa, dysfunction of the liver and pancreas, saliva begins to be released reflexively. Excessively hot or spicy foods, as well as diseases - ulcers, gastritis, benign tumors, etc., can cause stomach problems.
The most common cause of hypersalivation associated with the gastrointestinal tract is increased acidity.
Video: drugs to reduce stomach acidity
Nervous diseases
In some cases, hypersalivation is associated with dysfunction of the central nervous system, as well as with irritation of the vagus nerve, which results in excessive salivation and nausea.
The initial stage of Parkinson's disease, trigeminal neuralgia, and frequent vomiting can cause irritation of the vagus nerve.
Increased salivation also occurs in cerebral palsy, primarily due to incoordination of the oral muscles.
Deviations in the functioning of the thyroid gland
Hormonal imbalance can stimulate increased salivation, i.e. disturbance in the production of hormones. This often occurs in people who have problems with the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Diabetes mellitus, which is an endocrinological disease, also sometimes leads to hypersalivation.
Video: thyroid diseases
Pregnancy
In pregnant women, due to toxicosis, normal blood circulation in the brain may be disrupted, so this symptom can be called a side effect of this period.
The appearance of hypersalivation is also influenced by the fact that, due to nausea, women find it difficult to swallow saliva, and it begins to flow out. Another pregnancy-related problem, heartburn, can also cause excessive drooling.
Since a woman's body becomes more sensitive to all medications, some medications may unexpectedly cause hypersalivation.
Side effects of drugs
Some pharmaceuticals may cause by-effect in the form of increased salivation.
The most common drugs that have this effect are nitrazepam, pilocarpine, muscarine, physostigmine and lithium.

The problem can be solved simply - by reducing the dose of the drug or stopping it, but you cannot make such a decision on your own, without consulting your doctor.
Helminths
A fairly common cause of excessive drooling, especially in children, is helminth infestation. It is more common in children because they tend to put things in their mouths and bite their nails.
With helminthiasis, increased salivation is observed mainly at night.
Causes of hypersalivation at night
During sleep, less saliva is produced than during wakefulness. But sometimes there is increased salivation, which appears in a person during sleep.
Not only is it a very unpleasant and inconvenient phenomenon, but prolonged hypersalivation at night can eventually lead to the person one day choking on his own saliva.
However, if characteristic marks on the pillow appear infrequently, there is no need to worry - this only indicates that the body woke up before the person.
Mouth breathing
The habit of breathing through the mouth can lead to hypersalivation at night. If mouth breathing is just a habit, then there is no other way but to get rid of it.

But sometimes a person breathes through his mouth at night due to ENT diseases, allergic rhinitis or problems with the nasal septum. This situation requires consulting a doctor and appropriate treatment.
Video: mouth breathing as a cause of many diseases
Features of the structure of the jaws
An incorrect bite in a person, that is, the lack of proper closure of the jaws, can lead to hypersalivation at night, because the mouth will open involuntarily.
For the same reason, increased salivation at night is observed in many elderly people - in a supine position, their lower jaw relaxes, their mouth opens slightly, and saliva begins to flow.

Sleep disorders
The severity of disorders associated with salivation normally depends on the functional state of the brain during sleep and wakefulness. If these regimes are violated, hypersalivation increases.
In addition, if a person sleeps very deeply, he loses control of his body during sleep, which can lead to increased drooling from the mouth.
Causes of increased salivation in children
Hypersalivation in children between 3 and 6 months of age is a normal condition that does not require any intervention. The smallest children salivate at the level of unconditioned reflexes.

In some cases, increased salivation may also occur in a child aged 9–12 months if teething began during this period. The very fact of teething is already a normal reason for drooling.
Everything else and any other age is already a pathology. Increased salivation in children can also serve as a symptom of such serious conditions as concussion and head injuries.
In infants
Infants most often suffer from hypersalivation due to infections and irritants entering the oral cavity.
Problems with the gastrointestinal tract and viral diseases - stomatitis - can lead to increased salivation in the youngest children. of different origins, viral sialadenitis, lead poisoning.
In infants, false hypersalivation also occurs, in which the amount of saliva secreted by the body remains normal, but it is not swallowed. This may occur due to a swallowing disorder associated with paralysis or inflammatory processes in the throat.
In an older child
If excessive salivation occurs in older children, the reasons may be the same as in infants and adult children, but psychological problems are also added to them.
With the development of higher nervous activity Children sometimes experience strong emotional experiences, stress, etc., which can cause increased drooling.
In older children, hypersalivation can lead to dysarthria, that is, a violation of the pronunciation part of speech, because due to the large amount of saliva in the mouth, it is difficult for the child to pronounce words correctly.
Dysarthria is a common cause of developmental delay.
The appearance of this symptom in children should necessarily be the reason for visiting a pediatrician or pediatric dentist.
FAQ
Does smoking affect the amount of saliva produced?
Yes, smokers often experience increased salivation. This occurs due to the effect of saliva and nicotine on the body, as well as hot air on the oral mucosa.

Photo: Smoking can lead to hypersalivation
Can salivation increase after a visit to the dentist or nasopharyngeal surgery, such as tonsil removal?
Yes, hypersalivation during this period is a normal condition, because due to local anesthesia receptors in the oral cavity are irritated.
Does menopause affect saliva production?
Yes, during menopause, increased salivation periodically occurs during hot flashes in more than half of women.
How much saliva is normally produced by the body per day?
Up to 2 liters, or up to 2 mg every 10 minutes. The normal state of salivation is when it does not flow out of the mouth and there is no need to spit out excess.
What are the causes of hypersalivation after eating?
The mechanism of saliva secretion is as follows - it occurs as a response of the body to the smell and type of food.
That is, salivation is a response to the influence of conditioned stimuli. Small salivary glands work constantly because their task is to moisturize the oral mucosa.
But large glands secrete saliva precisely because conditioned reflex for food. And if the food has too rich, spicy, sour or other strong tastes, then the salivary glands may not stop producing saliva in time.





