Thanks to language, people are able to maintain communications, express their thoughts, distinguish between a variety of tastes and respond to temperature changes in food. All these important functions are complemented by another cognitive feature of language. It can be regarded as an independent diagnostic organ that gives signs of disorders in the body.
All a person needs is to inspect appearance language and assign meaning to any suspicious changes. It is especially worth taking a closer look at the color shades of plaque accumulating on the surface of the organ. What does a brown coating on the tongue mean in adults, and what are the reasons for its occurrence, it is useful to know for everyone who cares about their health. What does it mean, what are the causes and treatment?
A brownish coating covering the tongue of an adult may appear various reasons. The surface of the organ is rough and easily stained with food colorings. characteristic color, caffeine, nicotine tar.
When the accumulation of deposits is not associated with banal preceding factors, then, most likely, the tongue informs a person about the course of hidden diseases.
Before you begin diagnosing your own tongue, you should make sure that its color is not influenced by external circumstances.
Common reasons
A set of common reasons that provoke the appearance of a brown coating on the surface of the tongue:
- nicotine addiction;
- low level of hygiene oral cavity, especially if a person forgets to clean the tongue during procedures;
- addiction to coffee, black tea, and other coloring drinks;
- abuse of diuretics, diarrhea, vomiting or other causes leading to dehydration;
- decreased secretion of the salivary glands;
- the presence of hypocortisolism or Addison's disease;
- nicotinic acid deficiency;
- advanced stomatitis;
- fungal infections of the oral mucosa in advanced form;
- a course of treatment with drugs containing chemical bismuth;
- antibacterial course of treatment. Tablets can lead to an imbalance of bacterial flora in the oral cavity;
- using rinses with peroxide, witch hazel, and menthol on a regular basis.
To correctly determine why brown spots appear on the tongue, it is necessary to take into account various nuances during examination. Important in diagnosis have thickness, consistency, localization, shade, time and frequency with which the brown spot appears. For example, the rapid appearance of plaque on the tongue of an adult in the morning after hygiene may indicate the presence of a chronic disease.
Evaluation signs:
- brown color with a yellow tint often occurs in people who chronically drink alcohol, or who have diseased lungs, bronchi, or organs of the digestive system; sometimes the plaque is due to intoxication chemicals or medications. A pale brown color may indicate that the joint apparatus needs to be examined, Airways, lymphatic system;
- A dark brown tongue indicates problems in the gallbladder, liver, and the development of serious pathological abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract). Often the surface of the organ becomes brownish due to viral infection or dehydration;
- placement of deposits on the tongue. This may be a single spot or multiple spots on different areas surfaces, or extensive covering over the entire area;
- in the early stages of pathology, with viral diseases the brown coating will have a thin layer. If the masses accumulate on the tongue in a dense thick layer, then this indicates the presence of chronic diseases or the course of an infectious process;
- The nature of the course of the pathology can be judged by the consistency of the plaque. Its texture can be dry, greasy, or moist;
- how difficult it is for plaque to peel off from the surface. A bad sign It is problematic to cleanse the tongue of brown plaque - this indicates advanced forms of disease.
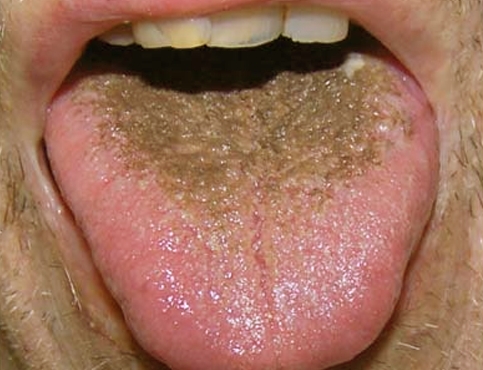
One of the shades.
You need to conduct independent observation of your tongue for no more than 3–4 days. If a person regularly cleans his tongue and has eliminated external triggers for staining, but his tongue still becomes covered with a brown coating, he should consult a dentist or therapist, since this condition is not normal.
The video below shows how to properly clean your tongue:
Digestive tract diseases
If speak about pathological reasons, then in many cases the cause of brown deposits is various disorders of the digestive system. Particular attention should be paid to the condition of the lingual surface in the morning, immediately after waking up.
Suspicions of gastrointestinal disorders are confirmed by the regular accumulation of brown deposits, and the thickness of the layers may vary. According to medical criteria, a slight occurrence of whitish deposits is considered normal. This plaque is physiological; it is quickly removed with hygiene.
Brown plaque with different shades often appears with the following diseases of the digestive system:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach due to alcoholism;
- enterocolitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- dysbiosis (intestinal microflora is disturbed);
- corrosive gastritis;
- fibrinous gastritis against the background of scarlet fever, sepsis, measles;
- duodenitis;
- reflux;
- intestinal sluggishness;
- poor functioning of the bile ducts, cholecystitis, liver diseases.

To exclude the presence of these diseases, it is necessary to undergo examination by a gastroenterologist. He will be able to tell why this raid appeared.
Dehydration
This reason very often follows from the problem described above, if a person has not independently brought himself to dehydration through diuretics. Chronic abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract can provoke dehydration against the background of constant diarrhea and vomiting. Under such circumstances, the daily volume of fluid should be monitored and the recommended amount (1.5 l) taken into account. But this measure alone will not solve the problem; it is imperative to engage in treatment together with a gastroenterologist. The plaque will gradually disappear from the tongue as the underlying disease is cured.
Diagnosis and treatment
A therapist will help you determine the factor that causes a brown coating on your tongue. If necessary, he will refer you to specialists for additional diagnostics. One visual inspection the tongue is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis, so the patient will need to donate blood, urine, feces for clinical studies, examine the organs of the digestive tract using endoscopy, and the lungs using fluorography.
Once the true cause of your brown tongue (the root of the problem) has been determined, your doctor will come up with a suitable plan for how you will be treated. In the process of treating the underlying disease, the appearance of the tongue will gradually return to normal.

This is already black, not brown. Without a doctor it is difficult to distinguish, and the problems may be completely different.
Preventive measures
To keep your tongue always looking clean and healthy, the following recommendations will help:
- enrich the diet with fresh fruits and vegetables. Fiber promotes natural cleansing of the oral cavity;
- give up caffeinated drinks for at least one month, or reduce consumption to 1-2 cups per day;
The appearance of plaque on the tongue always causes concern and signals health problems. This means that you need to immediately consult a doctor, carry out the tests prescribed by him and undergo an examination.
Brown coating on the tongue - causes
The shade of plaque has great importance. Light brown plaque may indicate the following diseases:
- Disorders of lymph outflow.
- Inflammatory processes in the joints.
- Exacerbations of chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
A yellow-brown coating on the tongue indicates the following: possible problems with health:
- Diseases of the digestive system.
- Chronic alcoholism.
- Abuse of chemicals and drugs.
- Diseases of the lungs and bronchi.
If there is a dark brown coating on the tongue, the reasons may be:
- Acute respiratory viral diseases.
- Severe forms of gastrointestinal diseases.
- Dehydration.
- Liver and kidney diseases.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the gallbladder.
In the case when the tongue is covered with a brown coating for more than three days and its amount does not decrease, intestinal dysbiosis and, as a result, intoxication of the body can be assumed.
It should be noted that coffee and chocolate lovers always have a brownish coating on their tongue. It is easy to clean and does not pose a threat. To get rid of such plaque, simply limit your consumption of products containing cocoa and clean the surface of your tongue daily with a soft rubber brush.
In addition, such a coating is a common occurrence on the tongue of a smoker. It turns brown due to inhalation of resins and can be quite thick. The constant presence of dark plaque on the tongue causes the appearance of tartar and “smoker's plaque.”
Necessary measuresIn order to find out exactly why the brown coating appeared on the tongue, you need to consult a therapist. Recommendations for examination:
- take fluorography or a photo of the lungs;
- pass clinical tests and analysis for dysbacteriosis;
- do an ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Diagnosis solely by a brown coating on the tongue is impossible, because... The list of possible diseases is too long.
Brown coating on the tongue - treatment
Sometimes the brown coating that appears on the tongue disappears on its own within 5-7 days. This means that the disease or inflammatory process in the body were successfully overcome by its own immunity. In this case, no additional measures are required. To speed up the process of getting rid of plaque, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with antiseptic herbal decoctions up to 3 times a day.
The prolonged presence of a brown coating on the tongue should be treated after the diagnosis has been made, which provoked its appearance. General measures to maintain immunity and normal intestinal microflora:

The tongue, like any other human organ, is covered with a layer of epithelium, which has a different structure depending on where it is located. The lower side of the tongue is smooth, the upper is rough, and there are small papillae on it, thanks to which a person distinguishes various tastes. Normal healthy tongue pink, the surface of the papillae has a whitish-grayish tint.
After eating, tiny particles of food can get stuck between the papillae, in which bacteria begin to multiply. It is food particles and bacterial waste products that form the basis of plaque, which usually forms on the tongue some time after eating. It can be of various densities and shades. For example, the tongue becomes coated after drinking black coffee or chocolate. Easily removed with hygienic cleaning procedure teeth and tongue, and it does not appear in the future. But if plaque is difficult to remove and soon appears again, you need to pay close attention to your health. Let's try to figure out in more detail what this brown coating on the tongue is.
Causes
The reasons why a brown plaque has formed can be very diverse, ranging from eating foods with coloring properties to the presence of serious chronic diseases. Most often, a brown tongue signals diseases of the digestive system. Moreover, the more intense the color, the more complex and serious the disease.
However, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are by no means the only reason why there is a brown coating on the tongue.
In the morning after sleep
A brown, white-brown or yellow-brown coating on the tongue in the morning after sleep is a sign of problems in the functioning of the human body. Normally, a white transparent coating may be present in the morning, which can be easily removed with a toothbrush and toothpaste. Sometimes even light brown plaque in the morning is normal if it is easily removed and does not appear again after brushing your teeth. But if in the morning it has an intense color, it is difficult to remove, and some time after cleaning it appears again, you should pay attention to the condition of the bronchopulmonary system (located at the tip of the tongue) or the gastrointestinal tract (closer to the root).
Smoking
A brown coating on the tongue and smoking are, at first glance, incompatible things. However, this is only at first glance. In fact, it is quite common for smokers to have dark spots on their tongue and teeth. The thing is that the resins that make up cigarettes have coloring properties and over time paint not only the tips of the fingers, but also the teeth and even the tongue of the smoker a dark color.
Tea and coffee
Dark coloration of the tongue may cause large quantities hot chocolate, as well as dark chocolate bars. In this case, a brown coating forms on the tongue and teeth, which is easily removed by brushing.
A brown coating on the tongue from tea may appear if you consume too much tea. strong tea. In this case, as with the formation of chocolate deposits, the stains are easily removed after hygiene procedures. Coffee can also cause a brown coating on the tongue, which can be easily removed with a toothbrush and toothpaste.
Let us hasten to reassure everyone: such a plaque is not a sign of a disease and does not require special treatment. It may be advised not to overuse excessively strong tea and coffee, limit chocolate consumption, and also more thoroughly clean your teeth, gums and tongue using a toothbrush, toothpaste and special rinses.
Antibiotics and medications
The use of certain medications can also cause a patient to have a brown or dark brown tongue. For example, intense coloring is caused by the use of a drug such as faringosept (used for sore throats and other throat diseases). Plaque occurs after some antibiotics.
Malavit can also cause a brown tongue. There are a number of other drugs that have the same effect; usually the possibility of the formation of a brown coating is indicated in the instructions. In this case, after stopping the drug, side effects also disappear. By the way, a yellow-brown or white-brown coating on the tongue that has formed as a result of taking medications usually does not require discontinuation of the medications themselves or correction of treatment.
Fungal diseases of the oral cavity
Another fairly common reason why a brown coating forms on the tongue is the presence of fungal diseases of the oral cavity in the patient. With mycosis of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, a white coating that is difficult to remove appears at an early stage. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, it begins to darken. In advanced cases, a focal yellowish-brown plaque forms on the patient, which is usually located in the center of the tongue. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor and immediately start taking the prescribed medications.
Dysbacteriosis and food poisoning
A brown coating on the tongue, bitterness in the mouth, constipation or diarrhea, especially if accompanied by abdominal pain, usually indicate food poisoning or intestinal dysbiosis. In this case folk remedies If you cannot get by, you should immediately consult a doctor to determine the diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. Note that the root cause of the formation should be treated and eliminated, that is, disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system. After recovery, plaque on language will pass on its own, without any special treatment.
Quite often, the delay in starting treatment is due to the fact that, having noticed a brown coating on his tongue, the patient does not know which doctor to contact. If plaque formation is accompanied by nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, or a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, you should consult a gastroenterologist, as these symptoms indicate disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
If the cause of the formation of a brown coating on the tongue is unknown, you should consult a physician for a full examination, which will allow you to establish the correct diagnosis.
Stomatitis
A brown coating on the tongue in the morning may also indicate the development of stomatitis. In this case, as in many previous ones, at the early stage of the disease a white coating forms, which covers the mucous membranes of the mouth, and when removed causes pain. Usually, already at this stage, the patient consults a doctor and begins taking medications, so the symptoms of the disease stop developing. But if suddenly, for some reason, the patient does not seek help in a timely manner, the plaque gradually turns from white to brown, indicating the progression of the process. In this case, treatment should be started as quickly as possible.
Dehydration
If a patient has a brown tongue, the causes of this condition may lie in dehydration. Typically, long-term severe disorders and disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract are accompanied by dehydration. In this case, it will not be enough to increase the amount of fluid you drink; more competent treatment is necessary, including the use of medications under the supervision of an experienced gastroenterologist.
In this case, the thicker and darker the plaque, the more complicated condition patient. If during treatment the thickness and intensity of the color decreases, then the treatment is successful. If, on the contrary, the thickness of the plaque increases and its color becomes darker, it means that the treatment is ineffective and it needs to be corrected.
B vitamin deficiency and other causes
A brown tongue is a sign of such serious diseases as pellagra, lack of vitamin B, diabetic coma, Addison's disease and some others. In this case, only an experienced doctor can establish the correct diagnosis, based on laboratory tests.
A lack of B vitamins causes not only the appearance of dark brown or black plaque, but also the formation of painful cracks. If you do not start taking the necessary medications in a timely manner, your tongue will later become bright red and as if varnished.
Plaque in children
In children, a brown coating on the tongue can indicate the same problems as in adults. First of all, an experienced doctor will determine the location of the greatest accumulation of plaque. If a thick layer is located on the tip of the tongue, then this most likely indicates problems with the lungs and bronchi. If plaque spots are located symmetrically on the tip of the tongue, then this may even be a sign of incipient double pneumonia. If a child has a predominantly brown coating located in the center of the tongue, then this most likely indicates problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Be that as it may, the child should be shown to an experienced pediatrician as soon as possible. Only he will be able to refer you for examination, establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
How to remove
If a patient has a brown plaque, treatment should be aimed at eliminating the cause that causes it. First you need to thoroughly clean your teeth, gums, inner surface Remove plaque from cheeks and tongue using a toothbrush and toothpaste. Next, you should observe whether the plaque appears again and, if so, how quickly. And depending on the result obtained, whether or not to consult a doctor. If, after careful hygiene procedures, the plaque disappeared and did not appear again, then it was most likely the result of staining with food or medicine. In this case, there is no reason for alarm or treatment.
But if plaque appears again and again, is difficult to remove, and stays on the tongue for longer than five days, then this is a serious reason to consult a gastroenterologist, since a brown tongue primarily indicates problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Rinsing the mouth with a decoction of chamomile or calendula flowers will help you deal directly with plaque. You can also chew a small piece of propolis for a few minutes; it has excellent bactericidal properties.
And remember: if the reason that caused the formation of a brown coating on the tongue is eliminated, it will disappear on its own without any measures within a few days. Therefore, you should fight the cause that causes it.
Is a reflection internal state human body. Changing its condition (color, structure, appearance unpleasant odor) may signal a dysfunction of any of the organs. The most common phenomenon is a brown coating on the tongue.
Features of the change under consideration
The surface of the tongue is made up of epithelium. The structure of the latter differs in different parts of the organ. It is smooth below, rough on top (contains papillae that allow a person to sense tastes). U healthy person the tongue is pink with a slight gray-white tint.

Plaque on the organ in question is the smallest particles of food and waste products of bacteria. It is formed mainly after eating food (after some time).
Based on a number of signs of this plaque, one can judge the presence of possible diseases. When a brown coating appears on the tongue, first of all you should pay attention to such indicators as:
- location
- the ability to remove plaque with a toothbrush or the ease of separating the formation from the organ
- presence of bad breath
- presence of changes in organ structure
The location of the plaque may be as follows:
- On the anterior third of the organ. This indicates with a high probability the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system or liver.
- In the middle. This change is presumably associated with ailments of the spleen or stomach.
- Based on the organ. This phenomenon indicates the presence of disturbances in the functioning of the intestines.
- Along the sides of the tongue while leaving the middle unaffected. Possibly during dysfunction.
- Brown plaque indicates pathological changes in the functioning of the digestive system. In the presence of such changes, it is important to pay attention to the possibility of removing the tumor with a toothbrush. If this cannot be done, then we can talk about a high probability of having diseases associated with the respiratory system (lungs or bronchi).
- Plaque can be dry, wet, greasy, and so on. Based on these signs, one can judge the stage of the disease that caused it. They allow us to judge the severity of the developing disease and the ease or difficulty of removing the formation. The presence of difficulties indicates the neglect of the pathology.

There are cases when the plaque lasts 5-10 days, and then disappears on its own (without any treatment). This situation indicates that the body has coped with the developing disease without additional help.
Such observations are not the basis for making a diagnosis and prescribing the required course of treatment. The named signs only coordinate the specialist in the process of prescribing the required medical studies.
Causes of brown coating on the tongue
Before going to the hospital to find out the cause of the phenomenon in question, you should make sure that the plaque is not exogenous in nature. Such changes occur quite often after eating various coloring drinks or foods.
Foods that can cause your tongue to turn brown include:
- strong
- chocolate
- cocoa
The change in question may be a consequence of drinking alcohol, fried, salty or spicy food the day before. Distinctive feature Such plaque is easy to remove when using a toothbrush and does not reappear.

Other reasons for the appearance of the change in question include the following:
- taking medications (especially antibacterial drugs)
- biliary dyskinesia
- bowel dysfunction (diarrhea)
- lack of vitamin B3 in the body
- reflux
- chronic alcoholism
- tobacco product abuse
- inflammation of the vascular system
- duodenitis
- imbalance between beneficial and harmful bacteria in the intestines (dysbacteriosis)
- Crohn's disease
- Addison's disease
- oral candidiasis (the phenomenon in question is characteristic of the late stage of the disease and is characterized by the presence of a white tint)
- gastritis (fibrous or corrosive)
- hepatitis
- hereditary diseases characterized by autoimmune features
- inflammatory processes in the small or large intestine
- dehydration
- peptic ulcer
- diseases
- stomatitis (in the absence of proper treatment, the white plaque in the initial stages of the disease turns brown)
No matter how confident the patient is in the supposed cause of the formation of a brown coating on the tongue, the diagnosis should be entrusted to a qualified specialist.
Manifestation of a problem in a child

The formation of the changes in question in childhood is relatively rare. More common are cases of yellow or white plaque. In the first case, one can judge the presence of problems with the liver (progression of jaundice), in the second - the development of thrush.
If a child has a brown color, then it is most likely that this is caused by the food he eats. Food colorings They are found quite often even in foods approved for consumption by children. And no matter how hard we try caring parents To avoid such additives, sometimes this cannot be done.
The problem in question can be observed in infant during the period of introduction of complementary foods. This phenomenon does not depend on whether this occurs when the baby reaches six months or more. early age due to lack/absence of mother's milk.
This situation requires a detailed analysis of the relationship between the foods eaten and the presence of a reaction to them in the form of a change in the color of the tongue from pink to brown. If a dependence is found, then we can say that the child’s stomach does not have time to adapt to the new diet.
The situation considered does not pose any particular danger. However, ignoring it can be fraught with the development of various chronic pathologies.
The cause of a brown coating on a child’s tongue may be a history of acute respiratory viral infection. The methods of fighting in this case are quite simple. It is necessary to provide the baby with a nutritious diet and compliance with all required hygiene procedures.
Problem in children school age may be a consequence of the development of “adult” ailments. Therefore, a visit to a specialist is quite important and should be carried out as soon as possible.
A brown coating on a child’s tongue requires mandatory medical consultation due to the high vulnerability of the child’s body and the latter being at the stage of establishing future health.
Diagnosis and treatment of the phenomenon in question
An accurate determination of the cause of the formation of a brown coating on the tongue is carried out after undergoing a series of medical procedures. These include:
- endoscopic examination of the digestive system
- blood test (mostly a detailed form is prescribed)
- analysis

Treatment of a problem consists of eliminating the disease that caused it. So get rid of it:
- antifungal medications will help against candidiasis
- from a lack of vitamin B3 - vitamin complexes and foods rich in this element (milk, eggs, peanuts, liver, buckwheat, etc.)
- for gastrointestinal problems - a visit to a gastroenterologist and treatment prescribed by him
If the phenomenon in question is not associated with any illness, then you should try:
- Regularly (daily morning and evening) brush the entire oral cavity, not limited to just the teeth. In addition to the usual toothbrush and toothpaste, you should use scrapers, floss, spoons, and rinses.
- Review your diet. It is advisable to at least temporarily avoid excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, sour, salty, fried and food containing dyes.
- No smoking. If possible, this should be followed until the cause of the problem in question is determined or the plaque disappears.
If plaque appears again and again without any identified dysfunction internal organs, preventive measures should be taken. The duration of the latter must be at least one month. The following rules should be followed:
- include exclusively “healthy” foods in the daily menu
- drink at least two liters of still water per day (you should start in the morning on an empty stomach)
- to refuse from bad habits
- control microflora
- eliminate the consumption of black tea and coffee, replacing them with compotes and herbal teas
- enrich your diet with food high concentration fiber (legumes, nuts, wheat bran, whole grain bread) and natural fermented milk products
- take multivitamins (ideally these should be prescribed by a specialist, taking into account individual characteristics body)
- play sports (to combat the problem in question or prevent it, special attention should be paid to the lower body)
Such preventive measures are general strengthening and will help not only to avoid relapses of the formation of brown plaque on the tongue, but will increase protective properties body.
While watching the video you will learn about what the color of the tongue says.
Despite the fact that a brown coating on the tongue does not cause much concern, this problem should not be ignored. In this way it can signal that help is needed. Sometimes this may be a simple lack of oral hygiene, but sometimes such a change is a sign of a developing serious disease.
Every person knows that the tongue is a mirror image of the health of the digestive organs.
The presence of a brown coating on the tongue is the first sign of concern.
It is urgent to establish the cause of its occurrence and select effective method treatment.
Below we will look at the common causes of brown plaque and methods for eliminating it.
A person’s tongue may thicken, change color, or become coated due to various reasons. In any case, a person should immediately think about the occurrence of a problem in the body’s functioning.
Brown plaque appears most often. If such observations are not regular and the natural color of the tongue returns after cleaning the mouth, there is no reason to worry. But the regular appearance of a brownish coating indicates the presence of a disease.
The tongue is an unpaired muscular organ with a heterogeneous surface. This is where it all begins digestive system. It serves as a means of talking, eating, and tasting food.
These actions help to perform the outgrowths of the mucous membrane of the tongue, in which the receptors are located. They are divided into several types, each of which recognizes a specific taste. The epithelium covers the entire surface of the tongue, including growths on the mucosa.
 Under influence various factors Some cells in the multilayer epithelium are destroyed, and pronounced keratinization appears. Some of them may not be cleanable during hygiene procedures and contribute to the formation of deposits on the surface of the tongue.
Under influence various factors Some cells in the multilayer epithelium are destroyed, and pronounced keratinization appears. Some of them may not be cleanable during hygiene procedures and contribute to the formation of deposits on the surface of the tongue.
In addition, during eating, food particles remain in the space between the outgrowths, creating favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
Life activity pathogenic microorganisms on the unpaired muscular organ of the oral cavity leads to the formation of plaque.
However, it is not worth stating unequivocally that the cause of plaque lies solely in the death of epithelial cells and the fault of dangerous bacteria. There can be many reasons why plaque forms.
The color of deposits on the tongue can vary from light yellowish to various shades of brown. In addition, it can change size, structure, density, etc.
Characteristics
If you evaluate plaque based on its characteristics and features, you can determine the cause of its formation and preliminarily recognize the disease itself.
Brown plaque can be characterized by various shades, which will indicate the presence of a particular ailment:
- Light brown. Occurs due to diseases respiratory system, that is, organs that provide the function of external respiration.
- Dark brown. Temporary intensification of existing and appearance of new symptoms associated with the dynamics of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidney disease, ARVI, exicosis (a pathological condition of the body caused by a decrease in the amount of water in it), vitamin deficiency.
- Yellowish tint. Alcohol abuse, regular digestive disorders, negative effects of medications.
Based on localization, the brown tongue surface is divided into two types:
- Local. This indicator on the tongue is characterized by the presence of spots in some areas.
- Diffuse. Plaque covers the entire tongue with a veil.
The thickness of the layer of keratinized epithelium can be:
- Thick. Indicates the presence of a chronic disease that has progressed to the acute stage. Also, this signal from the body may indicate the presence characteristic features infectious disease. The deposit is difficult to clean off during hygiene procedures.
- Thin. Signals about the initial stage of diseases of internal organs and viral infections.
Depending on the degree of thickness and nature of the consistency, plaque can be:
- dry;
- wet;
- scanty;
- bold.
Usually, the degree of density indicates the course of the disease and its characteristics.
Separation from the taste organ occurs:
- Light. The disease is at the primary stage; with proper and timely treatment, the symptoms and manifestations will quickly disappear.
- Complicated. Indicates an exacerbation of a chronic disease, that is, a worsening of the causes.
Causes
Brown deposits on the organ of taste can appear either as a result of a serious illness or as a result of eating foods that can stain the surface of the organ.
Typically, brown deposits on the tongue indicate problems in the gastrointestinal tract. The thicker their layer and the darker the shade, the more complex the disease.
Let's look at the most common reasons.
Gastrointestinal diseases
 When the first signs of diseases of the digestive system are present, changes occur in the transmission of information by nerve impulses from neurons to other tissues of the body.
When the first signs of diseases of the digestive system are present, changes occur in the transmission of information by nerve impulses from neurons to other tissues of the body.
During normal functioning of the digestive tract, taste buds deliver information to all organs of the system.
This starts the process machining food in the digestive canal, its enzymatic breakdown into simple substances that enrich the blood with essential elements.
However, if a person suffers from a certain disease, the process of impulse transmission is disrupted and runs in the opposite direction. In this case, the affected organ signals the presence of a problem.
Tongue receptors begin to respond to the signal, changing the thickness and shade of deposits on the tongue, thereby providing themselves with protection.
Consider the list of diseases associated with the digestive system, which, according to experts, can provoke the appearance of brown deposits on the tongue:
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the walls of a hollow muscular organ in the digestive tract(fibrinous and corrosive gastritis). Occurs due to measles, blood poisoning, acute intestinal infection, intoxication of the body with manifestations of sore throat, fever and pinpoint rash (scarlet fever).
- Chronic damage to tissue integrity on the inner walls of the stomach or duodenum , which are subsequently corroded by gastric juice, forming ulcers and wound areas (peptic ulcer disease).
- Disruptions in the normal disposal of intestinal gases(dysbacteriosis).
- Terminal ileitis. A complex inflammatory disease that affects the entire digestive system without exception.
- Simultaneous inflammation of the small and large intestines(enterocolitis).
- Duodenal disease, which is inflammatory in nature with significant damage to the mucous membrane.
- Biliary dyskinesia- violation of the outflow of bile.
- Liver diseases inflammatory in nature, including hepatitis.
- Complications of gallstone disease, cholecystitis.
In addition, all shades of brown coating on the tongue may indicate dehydration.
Other diseases
Other diseases not related to the digestive tract can also cause a brown coating on the tongue:
- oral thrush caused by yeast-like fungi;
- common lung diseases;
- niacin deficiency;
- genetic diseases of the blood system, autoimmune pathologies in which the immune system destroys its blood cells. These include Gunther's disease and anemia;
- bronze disease, as a result of which the adrenal cortex has acute insufficiency;
- HIV infection. Quite often, the presence of a retrovirus that turns into immunodeficiency causes a brown coating on the tongue;
- damage to the oral mucosa(stomatitis). A number of forms of this disease in an advanced stage lead to the formation of plaque.
Minor Factors
 In addition to various diseases, the presence of plaque may be due to the influence of external and internal factors:
In addition to various diseases, the presence of plaque may be due to the influence of external and internal factors:
- Coloring drinks. Excessive consumption of coffee and tea can cause a white film on the tongue. These drinks contain tannins and natural dyes that color the surface of the taste organ.
- Smoking. The tars contained in tobacco smoke have a brown tint. During smoking, they are deposited on the enamel of teeth, the surface of the tongue and the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
- Chocolate-based confectionery. Excessive use chocolates, bars, hot drinks based on cocoa provokes the formation of plaque on the tongue.
In all of the above cases, there is no need to worry about your health. The deposit can be easily cleaned with a thorough hygiene routine using a brush and oral products.
A brown coating may form after ingestion of:
- Antibiotic group drugs. When treating diseases with antibiotics, dysbiosis occurs in the intestines, which is indicated by the presence of brown plaque.
- Medicines containing bismuth. This metal, entering the digestive tract, colors mucous secretions brown.
- Medicines with increased narcotic activity. Such drugs are most often responsible for the appearance of plaque.
- Treatment and prevention with Malavit and Faringosept. Once these medications are stopped, the plaque disappears.
The appearance of a brown coating on the tongue as a result of taking the products listed above cannot be a cause for concern and cessation of therapy.
Most often, a brown coating can be observed on the tongue. light shades after waking up at night. Don't worry about it this feature considered the norm.
Its occurrence is due to the death of epithelial cells that are not removed on their own.
However, if a thick layer with a bright, rich brown color is observed, you must immediately seek help from a specialist for proper diagnosis of the disease.
Occurrence in children
 In childhood, plaque forms for the same reasons and diseases as in adults. The exceptions are smoking, drinking alcohol and using drugs.
In childhood, plaque forms for the same reasons and diseases as in adults. The exceptions are smoking, drinking alcohol and using drugs.
If plaque appears, you should take into account its location on the surface of the taste organ:
- in the middle and in the root area. Most likely, the reason lies in pathological disorders and ailments of the digestive system;
- symmetrical spots. More often formed with problems with the lungs;
- tip. Disturbances in the respiratory system associated with infection and colds.
Coloring of a child's tongue can occur when eating foods that contain dyes. Often, a brown coating appears when eating food that was previously absent from the child’s diet.
Remember! If there are problems with the child’s stomach, the process of digesting food is disrupted, which inevitably leads to the appearance of a brown coating on the tongue.
The patient's first actions
You need to understand that getting rid of plaque implies not only hygienic cleansing, but also the elimination of the disease itself, due to which the coating of the tongue has acquired a brown color.
To do this you need to carry out a number of actions:
- Perform thorough hygienic cleaning. Be sure to use products for the oral cavity, treat the dentition, the surface of the tongue and gum tissue.
- Monitor the condition of the organs and tissues of the oral cavity. If the taste organ has a natural pink tint and the deposition does not resume, this indicates that its appearance was due to drug therapy or consumption of coloring foods.
- Check the appearance of plaque for stability. If the surface of the unpaired organ of the oral cavity has again acquired a brown tint and the plaque is difficult to remove, you should immediately consult a specialist. The presence of deposits that are not cleared within several days most often indicates a malfunction in the digestive system, and this is dealt with by a gastroenterologist.
- For prevention, decoctions are considered the most effective medicinal herbs . Chamomile and calendula have worked well here. Bee glue has special bactericidal properties, which fights microbes, which significantly reduces the likelihood of plaque formation.
Rinsing with antiseptic agents should be performed up to 7-8 times during the day for a long time.
To rid the body of minor digestive problems, it is useful to consume a decoction of flaxseed.
As for diagnostics, experts recommend:
- examine the abdominal cavity using ultrasound;
- take a picture of the respiratory organs (lungs) or conduct an X-ray examination;
- check for dysbacteriosis by taking tests.
Prevention
 Based on the fact that plaque appears due to the activity of bacteria, you need to follow a few simple rules that will help stop their proliferation:
Based on the fact that plaque appears due to the activity of bacteria, you need to follow a few simple rules that will help stop their proliferation:
- Pay attention to nutrition. Eliminate fatty and high-calorie foods from your diet. Stop drinking alcohol and smoking. The amount of coffee and black tea you drink should be limited.
- Enrich your diet with fiber, drink plenty of liquids, including fermented baked milk, kefir, yogurt, whey, yogurt.
- Drink herbal infusions and green tea regularly.
- After a night's sleep on an empty stomach, drink 250 ml of purified water, and take food in small portions 4-5 times a day.
- Do gymnastics several times a week to improve the functioning of the digestive system. This could be muscle exercises. pelvic floor, boat pose, sit-up press, forward bends, breathing exercises.
To learn how to determine the diagnosis by the color of the tongue, watch the video.





