A common reason for visiting a dentist is a wisdom tooth, why is it needed and do people exist without these "gifts of fate"? After all, until a certain age we all live without these teeth and do not feel deprived.
Dentistry in ancient times
The first attempts to cure teeth were made in ancient times:
- There was no question of any pain relief;
- The tools used were the same as for building houses;
- I had to live with unbearable pain for months;
- The consequences of unskilled intervention are not difficult to predict.
A blow to the back of the head with a wooden mallet is not a joke, but quite a real version of pain relief in ancient Rome.
To visit the predecessors of dentists was not just scary, but life-threatening. But given the peculiarities of anatomy - the presence of nerve tissue and a rich blood supply, do without help simply impossible... Either excruciating pain, or inflammation, suppuration and all the same excruciating pain.
Besides all this:
- Only the wealthiest people of that time could afford medical care;
- Knowledge in anatomy was too low to provide truly qualified assistance;
- The rules of asepsis and antisepsis were not followed due to their absence;
- There was no prevention either.
And that was one of the factors that drove average life expectancy by 30 years ... However, wars and epidemics have made a greater contribution to the formation of this indicator.

In this video, dentist Timur Cherokin will tell you some interesting facts about ancient dentistry:
Wisdom tooth: how old does it appear
This moment is a purely individual phenomenon:
- Some people never get wisdom teeth;
- The lower age threshold for their eruption is 14 years;
- Most often they acquire "wisdom" in the region of 20 years;
- Cases of the appearance of these teeth have been recorded at the age of 45.
The human skull has been forming over many millennia. Initially, the facial section prevailed over the brain:
- The head shape of primitive people was very different from today's standards;
- The skull was more elongated;
- The brain took up less volume;
- The cheekbones and jaws were massive.
But evolution did not stand still and today we have the most optimal "design". Perhaps the people of the future will look a little differently, and against their background we will already become “primitive savages”.
Change doesn't happen too quickly for all the time our jaws have decreased by only 20%, in this regard, "wisdom teeth" have become rudimentary organs, for which there is simply no place in the new maxillofacial apparatus.
Taking care of your own smile
Dental treatment should be done at any age:
- It's never too late to improve your health;
- The more you work on your health, the less problems should arise in the future;
- The aesthetic moment is always important, regardless of the number of years;
- Over the years, problems tend to accumulate, so it is best to resolve them as they become available.
First of all, choose your dentist. Going to the first clinic you come across to an unfamiliar specialist is not a good idea. Use the advice of friends, family and colleagues. Perhaps there is a highly qualified specialist in your environment.
Before visiting the office, remember that:
- Modern anesthesia makes the process no more painful than cutting nails;
- Between the receptions, it is better to take a break of several days in order to observe the result and possible complications;
- Don't skimp on your own smile;
- A filled tooth with removed nerves will never hurt again. Even if the seal breaks out.
Every year, all manipulations become less painful. Even 20 years ago, they did not even dare to dream of such a luxury.

How many wisdom teeth does a person have?
The second name is "eights":
- They are the outermost teeth of each jaw;
- There are four of them in total;
- Due to a lack of space, they may grow to the side or remain under the gum;
- An inconvenient location makes it difficult to care for them;
- They are a common reason for visiting the dentist.
Some people may never have wisdom teeth. This does not indicate any genetic defect, because the "eights" are rudimentary organs that do not participate in the act of chewing food.
By and large, wisdom teeth are simply:
- Collect food in the cracks;
- Injury to the tongue or cheek;
- Become the cause of the inflammatory process;
- Can cause decay or damage to adjacent teeth.
Another name for them is the third molar. If at least one of them began to erupt, then three others should be expected. Painful sensations will have to endure 4 times.
On the one hand, we can safely talk about a smile of 32 teeth. On the other hand, there is simply no practical sense in these "new clothes". Despite the difficulties with access, it is necessary to pay attention to the "eights" while brushing your teeth, caries does not sleep and is just waiting in the wings.
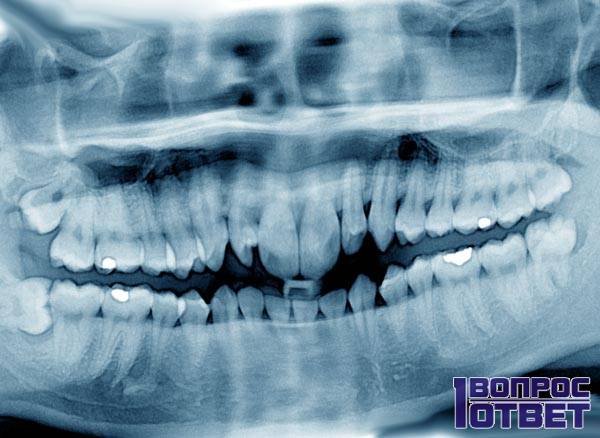
Wisdom tooth: removal - consequences
This is one of the most "delicate" operations in dentistry. Specifically, with this tooth, you should go to the best doctor to whom you only have access.
Directly during manipulation:
- An adjacent tooth may be damaged;
- It is not always possible to avoid soft tissue ruptures;
- Due to inaccuracy, damage to the maxillary sinus occurs;
- Mandibular fractures and dislocations are more common than meets the eye.
These troubles are not always associated with a low qualification of the dentist. Main problem - oral health... Malnutrition of adjacent teeth, inflammatory and atrophic processes can make the underlying structures more vulnerable.
After the removal of the ill-fated "eight", patients are faced with:
- With pain syndrome, as soon as analgesics cease to work;
- With inflammation, due to damage to the gums and the presence of a wound surface;
- With an increase in temperature, due to the addition of an infection;
- With recurrent bleeding due to the peculiarities of the hemostatic system.
All these troubles can arise, or they can bypass. It all depends on the amount of intervention and the complexity of the manipulation itself. Tooth extraction is too general a concept. There are always nuances that only a doctor dealing with a specific case can determine.
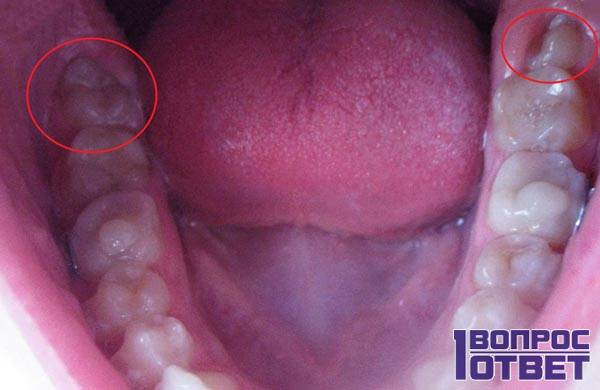
What are the G8s?
Third molars are rudimentary "processes" that do not take part in the act of chewing food and are located at the edges of each jaw. There are 4 of them and they "close" the dentition.
From the negative:
- Difficult to access - they are often affected by caries;
- Due to a lack of space, they can grow in the wrong direction, damaging nearby tissues;
- The manipulations associated with the "eights" are always the most difficult;
- They cut through in adulthood, causing additional discomfort.
Some lucky ones with wisdom teeth do not "collide". In this case, you can joke about the next stage of evolution and catch the envious glances of those whose third molars grow in the cheek or injure the tongue.
Less fortunate people have to hope that after removal does not appear:
- Severe pain;
- Swelling of the cheeks and gums;
- Temperature increase;
- Bleeding.
If something went wrong, do not immediately blame the dentist for all the troubles. In some complicated cases, you have to crush a tooth, what can we say about possible complications.
Almost all of us have a wisdom tooth, why is it needed and why it grows somewhere in the side, only dentists and anthropologists know. And the average person can only hope that toothache and swelling of the gums will bypass him.
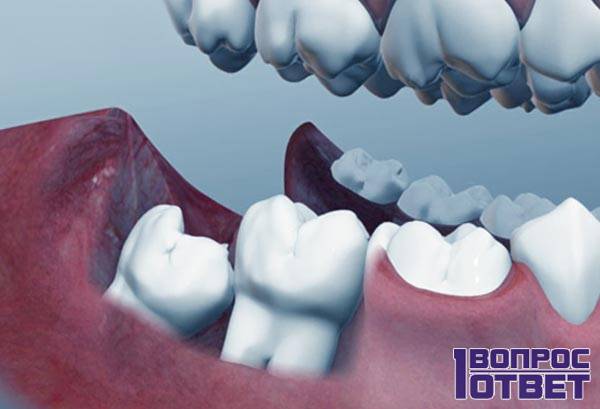
Video: why do wisdom teeth grow?
In this video, Stepan Shiyanov will tell you what the wisdom teeth are for in humans, what functions they carry: