Stomatitis treatment is a whole range of measures - from regular rinsing to antibiotic therapy.
The duration of the course of taking medications and the scheme of using medications depends on the form in which the disease proceeds and how much the inflammatory process has developed.
Most often, treatment is carried out at home, however, a doctor's consultation is necessary to diagnose and select a specific drug.
![]()
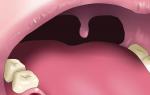
The first symptoms of herpetic stomatitis appear 4 days after the herpes virus enters the body.
In adults, the manifestations of the disease are often a relapse of a childhood illness. Reduced immunity, stress, overwork or other factors that disrupt the normal functioning of the body can provoke an ailment.
A characteristic feature of this type of disease can be called fluid-filled bubbles that form on the oral mucosa, which, after rupture of the membrane and fusion, create painful erosion.
If the disease affects the adult body, with timely treatment, in most cases, there is an absence of obvious symptoms of intoxication and high fever.
How to get rid of such an unpleasant disease forever or what to do to avoid relapse?
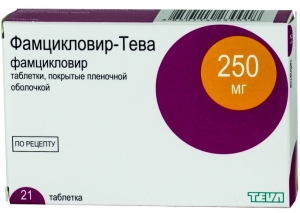
Tableted antiviral drugs
One of the popular methods of medical treatment of herpetic stomatitis is intensive one-day therapy with the appointment of a high dose of modern antiviral drugs. The effectiveness of daily treatment and the equivalence of such a technique with weekly therapy have been proven by numerous studies.
The following drugs allow you to achieve the best result:
Local antiviral agents
We are talking about antiviral gels and antiseptic rinses (it is important that the composition contains substances that neutralize the herpes virus):
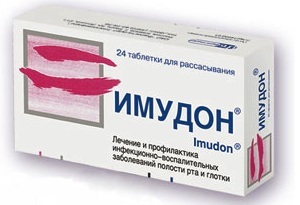
Immunostimulants
Such funds are used, as a rule, to prevent the recurrence of the disease. The most popular are:

Vincent's ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis
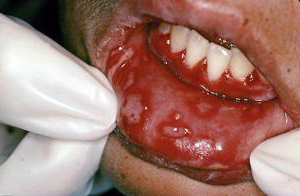
The disease occurs due to the simultaneous action on the body of a spirochete and a spindle-shaped bacillus, which are always present in the oral cavity in small quantities.
The development of pathogenic flora provokes insufficient oral hygiene, the presence of periodontitis, viral infection, vitamin deficiency, overwork or stress, malnutrition, that is, reasons that negatively affect the immune system.
This pathology is not contagious, but dangerous to health due to the risk of developing osteomyelitis.
Typical symptoms are headache and weakness, fever, pain in the joints, bleeding gums, dryness and burning of the oral mucosa.
After a short period of time, ulcers are found on the gums in places prone to injury from crowns, tartar, and decayed teeth.
Then the inflammation spreads to the rest of the mucous membrane, causing swelling, redness and soreness of the gums, the appearance of a necrotic white or white-gray mass in the mouth.
Antibiotic therapy
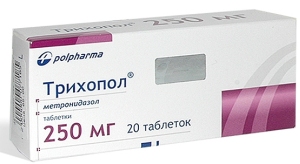 To cure ulcerative stomatitis, not one antibiotic is needed, but a combination with the use of Metronidazole (Trichopolum) in tablets, Lincomycin injections. Alternatively, Metronidazole can be supplemented with Amoxiclav tablets or Claforan injections. The therapy is carried out within 10 days.
To cure ulcerative stomatitis, not one antibiotic is needed, but a combination with the use of Metronidazole (Trichopolum) in tablets, Lincomycin injections. Alternatively, Metronidazole can be supplemented with Amoxiclav tablets or Claforan injections. The therapy is carried out within 10 days.
How to rinse your mouth?
Usually a solution is used Chlorhexidine in a dosage of 0.05%, a procedure lasting 1 minute is carried out 3-4 times a day. The course of treatment is similar to taking antibiotics.
Gels for mucous membranes
Such drugs are applied to the affected areas immediately after rinsing, pre-drying the mucous membrane in the mouth with a gauze swab. The agent is used to treat all inflamed areas, including the marginal gum surrounding the teeth, gingival papillae and other parts of the mucosa. The best result is provided by:

Symptomatic therapy
Reception of antiallergic drugs is acutely indicated for necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis. Tavegil, Suprastin, Pipolfen are ideal.  You can also use other antihistamines (course - 10 days).
You can also use other antihistamines (course - 10 days).
In the presence of fever and severe pain, drugs that eliminate these symptoms are additionally prescribed (Paracetamol). To increase the body's defenses, therapy is supplemented with immunostimulants, which must be taken before the end of the main treatment.
Fungal form of pathology
A disease with an incubation period of about 15 days most often affects people with reduced immunity and a history of such diseases as diabetes mellitus, HIV. Often, the fungus Candida, which is the main cause of candidal stomatitis, affects the body of young children (especially in infants).
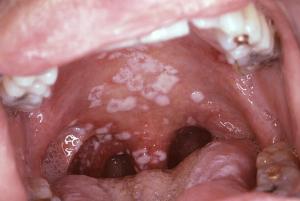
In the photo, candidal stomatitis
The characteristic white spots, covered with a curdled coating, which appear on the mucous membrane, help to diagnose the ailment. Removal of plaque leads to the opening of a reddened edematous focus of inflammation.
Other symptoms include seizures in the corners of the mouth, dryness and burning sensation in the mouth. As the disease progresses, fungal formations are layered on top of each other and are covered with a dense film, forming highly painful erosion.
Systemic antifungal therapy
How to treat this type of stomatitis in the mouth? Therapy is impossible without the use of special antifungal agents produced in the form of tablets (the duration of the course is from 5 to 7 days). The main drugs are:
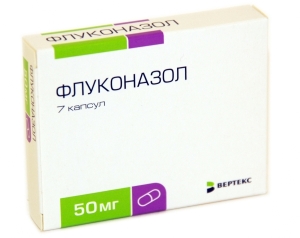
The systemic drug is supplemented with local antifungal agents using special preparations for irrigating the oral cavity.
How to rinse your mouth?
![]() Regular rinsing is extremely important for candidal stomatitis. It is most effective to use local antiseptics that will not harm the oral mucosa. Topical preparations include a solution of Furacilin, sodium tetraborate in glycerin (the number of rinses per day should be at least 5).
Regular rinsing is extremely important for candidal stomatitis. It is most effective to use local antiseptics that will not harm the oral mucosa. Topical preparations include a solution of Furacilin, sodium tetraborate in glycerin (the number of rinses per day should be at least 5).
Also, rinsing with Hexoral gives a good effect (when buying a drug in the form of a spray, you can use it for irrigation).
This drug quickly destroys microbes, providing an anti-inflammatory effect. The tool is applied in a course for a week, twice a day.
Oral cavity treatment with Candide
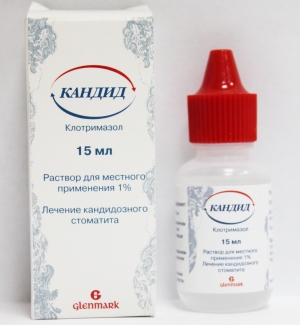 The best way to fight yeast infections because contains clotrimazole. Before applying Candida to the mucous membrane, it is necessary to completely clean the inflamed areas from plaque using a gauze swab soaked in an antiseptic.
The best way to fight yeast infections because contains clotrimazole. Before applying Candida to the mucous membrane, it is necessary to completely clean the inflamed areas from plaque using a gauze swab soaked in an antiseptic.
Candide is applied with a cotton swab three times a day until the symptoms of the disease go away. With a weakened immunity, it is advisable to use the agent for at least 7 days after the end of the course of treatment (the number of treatments per day is reduced to one).
It should be remembered that Candide is not suitable for rinsing due to its toxicity (ingestion of the digestive system provokes vomiting and nausea).
Help for the little ones
Treatment of candidal stomatitis or thrush in newborn babies is carried out using a soda solution. With a large area of inflammation, antifungal drugs are additionally prescribed (externally - Candide and internally - Nystatin). Treatment is carried out until symptoms are completely eliminated.
Aphthous stomatitis
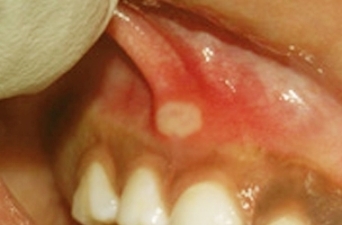
In the photo, aphthous stomatitis on the gums
The most affected areas of the oral mucosa are the inner side of the cheeks and lips.
Due to constant trauma to teeth or rough solid food, to which factors such as allergies, decreased immunity, insufficient oral hygiene are added, symptoms of the disease appear in the form of round or oval aft, reaching 1 centimeter in size.
A bright red rim is formed around the aft (due to inflammation of the mucous membrane), the formations themselves are covered with a gray-white bloom. More often, the disease proceeds with the formation of one aphthae or a maximum of three.
At the same time, there is a slight weakness and a slight increase in temperature. Due to the painfulness of the formations, food intake becomes extremely difficult. Such stomatitis is not contagious, therefore it is not transmitted to others by contact.
 Antihistamines
Antihistamines
For the treatment of aphthous stomatitis, antiallergic drugs are primarily prescribed, which include Tavegil, Erius, Claritin and others. Duration of admission is at least 10 days.
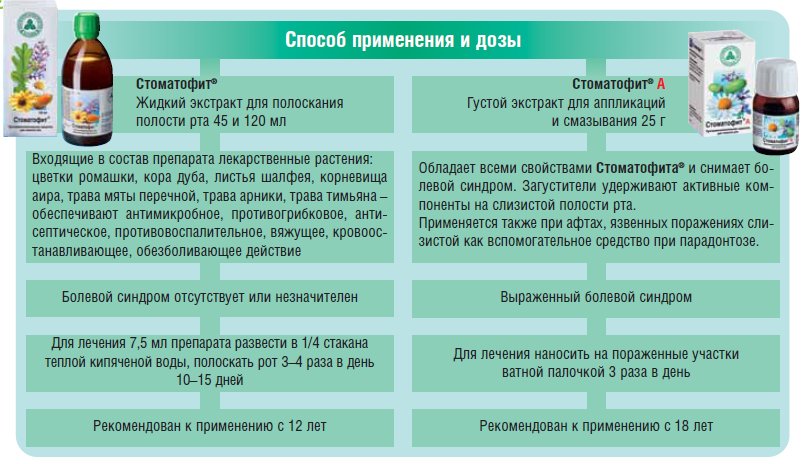
Local funds
Used for aseptic rinses and topical applications. The choice of the drug depends on the duration of the aft:
Immunostimulants
To increase the body's resistance to pathogenic bacteria, as a rule, Imudon is used (the course of treatment is 15 days).
FAQ
What is most often of interest to people who are faced with this disease, is the use of the following means effective:

 How to cauterize stomatitis?
How to cauterize stomatitis?
Quite often, in the treatment of stomatitis, cauterization of erosion is used with iodine, brilliant green or hydrogen peroxide. Such therapy causes conflicting opinions due to the strong irritating effect that the listed solutions have.
In other cases, cauterization therapy is not the main one, but can only be used as an auxiliary treatment, if such a method is justified.
What to do to prevent inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity:
Can teeth be treated during infection?
It is not only possible, but also necessary. Untreated teeth are a source of infection and a traumatic factor for the mucous membrane, leading to the development of inflammation in the oral mucosa.
Dental treatment is a curative and effective preventive measure for stomatitis in the mouth.
Why is the disease dangerous?
Complications of stomatitis in adults can be provoked by only one factor - untimely inappropriate treatment. With early diagnosis and proper therapy, negative consequences are minimized, and recovery occurs in a matter of days.

Necrotizing ulcerative gingivostomatitis
If the disease proceeds in a severe form with the formation of deep ulcers and erosions, the consequences can manifest itself in the form of gangrenous conditions, in which irreversible disorders occur not only in the gum tissues, but also in the jaw bones (for example, osteomyelitis).
The advanced forms of stomatitis lead to tooth loss, destruction of soft tissues, or become the cause of the chronic course of the disease, when any risk factor causes a new exacerbation.
Obviously, therapy should start as early as possible. The first signs are already a reason for going to a doctor, who correctly diagnoses the type of disease and prescribes complex treatment that prevents the transition of the disease to a severe form.