The first thing that parents should understand is that the development of children is always individual, so the question of whether teeth can be cut at 3 (three) months can be answered unequivocally in the affirmative. Do not be alarmed if by this period of life your child has signs such as anxiety, moodiness and loss of appetite, it may be time to buy a teether and be patient. Let's take a closer look at how to respond to teething at the age of three months, what you should pay attention to, and what is considered completely normal at this stage of a child's development.
Of course, we will talk about those norms according to which the optimal time and order of appearance of the first molars is determined. But do not be upset if the baby's personal schedule is lagging behind or in a hurry in relation to this "schedule". The discrepancy may well reach six months in one direction or the other, so if the teeth are already making themselves felt at 3 (three) months, this should not cause concern.
There is the following scheme for the eruption of milk molars:
- 5-7 months - a pair of lower frontal incisors;
- 8–10 months - front upper incisors;
- 10–12 months - a pair of lateral incisors in the upper jaw;
- 11-14 months - lower lateral incisors;
- 12-15 months - first the upper first molars, and then the lower;
- 16–23 months - upper, then lower canines;
- 24-30 months - upper, lower second molars.
If the frontal incisors climb at three months, this is normal, but make sure that the first pair is formed first, and only then, for example, one of the lateral incisors. It is important to immediately exclude pathology in order to take the necessary measures in time.
Remember, the main thing is that the first teeth are erupted before one year. At the same time, do not expect that the process itself will proceed as in a textbook - some children tolerate it easily and almost imperceptibly, others experience intense unpleasant sensations.
Sometimes teeth at 3 (three) months begin to declare themselves very seriously, for example, tissue soreness, refusal to eat and high fever. Runny nose and vomiting are possible as a result of abundant discharge.
Regarding the order of eruption and what symptoms appear and how easy or difficult the process itself is, a genetic factor is often of great importance here. Ask how everything went with you, and you can compare the picture of manifestations, draw certain conclusions for the future.
How many first molars erupt
When the child has already got out several teeth, the parents have an idea of the duration of the process, but when the very first of them appears, it is still difficult to talk about it. The first symptoms begin to manifest themselves about a month before the actual eruption. For some, the duration is a month, for others, two weeks, everything is very individual.
By this, one can judge when all the baby teeth will appear in the baby (only 20 molars). Early teething suggests that the baby is likely to have a whole set of solid formations by the age of two. In such children, new molars appear almost every month, without serious difficulties. In others, the same set is formed only by the age of 3.5, which is also normal.
Signs of eruption
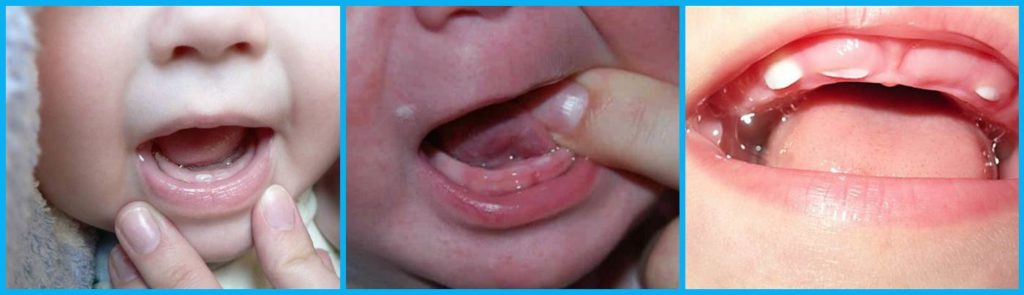
You can understand that the first molar will soon climb by the following signs - the gums begin to swell and hurt a lot, which is accompanied by increased salivation. In this case, a similar picture may begin several months before the actual appearance of the teeth themselves. Sleep becomes restless, the child is capricious, because of severe discomfort, children refuse certain meals, an irresistible urge to take various objects into their mouth appears.
As soon as the eruption is active, you will notice a thin white line on the gums or a whitish bulge. If you lightly tap on visible teeth with a teaspoon, you will hear a slight clatter, as some parents do, but if you decide to do this test, do it very carefully.

Some of the signs that are characteristic of the onset of molars in children often overlap with symptoms of infectious diseases. Therefore, if in doubt about this, it is better to seek the advice of a specialist.
Pay attention to the temperature - it can rise up to 38.5-39 degrees and keep for two days, this is normal. Paracetamol in small quantities is suitable for knocking it down, but if after this period the indicators do not decrease, you should not hesitate to go to the doctor.
Also, watery diarrhea often occurs due to profuse salivation, normally this is repeated up to 2-3 times a day. If this period is exceeded and blood inclusions appear, there is already a reason to make an appointment with a specialist.
Regarding a runny nose, transparent discharge that lasts 3-4 days does not cause concern, it is enough for parents to cleanse the sinuses from them in a timely manner.
If this period is exceeded, and the snot becomes whitish or greenish, do not hesitate to go to the doctor. The same applies to cough, if it lasts more than two days and is accompanied by sputum, consultation is needed.
Is it worth worrying
It is important for parents to understand that very often it is quite difficult, you should not be afraid of many manifestations. Let's figure out when you shouldn't panic, which is the norm. The following symptoms are not considered to be cause for concern:
- Copious flow of saliva. This is generally the case for most babies between 10 weeks and 4 months. Just stock up on bibs and you won't have to worry about hygiene;
- Skin irritation (area around the mouth, on the chin). This symptom is the result of the same salivation, so do not forget to wipe the baby's skin in time and use an emollient cream before bedtime;
- Frequent desire to breastfeed. This is explained by the desire to scratch the gums, this is normal and you should not refuse the child this, it usually goes away pretty soon.

In order for the new molar to erupt as easily as possible, it is necessary to pay a lot of attention to the child, also each little man has his own pain threshold. Usually the most difficult in this regard is the appearance of the very first teeth, as well as incisors.
Sometimes, while sucking at the breast, the child's pain increases so much that he begins to refuse to eat. If you miss 2-3 feedings, do not worry, but if this number is exceeded, you need to consult a pediatrician.
Also, loose stools are not considered the norm, it is caused by profuse salivation during teething. As described above, persistent bloody diarrhea should not be underestimated.
What else to look for
It happens that small bumps appear on the gums, that is, a slight hematoma. But you should not be afraid of this, the formation dissolves on its own, cold compresses help well.
Sometimes, when the incisors are about to appear, pain also occurs in the chin and ears. The child begins to rub his face or chin, but sometimes it is also a symptom of an inflammatory process in the auricle, so consultation with a specialist will not be superfluous.
A little advice, if the baby is spinning in bed and does not fall asleep, you should not immediately reassure the child, it is better to let him cope with this on his own. You need to pick up and drink milk when you can't fall asleep for a long period of time.
Another difficulty is increased salivation, due to which the child begins to cough, when mucus enters the nasopharynx, a concomitant runny nose develops. If there are additional symptoms that cause concern, you should contact your pediatrician.
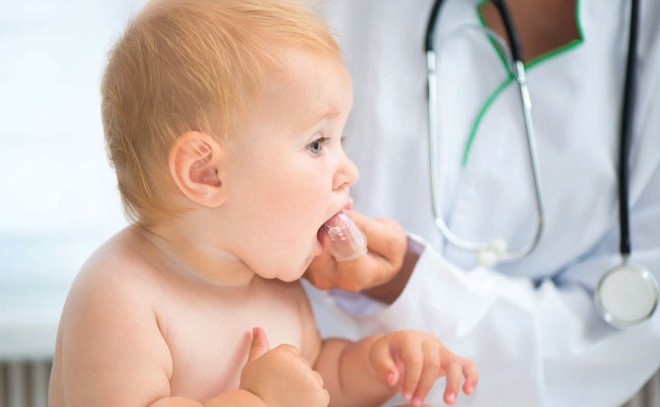
During this period, the growing body of the baby undergoes important changes, and the support of adults and their care can significantly alleviate this condition. First, take your child more often in your arms so that he feels support, tactile contact will additionally calm and distract him. Secondly, make sure that he drinks the prescribed amount of water - usually the baby begins to refuse the bottle, just drink it from a spoon.
You can apply the baby to the breast to calm it down, do not forget about the massage of the gums, which is best done with a special attachment on the finger.
What to use
If elementary techniques do not save the day, it is worth resorting to auxiliary options. If the pain is intense, try a local "anesthetic." For this, special gels containing benzocaine / lidocaine are suitable, which are applied directly to the gums several times a day. They have a short-term effect and are safe for a small organism, but it is still recommended to consult a specialist beforehand.
For relieving fever, drugs based on ibuprofen or paracetamol are well suited. You can take it several times a day, the funds fight high fever and partially relieve pain.
But folk recipes should not be ignored, as it will be useful to make infusions of mint, chamomile, lavender, sage. The resulting substance is impregnated with a cotton pad, with which it is necessary to wipe soft tissues. You can also replace the infusion with a soda solution; this will require a glass of boiled water and 1 teaspoon of baking soda.
Additional methods
At an early stage of life, it is especially important to support the child, since any load on a small organism is felt very sharply. A special reaction to teething requires a special drug, for example, the Dentokind remedy copes well with all the symptoms - it is anesthesia, anti-inflammatory, calming effect, sleep stabilization.
To satisfy the child's urge to take various objects in his mouth and at the same time to alleviate his condition, buy a special rubber ring, which is placed briefly in the freezer for cooling and given to the child.
Perhaps the kid will not like such a ring, then watch what he likes. The main thing is that the objects do not have sharp corners and cannot damage the gums, for example, it can be a bagel or bread crust.
Try to distract the child as much as possible, switch your attention to the game, an interesting cartoon. Daily walks will also help if there is no temperature and the condition allows.