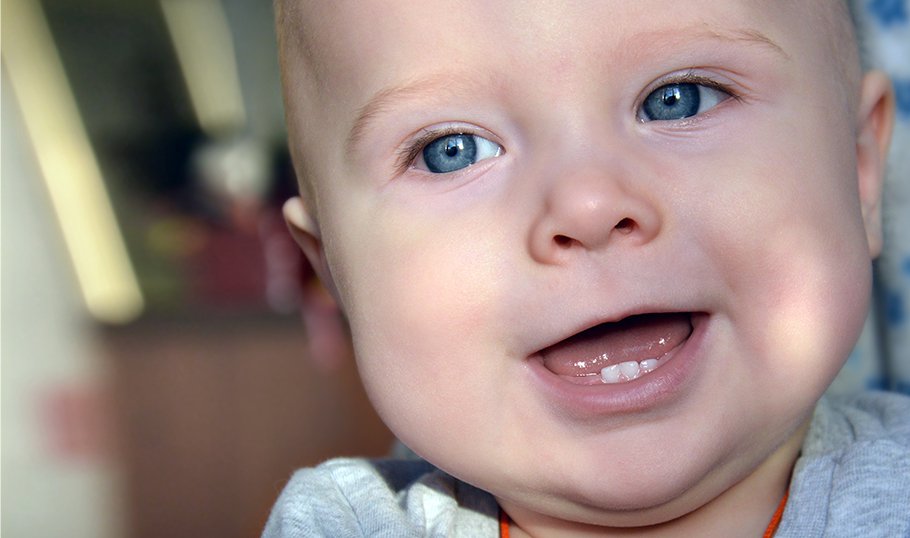
Young parents usually have many questions about how their children’s teeth climb. There is an opinion that most children find it very difficult to endure this period. In many cases, the process of teething is actually accompanied by various unpleasant and painful symptoms. But in some babies, teeth can erupt completely imperceptibly, without causing them suffering and special discomfort. Consider how teeth are climbing in children, what are the main possible symptoms of this process, and how can a child be helped?

How do children get teeth?
Pediatricians indicate that normally a child's teeth appear in a period of 4-7 months. Although there are cases of both earlier and later appearance of the first teeth. In general, the time when the first tooth appears depends on many factors. First of all, genetic predisposition is taken into account. If the parents, especially the mother, have their first tooth late enough, do not expect the child to have early teeth. In addition, the beginning of teething depends on the general condition and rate of development of the baby's body, the presence or deficiency of certain vitamins and microelements.
The order of priority of teething is usually the same for all children. In some cases, it can change, but not significantly. And again, as a rule, it depends on the hereditary predisposition. So, how do children get teeth?
Usually, a child will have two lower incisors first, then two upper ones. After that, the upper lateral incisors appear, followed by the lower lateral incisors. Then the upper premolars, lower premolars, canines, and molars climb.
As a rule, a two to three year old baby should already have twenty teeth. Milk teeth are finally formed by the age of three.
In addition to the question of how children's teeth climb, parents are often worried about the main symptoms of this process.
What are the symptoms that a child's teeth are coming out?
The signs of teething are individual for each baby. Moreover, in the same child, the symptoms of this process may change with each subsequent tooth. But you can still highlight the main ones that are typical for most children.
About two weeks before the eruption of a tooth, the child's gums turn red and swell at the place of its appearance. This process is accompanied by increased salivation. Due to constant discomfort in the oral cavity and frequent pain sensations, the baby becomes restless, irritable, naughty, and cries a lot. The molars of a child are especially hard to climb. This is because the molar is wider and needs a larger gum area to erupt. Which, of course, increases the pain in the baby.
During teething, the child pulls into his mouth, everything that falls under his arm. And not just pulls into the mouth, but tries to scratch the gums, thus reducing discomfort. Parents can help their child during this difficult period. You can buy a special gel or droplets on the gums at the pharmacy, which have a cooling and analgesic effect and from time to time lubricate the swollen gums with them. There are also teether toys for the baby with which he can scratch the gums.
Often, children during the teething period have other, more complex symptoms - diarrhea, fever, runny nose, cough. Although many pediatricians do not associate these symptoms with teething. They explain them by the fact that during this period the baby's body is too weakened and he is more susceptible to various infections, which cause such manifestations. But many parents observe the above signs during teething in children. Therefore, we will consider them in more detail.
Diarrhea (diarrhea) is one of the most common symptoms of a child's teeth growing. Its appearance is associated, first of all, with the imperfection of the baby's digestive system at this age. The provoking factors can be called nervous spasms of the stomach due to constant painful sensations in the oral cavity, large amounts of saliva entering the digestive tract. Diarrhea during this period usually has a watery consistency, not very frequent (about 2-3 times a day) and disappears after two to three days. As a rule, it does not require special treatment. It is necessary to ensure that the baby receives a sufficient amount of fluid during this period. If necessary, according to the doctor's prescription, you can give him a solution of Rehydron, Smekta. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe the child to take a drug containing beneficial bacteria, such as Linex. But if the baby's stool contains traces of blood, becomes more frequent, or lasts more than three days, it must be shown to the pediatrician. It should be noted that diarrhea often develops when a child's molars are climbing.
Another, rather common symptom of teething in children, is an increase in body temperature. This condition is explained by the fact that when a tooth erupts, an increase in the production of biologically active substances is observed. In addition, when a tooth climbs, it causes the development of an inflammatory process in the gum area. All this together leads to an increase in body temperature. If a child's teeth are getting out, the temperature usually rises to 37.3-37.7 ° C. But in some cases, the mark of the thermometer can show 38 ° C and more. Pediatricians do not recommend bringing down the temperature of a child if it does not exceed 38 ° C. But parents should monitor the condition of the baby. If it gets worse, you need to lower the temperature. Be sure to lower the temperature if the child develops seizures, the baby's age has not reached three months, and the temperature does not drop below 38 ° C. Also, if a child's teeth climb, the temperature is knocked down if he has diseases of the cardiovascular, nervous, bronchopulmonary systems. It is important to remember that if the body temperature exceeds 39 ° C, lasts more than three days, the baby has other unpleasant symptoms, you must call a doctor. All these signs can indicate the development of dangerous infections.