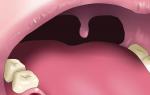
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral cavity that occurs in response to the influence of internal and external pathogenic factors. It mainly manifests itself in the form of white sores and is accompanied by pain in the place of their localization.
External factors provoking stomatitis:
- Mechanical- inflammation begins due to a cut, scratch, or injury from solid food, fragments of teeth or dentures.
- Thermal– due to the consumption of hot/cold food and drinks.
- Chemical- due to the effects of acids and alkalis on the oral cavity. Spicy, sour or too salty foods corrode the mucous tissue.
- Bacterial.
- Viral.
- Smoking and alcoholism.
Internal factors:
- Changes in the functioning of the digestive system.
- Allergic reactions.
- Reduced immunity.
- Failure and change in the level of metabolism.
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular, nervous and endocrine systems.
- Heredity.
- Chronic diseases.
Insufficient/incorrect oral hygiene belongs to a separate group of factors. The use of toothpastes with SLS (sodium lauryl sulfate) contributes to dry mouth by lowering the protective barrier and exposing the mucous membrane to various inflammatory processes. The presence of tartar and caries- a favorable environment for bacteria, which means for the appearance of stomatitis too. Poor brushing is in the same category.
The mechanism of the onset of the disease is not fully understood, you need to consult a dentist and analyze your own observations to identify its sources. In some cases, stomatitis manifests itself against the background of several causes and may be a precursor to more serious ailments.
Types of stomatitis

Depending on the causes and external manifestations, stomatitis is divided into types:
- Traumatic;
- Allergic;
- Herpetic (viral);
- Fungal;
- aphthous;
- ulcerative;
- Prosthetic (allergic, bacterial);
- Smoker's stomatitis (nicotinic).
Herpetic stomatitis
Herpetic stomatitis (viral) develops due to herpes simplex type I (HSV-1). Having been ill with a virus at least once, it remains in the body forever. And in case of weakened immunity, it can manifest itself on the oral mucosa.
Often seen in children under 1 year of age when the herpes virus first enters the body. Infection occurs by airborne droplets, contact or through the blood. Children tolerate herpetic stomatitis worse, up to high temperature and deterioration of the general condition of the body.
In adults, it can be triggered by other diseases that occur against the background. External manifestations are accompanied by vesicular rashes characteristic of herpes stomatitis.
Viral inflammation symptoms:
- Increase in body temperature;
- Chills;
- Weakness;
- Pain in muscles and joints;
- increased sweating;
- Headache;
- Swelling and redness of the oral mucosa;
- The vesicular structure of inflammation, turning into ulcers and erosion;
- Painful rashes;
- Dry lips;
- Strong salivation;
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
Aphthous stomatitis
This is a type of inflammation of the oral cavity. His characteristic feature are aphthae, or white ulcerative formations of a rounded shape, diameter up to 5mm. The number of afts varies from one to several. In especially acute forms, multiple sores are observed on the inside of the lips, palate and cheeks. Occurs due to a number of reasons: low immunity, injuries, allergies, vitamin deficiency in the body, heredity and diseases of the circulatory system.
Signs of aphthous stomatitis:
- Weakness, lethargy;
- Enlarged lymph nodes;
- The presence of sores (aft), covered with a white or yellow coating;
- Pain and burning sensation in the affected areas;
- Redness and swelling of the mouth;
- elevated temperature,
- Profuse salivation;
- Pain when speaking and swallowing.
Ulcerative stomatitis (necrotic)
Acute inflammation of the oral cavity with the development of ulcers and the death of the affected tissues. More common on the gums. The ulcers are covered with a gray film. It is a complex type of disease and requires immediate medical attention. If left untreated, death will continue further down to muscle tissue and bone.
The reasons for the appearance should include: extremely weakened immune system and exposure to bacteria. Ulcerative stomatitis in some cases occurs due to the lack of treatment of inflammatory processes in the mouth. Scars remain on the sites of ulcerative wounds after treatment.
Signs of ulcerative stomatitis:
- Weakness and general malaise;
- severe pain in the mouth;
- Persistent headache;
- The presence of deep ulcers with a gray coating, aphthae, less often - vesicles and erosions. Localization is extensive, not pinpoint.
- Very bad breath;
- Edema and hyperthermia of the oral mucosa;
Prosthetic stomatitis (PS)
Pathological inflammation arising from the impact of dentures on the microflora and the surface of the oral cavity. Most commonly affects older people with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and other body systems. When wearing dentures injuries can form that lead to the development of stomatitis. This problem can be avoided by carefully correcting and polishing the denture.
At the first stage solitary aphthae become inflamed, which are easily treatable. If you let the situation take its course and continue to wear a traumatic prosthesis, the disease progresses, up to the development of ulcerative formations and necrosis.
Reasons for PS: injuries from prostheses, allergies to the chemical composition of the material of dental structures, non-compliance with the rules of care and hygiene for the oral cavity and dentures. The state of the general health of a person is important - the more healthy he is, the less he is prone to prosthetic stomatitis.
Signs of prosthetic stomatitis:
- Painful sensations from prostheses;
- The appearance of ulcers and erosions in the place of attachment of prostheses;
- Redness and swelling in the mouth;
- Profuse salivation;
- Weakness.
Smoker's stomatitis
It develops from the toxic effects of nicotine on the mucous membrane. When smoking, the jet of smoke burns and causes microtrauma in the mouth, and nicotine resins destroy the microflora. Dry mouth appears and the risk of developing inflammatory processes is high.
Signs of nicotine stomatitis:
- Painful ulcers and damage to the mucous membrane;
- Redness and swelling of tissues in the mouth;
- feeling of dryness;
- The smell of cigarette smoke from the mouth;
- Uneven areas of keratinized and inflamed epithelium;
- Hardening and appearance of gray color in the sky.
Causes of stomatitis in adults
The causes of stomatitis in adults are quite diverse and are identified by taking an individual history and questioning the patient.

But there are a number of reasons that most often provoke the disease:
- Damage to the mucous membrane (brushing teeth with a hard brush, rough food).
- Decreased immunity from diseases, anemia, beriberi, the use of heavy drugs in the treatment of serious diseases.
- Stress.
- Caries, tartar and plaque on the teeth.
- Smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Allergy.
- Viral infections.
- bacteria.
- Taking drugs that inhibit the formation of saliva.
- Diseases of the digestive system.
- Hormonal surge.
Symptoms of stomatitis in adults
With various types of stomatitis, common symptoms can be distinguished. Initially itching and redness appear. In places of redness, single or multiple round wounds. The edges are smooth, with a red halo. Plaque gray or white. Pain when talking, swallowing and chewing food. There is swelling of the epithelium. excessive salivation and t up to 39º. General health and mood worsens.
Treatment of stomatitis in adults is complex
Only the right integrated approach will help get rid of the disease quickly and painlessly.
To combat stomatitis, you should go through the following steps:
- Removal of pain syndrome.
- Reducing inflammation.
- Determination of the source of the disease.
- Destruction of pathogenic flora.
- Healing of epithelial tissue.
Painkillers help relieve the severe pain that accompanies this disease. For this, local analgesics are used: Anestezin, Lidocaine, Lidochlor and Geksoral tabs. These drugs help relieve pain and have an antimicrobial effect.
Anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate stomatitis are required, they have antiseptic and anesthetic properties. For example, Hexoral spray, Holisal, Vinyl gel, Igafitol are often used. Preparations in this category are available in the form of ointments, gels, sprays and even tablets for ease of use and effectiveness.
Antiviral, antifungal drugs are used after identifying the cause of inflammatory processes, respectively, and the type of stomatitis. Prescription drugs are prescribed to eliminate a specific type of disease.
Effective antiviral agents: Acyclovir, Zovirax, Immunal, Anaferon and Oxolinic ointment. Drugs that are treated for a fungal infection (candidiasis): Levorin, Fluconazole, Nystatin, Decamine, Clotrimazole, Mycosin.
Healing (restorative) agents contribute to the rapid regeneration of damaged tissues of the oral cavity. Solcoseryl (paste) is used from the very beginning of the appearance of ulcerative formations, helps to speed up the healing process. Propolis spray is convenient to use in hard-to-reach places, numerous herpes rashes, ulcers and inflammations. Due to its properties, it has a complex effect: it destroys microbes and viruses; relieves inflammation and pain; takes care of the mucous membrane; regenerates cells.
Treatment of various forms of stomatitis in adults
Allergic stomatitis provoke various allergens that affect the body. In particular, it can be plant pollen, dust, certain food, wool. For recovery, antihistamines are needed, which are used to treat allergic diseases.

The scheme of treatment of allergic stomatitis:
- Identification and exclusion of the allergen.
- The use of painkillers: Asepta, Lidochlor and the like.
- Taking anti-inflammatory medications.
- Removal of an allergic reaction with antihistamine drugs. Give preference to the well-known and effective: Suprastin, Centin, Fenistil.
- Regeneration of damaged areas with the help of healing preparations: Solcoseryl,
- Raising immunity with the help of vitamin complexes and immunomodulators.
Appears due to fungal infections. The essence of the treatment of candidiasis is the elimination of pathogenic pathogens (fungi of the genus Candida).
Therapy of viral (herpetic) stomatitis in many ways similar to the treatment of oral candidiasis.
Candidiasis and herpes stomatitis are treated in the following way:
- Anesthesia of the inflamed areas. Sprays Geksoral, Lugol, Kameton, Lidochlor gel, Chlorhexidine solution have proven themselves well.
- The use of anti-inflammatory drugs facilitating disinfection.
- Antiviral effect(with herpetic stomatitis). Zovirax and Acyclovir successfully cope with herpetic eruptions.
- Use of antifungal drugs: Pimafucin, Flucanosole, Kanesten, or Nystatin
- Restoration of healthy microflora in the mouth. This will help Laktuvit, Yogurt, Bifiform.
- Vitamin therapy and raising the general immunity of the body.
Treatment of aphthous and ulcerative stomatitis at home is possible only in the initial stages of the disease. With the initial appearance of ulcers, a series of actions should be urgently carried out:
- Anesthesia, disinfection, inflammation removal. Treatment of the oral cavity with Miramistin or Chlorhexidine. The use of broad-spectrum agents: Karotilin, Propolis-spray.
- Restoration of the mucosa with drugs that enhance tissue regeneration in extensive lesions.
- Strengthening immunity.
Prevention of stomatitis
To avoid the appearance of stomatitis in the oral cavity, you just need to take a number of preventive measures.
This will prevent recurrence of the disease:
- A balanced diet, excluding spicy, salty, sour and fatty foods. Sufficient fluid intake.
- Active lifestyle and no bad habits.
- Healthy sleep and lack of stress.
- Restoration of normal microflora in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Proper oral hygiene, rinsing.
- Timely treatment of diseases.
As you can see, with various types of stomatitis, the causes and methods of treatment are similar to each other. Stomatitis in the initial stages is easily treatable. The main thing is not to waste time and get the advice of a doctor as soon as possible in order to conduct proper treatment.
The main cause of the disease is reduced immunity due to negative factors. Actions aimed at increasing the body's defenses are the main measure for the prevention of stomatitis.