If a person wants his teeth and gums to be always strong and not subject to destruction, then he must carefully monitor the oral cavity. The general condition of the periodontal tissues directly affects the health of all teeth and gums.
Gum disease in adults is quite common. It is not so easy to get rid of these ailments, and in a few visits to a qualified dentist the gums cannot be cured, as can be the case with dental caries. In this regard, when the first signs appear and a particular gum disease is detected, a person should immediately react and begin treatment. There are several serious gum diseases that require immediate medical attention.
Gingivitis
If a person does not monitor the oral cavity well, then plaque, which contains many pathogens, may begin to accumulate on his teeth. These microbes multiply very quickly, subsequently penetrating the gums. Their development process promotes the release of toxins that adversely affect the gums, causing them to become inflamed. Then the gums become red and swollen. During this period, they tend to bleed, and a nauseating taste appears in the mouth and very often there is an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity. All of these symptoms are a signal that a person has inflammatory gum disease - gingivitis.
This disease affects everyone, without exception, from small children to the elderly. According to statistics, most often men and women from twenty-five to thirty years old suffer from gingivitis.
Gingivitis reasons
The main cause of gum disease is improper oral care. People often neglect personal hygiene, as a result, various diseases arise. But sometimes other factors can provoke disease of the teeth and gums, such as:
- incorrect position of the teeth;
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- improper dental treatment;
- disruptions of a hormonal nature in the body;
- diabetes mellitus;
- stressful and depressive conditions;
- malocclusion;
- malfunctions of the thyroid gland.
All these factors negatively affect the oral cavity, in particular the protective properties of the teeth. There is a change in microflora and the development of gum disease. During pregnancy, when a woman's body changes hormonal levels, the risk of developing gingivitis doubles.

Disease types
Gingivitis can be extensive and local:
- Extensive gingivitis covers the entire dentition, that is, all teeth are affected.
- Local gingivitis can only affect one or more teeth.
Gingivitis is chronic and acute. If a person suffers from a chronic disease, then its development occurs slowly, and symptoms tend to change. For a while, the symptoms may worsen, and then subside, and this continues throughout the entire period of the disease. Acute gingivitis manifests itself very quickly, its development occurs abruptly, without any delay.
The disease is divided into several types:
- Catarrhal gingivitis develops due to lack of or improper oral care. With such a disease, a person has slight bleeding of the gums and their itching.
- Hypertrophic gingivitis is accompanied by a bad breath and profuse bleeding from the gums.
- Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis occurs with the formation of ulcers on the gums and a large accumulation of gray plaque on the teeth.
If a person has all the symptoms of gum disease, then he needs to see a dentist as soon as possible. Indeed, in the absence of proper treatment, gingivitis can progress and cause a more serious disease - periodontitis, which is much more difficult to get rid of. And gingivitis can be cured with special medications prescribed by your doctor.

Gingivitis treatment
Gingivitis is a serious gum disease and must be treated promptly. If the disease has just begun to develop, then it is quite simple to cure it. The diagnosis and treatment of gums is carried out by periodontists and dental therapists.
In the treatment of gingivitis, specialists perform the following actions:
- The accumulated deposits are removed from under the gums.
- The oral cavity is treated with antiseptic preparations.
- The dentist will prescribe the correct oral care to the patient.
- And in conclusion, the patient is prescribed the necessary medications and vitamins to strengthen the gums.
Gingivitis is superficial, so it can be cured quite quickly with the right approach to the problem. To do this, use procedures such as rinsing, gel applications and careful oral care. Sometimes gingivitis is treated with antibacterial drugs. Basically, inflammatory processes are neutralized by rinsing with Chlorhexidine and Miramistin. Applications are made from Metrogyl Denta and Holisal gels. Prescribe vitamins C, P, PP and D. It is recommended to clean teeth with special therapeutic pastes Parodontax, Lacalut Active and Asepta. In some cases, your dentist may prescribe electrophoresis, ultraviolet therapy, or vacuum massage.
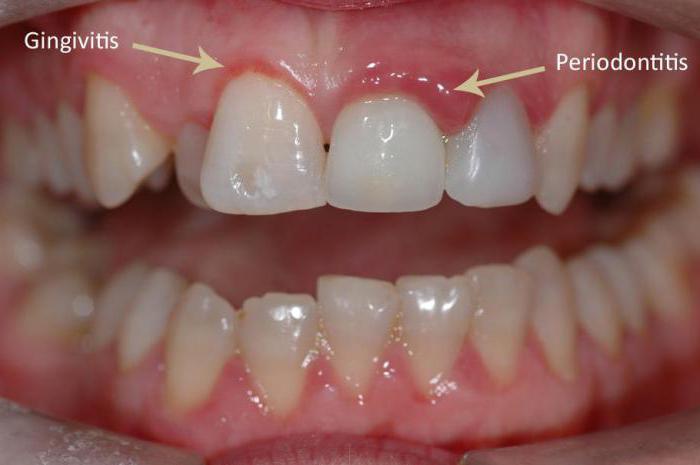
Periodontitis
If a person does not begin to treat gingivitis, then, without a doubt, he will acquire a disease such as periodontitis. In this gum disease, inflammation occurs throughout the mouth, including the tissues around the teeth. Harmful bacteria provoke the resolution of the periodontal fibers, which ensure a strong attachment of the gums to the teeth. All this leads to the fact that holes appear between the teeth and gums, which are called periodontal pockets. Plaque builds up in these pockets. They can also secrete pus and contribute to bad breath. Also, when a pocket appears, bone tissue is destroyed.
Periodontitis is a serious gum disease. You see a photo of the external manifestation of this unpleasant disease in the article. With periodontitis, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- severe pain in the gums;
- bleeding gums;
- the tooth necks are exposed;
- teeth begin to loosen;
- periodontal pockets secrete pus.
If an infection gets into the wound, a flux may develop.
Periodontitis grades
Periodontitis is divided into three degrees of severity:
- Mild form of the disease. If a person suffers from a mild form of the severity of the disease, then he has pain while eating and brushing his teeth, the gums become swollen and red.
- The average form of the disease. With an average form of severity of periodontitis, the patient's teeth begin to stagger or shift, and often the gums bleed spontaneously.
- Severe form of the disease. In a severe stage, the patient loses teeth prone to disease.

Periodontitis treatment
Treatment of periodontitis in adults can be lengthy and requires complex procedures. Compared to gingivitis, periodontitis cannot be treated at home. First of all, when treating this disease, the dentist cleans the periodontal pockets. All this is done through a special procedure with ultrasound or with the help of instruments with which a specialist scrapes the entire contents of the pocket. Then he puts a medicine in the cleared pocket, which stimulates the growth of bone tissue. This procedure is accompanied by severe pain, therefore, it is performed after the patient is injected with local anesthesia.
With a severe form of gum disease, gingivectomy is often performed, an operation to cleanse periodontal pockets, after which the inflamed areas are removed. This prevents plaque build-up in the pockets.
If a person suffering from periodontitis has lost his teeth, the dentist will install prostheses. Loose teeth are eliminated through a splinting procedure. The teeth are held together with the gums using fiberglass or aramid suture. Basically, a similar procedure is performed on the anterior row of teeth, since in the future this will allow the patient to eat normally without feeling discomfort.
In addition, periodontitis is treated with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic medicines. They are used as tablets for oral administration, rinses, baths and applications.

Periodontal disease
Periodontal disease is not an inflammatory disease. In this gum disease, a person experiences a slow loss of bone tissue. He feels awkward when eating, brushing his teeth, and when hot or cold gets on his teeth.
With this disease, periodontal pockets do not appear, there is no bleeding of the gums, they do not swell or redden. With periodontal disease, bone tissue is destroyed, as a result of which the teeth begin to wobble or fall out.
Causes of periodontal disease
The reasons for the appearance of periodontal disease are as follows:
- disruptions to the hormonal background;
- heredity;
- bad habits, such as smoking or systematic intake of alcoholic beverages;
- changes in blood vessels;
- lack of essential vitamins in the body.
Gum disease and their treatment. Periodontal disease
First of all, when treating this disease, a specialist identifies the cause of its occurrence. When periodontal disease occurs due to a disease of the digestive system, special diets are prescribed. They compensate for the deficiency of vitamins and cleanse the body of toxins.
At home, periodontal disease is treated by rinsing the mouth with various tinctures, such as calendula, propolis, immortelle. They also massage the gums using coriander or mint oil.
From medicines, antibacterial and hormonal agents, vitamins and esters are prescribed. When teeth fall out, splinting is prescribed or dentures are inserted.
With complex forms of the disease, surgical intervention can be prescribed. Specialists carry out bone augmentation.

How to prevent tooth and gum disease
As you know, the disease is better prevented. To prevent gum disease, a person should visit the dentist more often and carefully monitor the entire mouth. After all, it is better to go to an appointment several times than to be treated for months later. Therefore, a person needs:
- Reorganize the oral cavity twice a year.
- Take care of your teeth and gums.
- To ensure stable blood circulation in the gums, it is necessary to massage the gums with a brush every day.
- When brushing your teeth, you need to be careful with the gaps between your teeth, so you should clean those places carefully, without much pressure.
- If possible, eat the food that contains a lot of proteins.