Epithelial cells on the surface of the tongue are constantly exposed to quite aggressive factors: acidic food, temperature changes, bacteria. That is why their lifespan is not long, and after their desquamation, young cells appear. If the processes of changing cell layers are overly active, then the upper layers do not have time to peel off and remain on the surface of the mucous membrane in the form of a plaque.
Plaque on the tongue may indicate a serious illness.
Microorganisms can be another factor in the formation of plaque. Children often do not pay enough attention to oral hygiene, as a result of which microscopic food particles can remain between the lingual papillae, which become a place of active multiplication of bacteria. Taking antibacterial drugs often provokes the growth of pathogenic microflora in the mouth (fungi), some varieties of which are quite bright in color.
Reasons for the appearance of plaque in the tongue
There are a lot of reasons due to which a variety of plaques on the tongue may appear: from the banal use of food that can change the color of the tongue, to serious health problems requiring immediate medical attention.
The very first thing that needs to be done when an incomprehensible plaque is found in a child's tongue is to remember what the baby ate in the last 24 hours. Very often, sweet carbonated drinks, caramels or other sweets contain active dyes that can give the mucous membranes of the mouth the most exotic shades: raspberry, purple, green, orange and others. Even natural berries and fruits can drastically change the color of the tongue. Therefore, you do not need to immediately panic. You should ask your child to brush your teeth and tongue, and then assess their condition and color. If the plaque has not changed or reappeared without connection with food intake, then this is a reason to urgently visit your pediatrician.
So, what is the plaque on the tongue of a child, what may cause it to appear and how to treat it, we will consider further.
White
White plaque can be found in the oral cavity of an infant most often. This phenomenon also happens in the norm, when, after a night's sleep, a thin white coating without an unpleasant odor is found on the tongue, which disappears after carrying out hygiene procedures and does not cause any discomfort or discomfort.
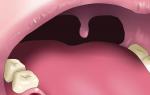
 In the photo: white plaque on the tongue of a child
In the photo: white plaque on the tongue of a child
The appearance of a dense whitish plaque, which is extremely difficult to remove from the surface of the tongue and does not disappear after brushing your teeth, can signal problems from the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, enteritis or dysbiosis). This phenomenon is often accompanied by bad breath. In addition, children may present complaints that may indicate a pathology of the gastrointestinal tract:
- abdominal pain of various localization;
- bloating;
- stool disorders;
- change in appetite
In order to get rid of such white plaque, it is necessary, first of all, to examine the digestive system and eliminate even the smallest disturbances in its work.
In infants up to 2 months of age, a frequent occurrence, especially after taking antibiotics or inaccuracies in the diet, a nursing mother has thrush or candidiasis of the oral cavity. With this pathology, abundant white curdled plaques appear on the tongue and cheeks, which are easily removed, and small ulcers are found under them. After the start of the treatment of thrush with antifungal agents and the treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions, the tongue and other mucous membranes are quickly cleared and return to their previous appearance.
Gray
A gray coating on the tongue can be a sign of some infectious diseases. For example, with scarlet fever, on the very first day, the mucous membranes are covered with a dirty gray bloom, which, starting from the tip of the tongue, gradually disappears and exposes a "raspberry tongue" - enlarged papillae on a bright red background, which is very reminiscent of raspberries.
With diphtheria, gray film deposits can be found at the root of the tongue, which are difficult to separate. Such plaques spread to the mucous membranes of the throat, palatine arches and are accompanied by coughing and asthma attacks.
Treatment of such infectious diseases is carried out only in a hospital setting. After healing, all plaques on the tongue disappear.
Dehydration of the child's body can also lead to the formation of gray plaque on the surface of the tongue. At the same time, the mucous membranes look dry and dull. Replenishment of the required volume of fluid quickly eliminates this symptom.
Yellow
A dense yellow coating on the tongue indicates a pathology of the liver or biliary tract. Often in children, diseases of the biliary system proceed without a vivid clinical picture, and the presence of stagnation of bile can only be suspected by a change in the color of deposits on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
If a child has a plaque in the tongue of a yellow tint, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor and conduct an examination of the internal organs and the biochemical composition of the blood.
Orange
The color of the tongue in orange is a marker that acidic contents from the stomach enter the oral cavity. This happens with exacerbation of gastritis with high acidity, with reflux disease, with pathology of the esophagus and the initial stages of ulcer development. In this case, the child may additionally complain of an unpleasant sour taste in the mouth, belching, and recurrent heartburn. Treatment will be to address the underlying cause.
Green
The appearance of green plaque on the mucous membrane of the tongue is often very frightening for parents, especially if it is found in a newborn or infant. The most common reason for this phenomenon is candidiasis, a fungal infection of the oral cavity that occurs due to imperfect immune defenses in the body of a 1 year old baby or against the background of taking strong antibacterial drugs.
Such plaque has a different intensity of color and can spread to other parts of the oral cavity, found on the cheeks, palate and lips. After removing it, you can see the red surface of the tongue with small blisters or sores that cause discomfort to the child.
It is necessary to start treating green plaque only after consulting a doctor. Therapeutic measures will consist in taking special drugs with antifungal action and local antiseptics to treat thrush and prevent bacterial complications.
Brown
A brown tongue in a child is not such a rare occurrence. There can be many reasons for this:
- Severe diseases of the digestive system, accompanied by inflammatory changes, stagnation of bile in the bile ducts, impaired digestion.
- Constant dehydration of the child's body due to high ambient temperatures or insufficient fluid intake.
- Insufficient intake of B vitamins.
- Taking some medications: antibiotics, antiseptic solutions, concentrated herbal decoctions.
It is very difficult to establish the exact root cause of the appearance of such a dark coating. This can only be done by an experienced doctor who, after additional examinations, will be able to prescribe the optimal treatment.
Black
The presence of black plaque on the tongue in a child looks scary enough, and there may be several reasons for this phenomenon:
- Bacterial sore throat is often accompanied by the appearance of dark deposits on the mucous membranes up to black. In this case, the child will have signs of inflammation in the tonsils: red throat, high fever, soreness when swallowing, weakness.
- Latent forms of diabetes mellitus, which lead to a persistent violation of the acid-base balance in the body. Excess acid or acidosis will cause the tongue to darken.
- Taking some antibiotics causes the growth of pathogenic microflora in the mouth, which gives persistent staining of the mucous membranes in black.
Treatment of such a plaque will be to eliminate the causes that caused its appearance. After sore throat is treated, medications are canceled, or diabetes mellitus is identified and compensated, such a symptom will most likely go away on its own.
Blue
A blue tongue is a sign of blood stagnation. Very often, various diseases of the cardiovascular (congenital heart defects, arrhythmias, heart failure) and the nervous system (hemorrhages, cysts, epilepsy) lead to the fact that blood flows through the tissues slower than necessary - cyanosis or cyanosis appears on the limbs, lips and language. Therefore, if you notice such a symptom in your child, then you urgently need to contact your doctor for advice.
Prophylaxis
In order to prevent the appearance of plaque in the child's language, there are a number of preventive measures that many specialists emphasize (for example, the Ukrainian pediatrician Komarovsky):
- The room in which the child lives should always be clean, well-ventilated and humidified.
- You should not give your child antibiotics on their own. Taking such medications must be strictly justified.
- It is necessary to closely monitor the health of the baby. If the slightest symptoms appear, indicating a possible illness from the internal organs, you should urgently seek medical help.
- Limit your child's consumption of sweets containing synthetic coloring pigments: sugary soda, hard candy, chewing gum. This will not only prevent the appearance of active staining of the tongue, but also preserve the health of delicate children's teeth.
If a plaque nevertheless appears on the tongue, you do not need to try to remove or treat it yourself. Consult with your doctor about the possible causes of this phenomenon and the necessary treatment for it.