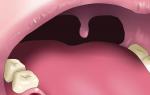
Inflammation of the gums or gingivitis in children is the most common inflammatory disease of the oral cavity between the ages of six months and 16 years. The reason for this is poor hygiene, ignorance of how to clean teeth and care for gums, gum papillae, and interdental spaces.
The immunological status of young children and adolescents also plays a role in the development of the disease, because the symptoms of gingivitis begin to appear during colds, internal pathological processes.
Treatment of inflammation at home is possible after consulting a dentist, the doctor prescribes medications and advises traditional methods of using medicinal plants.
Gingivitis in young children
The inflammatory process of the gums begins with slight redness around the tooth, enlarged papillae and slight soreness. If symptoms are detected and help is sought at this time, treatment will be carried out quickly and successfully. Otherwise, gingivitis will go into an advanced stage, the child's well-being will worsen, and it will be necessary to treat not only gum disease, but also the consequences of this process.
 Until the age of four, almost every child develops traumatic, allergic or toxic gingivitis. If it is not promptly treated, the disease can spread to the periodontal tissues, as a result of which periodontitis and periodontal disease develop. Acute gingivitis in children turns into a chronic process, and even then serious problems begin not only in the oral cavity, but throughout the child's body.
Until the age of four, almost every child develops traumatic, allergic or toxic gingivitis. If it is not promptly treated, the disease can spread to the periodontal tissues, as a result of which periodontitis and periodontal disease develop. Acute gingivitis in children turns into a chronic process, and even then serious problems begin not only in the oral cavity, but throughout the child's body.
Advice! It is possible to avoid the transition of inflammation to a chronic course only by timely identifying alarming symptoms and eliminating factors that negatively affect the gums and gingival papillae.
The pathological microflora, which accumulates during irrational oral hygiene, triggers the inflammatory process, the tissues around the tooth begin to increase, provoke soreness during chewing and touching with the tongue. At the same time, a small child begins to cry often, refuses to eat, since chewing is given to him with pain. Parents should know how this disease manifests itself and what kind of treatment for gingivitis in children should be carried out as soon as the first signs appear.
Risk factors for gum disease
Inflammation in children can be provoked by diseases such as advanced caries or infections in the oral cavity. In addition, children with reduced immunity, who suffer from chronic inflammatory diseases, even distant from the oral cavity, are at risk.
 The reasons for the appearance of gingivitis in young children:
The reasons for the appearance of gingivitis in young children:

 Any risk factor in the development of inflammation is equally dangerous for the child, and parents should not miss even the slightest changes in the oral cavity. It is possible to identify the symptoms of the initial development of the disease by examining the child's mouth: with gingivitis, the gums are bright red, the interdental papillae are enlarged, bleeding may occur when brushing teeth or chewing food.
Any risk factor in the development of inflammation is equally dangerous for the child, and parents should not miss even the slightest changes in the oral cavity. It is possible to identify the symptoms of the initial development of the disease by examining the child's mouth: with gingivitis, the gums are bright red, the interdental papillae are enlarged, bleeding may occur when brushing teeth or chewing food.
Advice! The first manifestations of gingivitis are rather blurred, but the child's complaints can clearly indicate the disease, they should not be ignored, since a timely visit to the dentist prevents periodontitis and even tooth extraction.
How does gingivitis manifest in a child?
The clinical manifestations of gum disease depend on the form of the disease, but there are also general manifestations:
- Acute gingivitis: the first symptoms are determined visually, an increase in the gingival margin, hyperemia, bleeding. When touching the tissues around the tooth, the child reacts painfully. It is difficult to chew at this stage, since any touch to the inflamed areas brings severe pain.
- Chronic gingivitis in children: symptoms are less pronounced, but visually the disease cannot be overlooked. The gums bleed, hurt when touched, the papillae are greatly enlarged. With a chronic advanced process, the causative tooth may loosen, which already speaks of damage to the periodontal tissues.
A child with gingivitis complains of weakness, loss of appetite, he becomes irritable, often cries. The amount of plaque gradually increases, both on the teeth and on the gums themselves, which is due to the impossibility of normal cleaning of the oral cavity against the background of severe pain.
Advice! With gingivitis, you do not need to spare the child and skip brushing your teeth, because this is the main reason for the appearance of inflammation and the development of complications. To reduce pain during hygiene procedures, you need to purchase a soft brush and neutral toothpaste without mint, which irritates sore gums.
Forms of childhood gingivitis
Depending on the form of inflammation, the clinical picture and treatment will differ. Only a dentist can determine the type of gingivitis in a small child, a visit to which is an obligatory stage in the treatment and prevention of complications. What diagnosis can a dentist make?
- Catarrhal gingivitis: often occurs at the time of teething, lasts a long time and with sluggish symptoms. Parents often ignore inflammation during bite changes, considering it normal, which is the main mistake. If you do not treat any inflammation in the oral cavity, there is a risk of dental disease and the transition of gingivitis into an advanced purulent process.
- Hypertrophic inflammation: the most severe manifestation of this ailment, during which the gum papillae and the gums themselves greatly increase, purulent exudate accumulates in them, which causes throbbing pain. In this case, the crown of the tooth can overlap with completely enlarged gums, under which pathological microorganisms actively multiply.
- Ulcerative inflammation: accompanied by the appearance of ulcers on the tissues of the oral cavity, which bleed and cause severe pain when touched. This form of gingivitis is very dangerous, as all tissues of the mouth can become infected, and then the whole body through open ulcers. Ulcers turn into necrotic areas, that is, the gums begin to die off, and it is already quite difficult to treat such inflammation, and at home it is completely impossible.
Diagnosis of inflammation is carried out after examining the oral cavity by a dentist and conducting a microbiological analysis. After the diagnosis is made, the doctor prescribes home treatment, which includes medications and local remedies. 
Medication for gum disease
It is necessary to start treating inflammation by eliminating the causative factor. Stone deposits are removed, professional cleaning is carried out. Then, at home, parents give the child lotions, lubricate the gums with anti-inflammatory drugs and change the diet.
Medications for gingivitis in young children:
- At home, you need to make antiseptic rinses with low concentration antimicrobial agents.
- Lubricate the inflamed area with antiviral ointments.
- Give the child vitamin complexes of A, D groups to drink.
- To mutilate the protein content in the diet, but at the time of acute inflammation, give only soft food and plenty of clean water.
The effectiveness of home treatment depends on the form and neglect of the disease. If the gingivitis is only getting worse, you need to see your doctor again to change the treatment.