The alveolus, or alveolus, is the depression in the jaw where the upper part of the tooth root is located. Inflammation of the socket of the tooth is called alveolitis and occurs for several reasons.
Treatment of the disease depends on the timely diagnosis and identification of factors influencing this process.
Causes
Inflammation can begin against the background of suffering immunity, which is a consequence of a chronic somatic disease. But basically, the process progresses after traumatic removal - when the recess and the periodontium surrounding it are injured.
The operation is considered difficult if the tooth:
- not completely cut through and closed by the gum;
- crumbles during the procedure;
- completely destroyed, and the doctor has nothing to catch on with forceps;
- the roots are irregular.
Both the patient who ignores postoperative care and the doctor who violated hygiene requirements are to blame for the appearance of the inflammatory process:
- improper treatment with an antiseptic of the oral cavity;
- getting into the wound of plaque;
- not carefully cleaned hole.
Risk factors play an important role in the occurrence of the inflammatory process. These include the presence of foci of caries and chronic infectious diseases of the nasopharynx.
In some cases, the course of wound healing can be disrupted by the washing out or complete destruction of the blood clot that fills the hole after surgery.
The alveolar thrombus is designed to protect the hole from infection. Normally, the clot falls off seven to twelve days after surgery. If prolonged bleeding is observed or the patient is fond of rinsing the mouth, then the clot is prematurely washed out, which can cause infection and the development of alveolitis.
Learn more about this in the following video:
First symptoms
After the operation, the hole heals quickly, and the pain disappears in a day. If the thrombus, which performs protective functions, has not formed, then the infection penetrates into the wound.
Self-medication and excessive rinsing leads to undesirable complications, including the occurrence of alveolitis.
The main first symptom of the disease is continuous, aching pain radiating to the ear and temple. After the action of anesthesia and tooth extraction, pain can begin immediately, but more often after a few days.
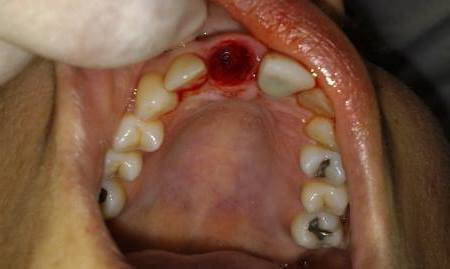
When examining a patient, the doctor feels fetid odor. The edges of the wound have a swampy brownish color, and the alveolar thrombus has a loose structure. The walls of the alveolar cavity are also inflamed and covered with a gray-green coating.
 The edges of the gums lose sensitivity to pressure, become loose and acquire a purple hue. The periodontium of healthy teeth is located in the inflamed area - therefore, when they are squeezed, pain and a feeling of fullness are observed.
The edges of the gums lose sensitivity to pressure, become loose and acquire a purple hue. The periodontium of healthy teeth is located in the inflamed area - therefore, when they are squeezed, pain and a feeling of fullness are observed.
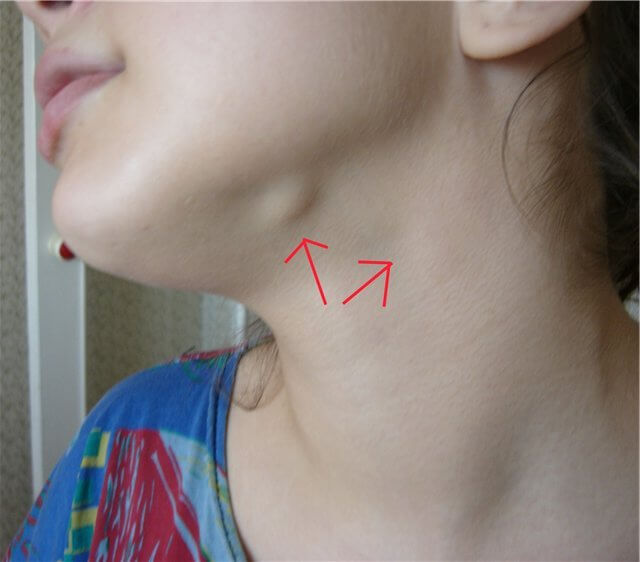
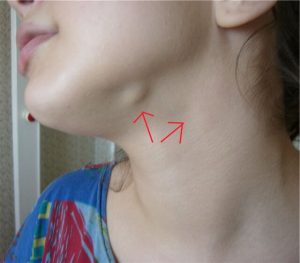
If the patient does not turn to a specialist in time, then a fever may begin, and the corresponding part of the face becomes swollen, submandibular lymph nodes enlarged(see photo on the right) - they become painful on palpation.
In more detail about the principle of progression of the disease, the types and accompanying symptoms, we will consider further.
Types of disease and their symptoms
Doctors distinguish three types of alveolitis: serous, purulent and chronic.
- Serous. It develops within 3 days after tooth extraction and lasts about a week, if left untreated, it turns into a purulent form. It is manifested by constant pain, aggravated by foreign substances (food, liquid, toothpaste) entering the wound.
The body temperature does not rise, the general condition does not worsen, the lymph nodes are not inflamed. On examination, the doctor sees a dry hole filled with food debris and saliva.
- Purulent. It is considered a complication after the serous form of alveolitis. It is characterized by constant severe pain, due to which eating is no longer possible.
Fever appears, body temperature rises to 38 degrees, regional lymph nodes swell. The hole is filled with purulent contents and edematous, the alveolar ridge is thickened, the surrounding tissues are inflamed.
- Chronic. Occurs in patients who tried to cure alveolitis on their own, because. the disease cannot be eliminated without the surgical intervention necessary to clean and locally disinfect the hole.
Rinses and lotions only stop the symptoms: the general condition improves, the temperature returns to normal, the pain subsides. But the hole continues to fester, pieces of dead tissue remain inside, granulation grows, the gum becomes bluish.
Features in the extraction of the figure eight
A wisdom tooth or otherwise - a figure eight, gives a person a lot of problems. Appearing when all the rest of his brothers erupted, he, like an uninvited guest, does not please with his visit.
When it erupts, swelling of the periodontal tissue often develops, a person is haunted by pain. Rudiment removal is necessary in the following situations:
- Deviation of tooth growth in an unpredictable direction, which contributes to injury to the oral mucosa and tongue;
- The presence of caries and the impossibility of treatment due to the inaccessibility of the tooth;
- Very slow cutting, which contributes to the formation of a "hood", which provokes inflammation;
- The negative impact of the "intruder" on neighboring teeth.
During the extraction of the third molar, it is possible injury to one of the nearby nerves, which leads to paresthesia of the corresponding part of the face. Sometimes adjacent teeth or dentures can be damaged during surgery.
But the worst consequence could be dry hole"- a complication after traumatic removal. She is the result of prolonged bleeding arising for various reasons. In this case, the likelihood of infection of the wound is high.
Given the specifics of modern operations on, the probability of alveolitis is high only in two cases:
- profuse bleeding from the wound, which requires the help of doctors to stop;
- non-compliance with oral hygiene, which provoked infection under the seam.
The fact is that after extracting the impacted tooth, the wound is sutured in such a way that the clot is protected from mechanical influences. But there remains a small hole for draining the ichor during the healing period of the wound, through which the thrombus can only be pushed out by a strong flow of blood.
If you do not brush your teeth and do not do antiseptic baths, the infection will enter the hole through the hole. Decomposing in a confined space, it will provoke alveolitis, despite the presence of a clot.
In case of untimely seeking medical help, inflammation leads to osteomyelitis of the jaw, which can spread to adjacent teeth. His treatment is described in the article.
Treatment
The choice of treatment method depends on the stage of neglect of the wound and the presence of complications. Some manipulations are performed by a doctor in the clinic, but most methods are available for home self-treatment.
Medical
Before starting treatment, the patient x-ray is prescribed. The picture will indicate the presence of foreign elements or fragments of the tooth in the gum cavity and will help to exclude complications.
If the treatment is started on time, then within a week the inflammatory process stops, the wound is covered with a protective epithelium, which indicates a positive dynamics of treatment. After that, the patient must follow the treatment recommendations and regularly visit a specialist for examination.
Folk remedies
After stopping the inflammation with medication, treatment can be continued at home. Traditional medicine offers rinsing with infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs:
- chamomile;
- sage;
- petals of calendula.
The composition of herbs contains valuable essential oils, anti-inflammatory natural components, thanks to which you can remove small inflammations and disinfect the oral cavity.
Infusion of sage
Sage has disinfectant and analgesic properties. To prepare the infusion, you need to take one tablespoon of dried herbs and pour a glass of boiling water.
Dishes with brewed grass must be wrapped in a towel and let it brew for an hour. Strain the solution, after which it is ready for use.
pharmaceutical camomile
The components that make up chamomile gently cleanse the oral cavity and relieve inflammation. Chamomile inflorescences should be brewed as in the previous recipe. Let it brew for 15-20 minutes under a towel. Strain the solution and rinse your mouth.
calendula petals
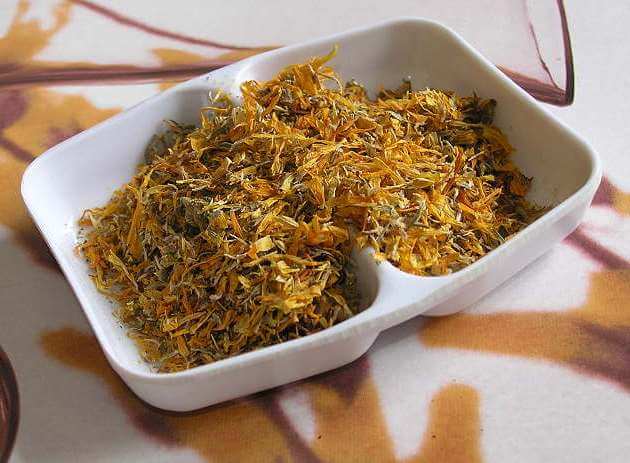 Calendula relieves puffiness, disinfects and promotes the speedy healing of the mucosa. One tablespoon of calendula inflorescences is poured with a glass of hot water, after which the resulting solution must be left for half an hour to infuse.
Calendula relieves puffiness, disinfects and promotes the speedy healing of the mucosa. One tablespoon of calendula inflorescences is poured with a glass of hot water, after which the resulting solution must be left for half an hour to infuse.
Herbal infusions are recommended to rinse at least ten times a day, and for the prevention of diseases 3-4 times. From herbal infusions, gauze compresses can be prepared and applied to the inflamed area in the oral cavity.
In pharmacies, you can buy alcohol infusions on medicinal herbs. But you can cook them yourself. Here is an example recipe:
- Poplar buds - 1 part;
- Vodka - 5 parts.
Pour the kidneys into a glass container, pour vodka and insist in a cool, dark place for several weeks, then strain. The tincture can be added to warm water for rinsing, as well as gauze applications on inflamed gums.
In any case, if symptoms occur that signal the development of an inflammatory process (swelling of the face and gums, fever, severe pain, putrid breath), you should contact a specialist as soon as possible. Such manifestations may be signs of the development of the inflammatory process.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of alveolitis after tooth extraction is simple - you need to follow the doctor's recommendations aimed at maintaining the integrity of the clot in the hole. It is the blood clot formed after the operation that protects the wound from the formation of a dry socket, infection and the development of inflammation.
The washing out of the clot is provoked by the following actions:
- Rinsing. The pressure created by water mechanically displaces the thrombus from its place, therefore, on the first day, and preferably 2-3 days, it is forbidden to do therapeutic rinses with decoctions and antiseptics, which are loved by many patients.
Baths are allowed on the second day; you need to take the decoction in your mouth, hold it and let it flow out.
- Physical activity. You need to be at rest, you can not go to the gym, do active housework, lift weights, etc.
All this provokes an increase in blood circulation, which leads to bleeding if a person has an open wound, and the clot is washed out with the blood stream.
- Hot food. The impact of high food temperature on the thrombus leads to its resorption, as a result, it gradually eliminates itself and the hole remains dry.
- Drinking through a straw and smoking. The negative pressure created during this pulls the clot out of the wound.
- Touching the hole. You can mechanically provoke the prolapse of a blood clot if you touch it with your tongue, fingers, cotton swabs or a brush.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.